What is the ICD 10 code for ulnar impaction syndrome of right wrist?
Oct 01, 2021 · Ulnar impaction syndrome of left wrist ICD-10-CM M24.832 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 564 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses with mcc 565 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses with cc 566 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses without cc/mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for ulnocarpal impaction?
Oct 01, 2021 · Ulnar impaction syndrome of right wrist ICD-10-CM M24.831 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 564 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses with mcc 565 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses with cc 566 Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses without cc/mcc
What is ulnar impaction syndrome?
Oct 25, 2017 · Taken from Orthopedic Coding Alert. The best choice is 718.83 (Unspecified derangement of joint; forearm) to represent instability. Ulnar impaction syndrome is also known as ulnar abutment syndrome, and can be a common complication after distal radial fracture. The term means the distal ulna is no longer in line with the distal radius, resulting in the ulna being …
What is the ICD 10 code for ulnar nerve entrapment?
Ulnocarpal Impaction Syndrome ICD-10. M24.831 - Other specific joint derangements of right wrist, not elsewhere classified. M24.832 - Other specific joint derangements of left wrist, not elsewhere classified. M24.839 - Other specific joint derangements of unspecified wrist, not elsewhere classified.

What is ulnar impaction syndrome?
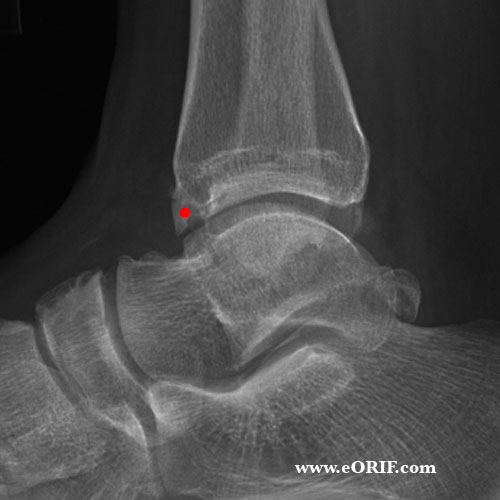
What is Ulnar Impaction Syndrome? Ulnar impaction syndrome occurs when the ulna is relatively larger than it should be when compared to the radius. This forces the ulna to bear more of the weight and force to the wrist on that side of the arm.
What is the ICD 10 code for impaction?
K56.41ICD-10-CM Code for Fecal impaction K56. 41.
Is ulnar impaction syndrome bilateral?
Bilateral Ulnar Styloid Impaction Syndrome Treated with Ulnar Styloidectomy.
What does ulnar impaction syndrome look like?
Common symptoms are: pain, occasional edema, decreased wrist range of motion, decreased forearm rotation, and tenderness to palpation dorsally just distal to the ulnar head and just volar to the ulnar styloid process. The symptoms are commonly aggravated by forceful grip, forearm pronation, and ulnar deviation.
What is the ICD-10 code for fecal retention?
ICD-10 | Fecal impaction (K56. 41)
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for constipation?
ICD-10 | Constipation, unspecified (K59. 00)
How do you get ulnar impaction syndrome?
Ulnar impaction syndrome is a progressive degenerative condition, most commonly resulting from repetitive abutment of a lengthened ulna, with the TFCC, lunate, triquetrum, and lunotriquetral ligament.
How is ulnar impaction syndrome treated?
The basis of treatment of ulnar impaction1 is mechanical decompression of the ulnocarpal articulation by decreasing ulnar variance. Shortening of the ulna or resection of the distal ulna significantly decreases forces across the ulnar wrist.
What does positive ulnar variance mean?
Positive ulnar variance describes where the distal articular surface of the ulna is more than 2.5mm distal to the articular surface of the radius. It plays important role in wrist pathology such as ulnar impaction syndromes and thinning of the triangular fibrocartilage complex.Apr 7, 2022
Is ulnar impaction syndrome serious?
This causes inflammation on the ulnar, or little-finger side, of the hand, and consequently, pain and swelling in the wrist. UIS is a degenerative wrist condition. Oftentimes, degenerative problems are irreversible as well as progressive. Fortunately, ulnar impaction syndrome is curable and treatable.Jul 10, 2015
How is ulnar abutment syndrome treated?
Ulnar abutment syndrome can be treated by a variety of nonsurgical and surgical methods. These range from anti-inflammatory medications, immobilization, and corticosteroid injections to TFCC debridement, ulnar shortening osteotomies, and arthroscopic wafer procedures.
Is ulnar shortening worth it?
This procedure has been the standard treatment for ulnar impaction syndrome for many years. Recent biomechanical studies have confirmed that an ulnar shortening osteotomy can improve the stability of the ulnar carpus and distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ).
What causes wrist pain?
Some wrist fractures are a result of osteoporosis. Other common causes of pain are. Sprains and strains. Tendinitis. Arthritis. Gout and pseudogout.
What is the tube that runs through your wrist called?
Your wrist is made up of eight small bones known as carpals. They support a tube that runs through your wrist. That tube, called the carpal tunnel , has tendons and a nerve inside. It is covered by a ligament, which holds it in place. Wrist pain is common.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M25.831 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Can repetitive motion cause wrist pain?
Repetitive motion can damage your wrist. Everyday activities like typing, racquet sports or sewing can cause pain, or even carpal tunnel syndrome. Wrist pain with bruising and swelling can be a sign of injury. The signs of a possible fracture include misshapen joints and inability to move your wrist.
The ICD code G562 is used to code Ulnar nerve entrapment
Ulnar nerve entrapment is a condition where the ulnar nerve becomes trapped or pinched due to some physiological abnormalities.
Coding Notes for G56.2 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G56.2 - Lesion of ulnar nerve'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G56.2. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What causes ulnar impaction syndrome?
Ulnar impaction syndrome is one of many possible causes of ulnar sided wrist pain, and requires multiple special tests and imaging to confirm diagnosis. If conservative treatment proves ineffective, medical management is indicated and should be followed by physical therapy to address resulting impairments in range of motion, strength, and joint mobility of the upper extremity.
What is the cause of ulnar wrist pain?
It is a degenerative condition in which the ulnar head abuts the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) and ulnar-sided carpals. This abutment results in increased load bearing across the ulnar head, TFCC and ulnar carpals, and subsequent degeneration of the TFCC, chondromalacia of the osseous structures involved (ulna and carpals, especially the lunate), and disruption of the triquetrolunate ligament.
Is Ulnar sided wrist pain a diagnosis?
Ulnar wrist pathologies often present very similarly in impairment and pain pattern. Thus, diagnostic imaging is often required to confirm diagnosis in the case of ul nar-sided wrist pain, and should be considered after the history-taking and clinical exam.
Can ulnar impaction be symptomatic?
Ulnar impaction syndrome is insidious and progressive, so patients can have the syndrome without symptoms or can be severely symptomatic when presenting to physical therapy. Common symptoms are: pain, occasional edema, decreased wrist range of motion, decreased forearm rotation, and tenderness to palpation dorsally just distal to the ulnar head and just volar to the ulnar styloid process. The symptoms are commonly aggravated by forceful grip, forearm pronation, and ulnar deviation.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for lymph node biopsy
- 2. icd 10 code for hyperdynamic left ventricle
- 3. icd 10 code for postoperative tibial nail
- 4. icd 10 cm code for fish hook in finger
- 5. icd 10 code for splinter right armpit
- 6. icd 9 code for paresthesias
- 7. icd 10 code for pain in left finger
- 8. icd 10 code for ptsd
- 9. icd 10 code for anterior rib sprain strain pain
- 10. icd-9-cm code for small fiber neuropathy