What is the best way to treat diabetes foot ulcers?
- Surgical
- Non-Surgical. ...
- Taking proper care of the wound by keeping them clean and properly dressed.
- Using the immobilisation devices such as a cast boot or total contact cast.
- Taking proper care of all the wounds to avoid the situation from turning worse. ...
How to deal with diabetic foot ulcer?
- Applying the gauze – Medical gauze usually come in rolls. ...
- Keep the dressed sore safe – Avoid moving around as excessive motion might cause the medical tape to loosen, making the medical gauze fall off. ...
- Change the dressing regularly – Dressings must be changed every 3 or 4 hours. ...
Why is a diabetic foot ulcer so hard to heal?
Why wound healing is slow
- High blood sugar levels. Your blood sugar level is the main factor in how quickly your wound will heal. ...
- Neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy can also result from having blood sugar levels that are consistently higher than normal.
- Poor circulation. ...
- Immune system deficiency. ...
- Infection. ...
Can a diabetic ulcer heal by itself?
While diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) can be difficult to heal, if left untreated they can become infected and lead to further complications. The good news is that these foot ulcers can be healed with advanced treatments and can be further avoided when patients take preventative actions.
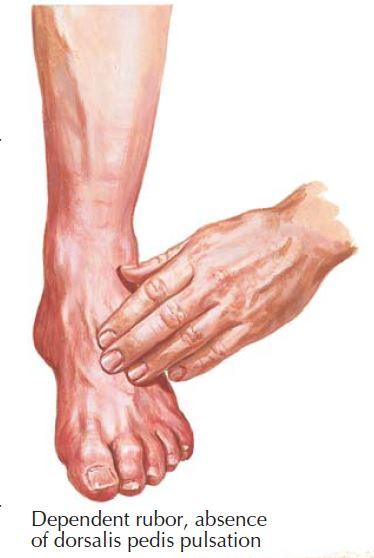
What is the ICD-10 code for foot ulcer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity L97. 509.
What is the ICD-10 code for left foot diabetic ulcer?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of left foot with unspecified severity. L97. 529 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.
How do you code a foot ulcer?
Of these options, the most commonly used codes for diabetic foot ulcers are E10. 621 (Type 1 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer) and E11. 621 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer). “Code first” indicates that an additional code is required, and it must be listed first.
What is the ICD-10 code for ulcer left great toe?
L97. 529 - Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of left foot with unspecified severity. ICD-10-CM.
Is a diabetic foot ulcer a pressure ulcer?
Skin necrosis and gangrene are also included in the current system as ulcers.” This definition is similar to that of the EPUAP, all-inclusive and, as such, any pressure ulcer on the foot of a person with diabetes is a diabetic foot ulcer — as is any traumatic wound, including a thermal or chemical injury.
Is a neuropathic ulcer a pressure ulcer?
Neuropathic ulcers occur when a patient with poor neurological function of the peripheral nervous system has pressure points that cause ulceration through the epidermal and dermal tissue layers. This is a common condition in the foot, and occasionally other body parts.
What is an ulcer on the foot?
Foot ulcers are open sores or lesions that will not heal or that return over a long period of time. These sores result from the breakdown of the skin and tissues of the feet and ankles and can get infected. Symptoms of foot ulcers can include swelling, burning, and pain.
Whats the difference between a pressure ulcer and a diabetic ulcer?
While diabetic patients can get pressure ulcers due to abuse or neglect in a nursing home, diabetic ulcers may appear in areas that are not typically subject to extended pressure—such as the bottoms of the feet when a resident has been lying down. In these cases, a diagnosis of a diabetic ulcer is more apt.
How do you code ulcer debridement?
Debridement should be coded with either selective or non-selective CPT codes (97597, 97598, or 97602) unless the medical record supports a surgical debridement has been performed. Dressings applied to the wound are part of the services for CPT codes 97597, 97598 and 97602 and they may not be billed separately.
What is the ICD 10 code for foot care?
Routine foot care, removal and/or trimming of corns, calluses and/or nails, and preventive maintenance in specific medical conditions (procedure code S0390), is considered a non-covered service.
What is ICD 10 code for Left foot Pain?
M79. 672 Pain in left foot - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
How do you code a venous stasis ulcer?
The stasis ulcer caused by venous insufficiency is captured first with the code for underlying disease (459.81) followed by the code for the location of the ulcer (707.13).
How do you code a venous stasis ulcer?
The stasis ulcer caused by venous insufficiency is captured first with the code for underlying disease (459.81) followed by the code for the location of the ulcer (707.13).
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot infection?
ICD-10 code E11. 621 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is ICD-10 code for diabetic wound infection?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other skin ulcer The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 622 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code a diabetic foot infection?
Wiki Diabetic foot infection???Code: E11.621.Code Name: ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer.Block: Diabetes mellitus (E08-E13)Details: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer. ... Excludes1: diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition (E08.-)More items...•
How are foot ulcers defined?
Typically, foot ulcers are defined by the appearance of the ulcer, the ulcer location, and the way the borders and surrounding skin of the ulcer look. There are different types of diabetic foot ulcers –
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Regarded as the most common reason for hospital stays among people with diabetes, a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is an open sore caused by neuropathic (nerve) and vascular (blood vessel) complications of the disease. Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot, these complex, ...
How many parts are there in the podiatry billing process?
9 Parts of The Podiatry Billing Process
What are the risk factors for ulcers?
The most common risk factors for ulcer formation include – diabetic neuropathy, structural foot deformity, kidney disease, obesity and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. The condition can be effectively prevented if the underlying conditions causing it are diagnosed early and treated correctly.
What is the most common foot injury leading to lower extremity amputation?
Diabetic ulcers are the most common foot injuries leading to lower extremity amputation. The blog provides a detailed overview of the condition with the ICD-10 codes.
How many people with diabetes have foot ulcers?
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA), approximately 15 percent of people with diabetes suffer from foot ulcers. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, about 6 percent will be hospitalized due to serious infections or other ulcer-related complications.
Where does neuropathic ulcer occur?
Neuropathic ulcers– occur where there is peripheral diabetic neuropathy, but no ischemia caused by peripheral artery disease. This type of foot infection generally occurs on the plantar aspect of the foot under the metatarsal heads or on the plantar aspects of the toes.
What causes ulcers in the body?
Ulceration caused by prolonged pressure in patients permitted to lie too still for a long period of time; bony prominences of the body are the most frequently affected sites; ulcer is caused by ischemia of the underlying structures of the skin, fat, and muscles as a result of the sustained and constant pressure. Codes.
What does type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( L89) and the excluded code together.
What causes diabetic foot ulcers?
A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury.
Why do diabetics get ulcers on their feet?
The American Podiatric Medical Association adds that “ (diabetic foot) ulcers form due to a combination of factors, such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation (such as friction or pressure), and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes.” They go on to note that “vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, reducing the body’s ability to heal and increasing the risk for an infection.”
What is a malum perforans pedis ulcer?
Neuropathy results in malum perforans pedis (a.k.a. bad perforating foot) ulcers. These are painless, non-necrotic, circular lesions circumscribed by hyperkeratosis. They often overlie a metatarsal head. Ischemic wounds manifest local signs of ischemia such as thin, shiny, hairless skin with pallor and coldness. These are often found at areas of friction and may be painful.
Why are pressure ulcers considered a patient safety indicator?
Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
Why should we specifically carve out pressure ulcers?
Why should we specifically carve out pressure ulcers? Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
What is non pressure ulcer?
The term “non-pressure ulcer” was coined to designate a primary mechanism other than shear or pressure. If there is poor circulation, such as that caused by venous or arterial insufficiency or excessive moisture or trauma, a patient may develop a non-pressure ulcer.
Where do pressure ulcers form?
Pressure ulcers form in sites that experience shear or pressure, typically in tissue overlying bony prominences such as elbows, the sacrum, hips, or heels. After sacral, heel ulcers are the second most common type of pressure injury. The etymology of the term “decubitus ulcer” is from the Latin, decumbere, which means “to lie down,” ...
What is the ICd 10 code for a left heel ulcer?
L97.422 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of left heel and midfoot with fat layer exposed . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic bilateral breast implant infection
- 2. icd 10 code for febrile leukopenia
- 3. icd 10 code for heriditary retinal degeneration
- 4. icd 10 code for hx of tonsillectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for gad with panic attacks
- 6. icd 10 code for left leg wound
- 7. icd 1o code for traumatic subdural hematoma
- 8. icd 10 code for left calcaneal fracture
- 9. icd-10 code for stool culture c diff
- 10. icd 10 code for verruca