Unstable angina. I20.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I20.0 became effective on October 1, 2018.
Is there a cure for unstable angina?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unstable angina. I20.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I20.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I20.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 I20.0 may differ.
Is unstable angina life threatening?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I20.9 Angina pectoris, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I20.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I20.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do medications treat unstable angina?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I20 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I20 Angina pectoris 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code I20 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Do I have unstable angina?
Mar 16, 2016 · 110 – Atherosclerotic heart disease of a native coronary artery with unstable angina pectoris 710 – Atherosclerosis of autologous vein coronary artery bypass graft (s) with unstable angina pectoris Other ICD-10 codes related to Angina Pectoris are: 8 – Other forms of angina pectoris 9 – Angina pectoris, unspecified
How do you code unstable angina in ICD-10?
Is unstable angina the same as angina pectoris?
What is the ICD code for angina pectoris?
Is angina pectoris stable or unstable?
What are the 4 types of angina pectoris?
- Stable angina.
- Unstable angina.
- Microvascular Angina.
- Vasospastic or variant angina.
What are the types of angina pectoris?
- Stable angina is the most common type. It happens when the heart is working harder than usual. ...
- Unstable angina is the most dangerous. It does not follow a pattern and can happen without physical exertion. ...
- Variant angina is rare. It happens when you are resting.
What is unspecified angina pectoris?
What is angina pectoris syndrome?
What is angina pectoris caused by?
How is stable and unstable angina diagnosed?
When does unstable angina occur?
What does it feel like to have angina?
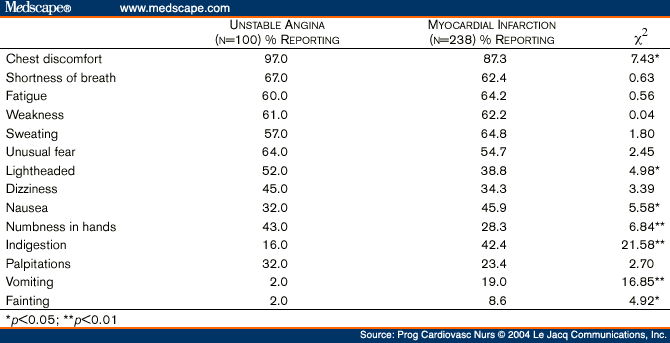
Angina is chest pain or discomfort you get when your heart muscle does not get enough blood. It may feel like pressure or a squeezing pain in your chest. It may feel like indigestion.
What is the most common heart disease?
Angina is a symptom of coronary artery disease (cad), the most common heart disease. Cad happens when a sticky substance called plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, reducing blood flow.there are three types of angina: stable, unstable and variant. Unstable angina is the most dangerous.
What is tobacco dependence?
tobacco dependence ( F17.-) A disorder characterized by substernal discomfort due to insufficient myocardial oxygenation. A heart condition marked by paroxysms of chest pain due to reduced oxygen to the heart. Angina is chest pain or discomfort you get when your heart muscle does not get enough blood.
What causes angina to be unstable?
Unstable angina is caused by poor blood flow through the blood vessels of the heart muscle, and is often a precursor to a myocardial infarction. Coronary spasm (I20.1 Angina pectoris with documented spasm) is a temporary constriction of the muscles in the wall of one of the coronary arteries.
What is angina equivalent?
Angina equivalent – A group of symptoms heralding angina pectoris that does not include chest pain (for example, dyspnea, diaphoresis, profuse vomiting in a diabetic patient, or arm or jaw pain) Angina of effort – Defined as angina pectoris precipitated by physical exertion.
Why does angina pectoris occur?
It is a result of inadequate oxygen supply to the heart. In most cases, angina pectoris is due to a narrowing of the coronary arteries resulting from arteriosclerosis. Angina usually occurs during exertion, severe emotional distress, or after a heavy meal.
How long does angina last?
It typically lasts between one and 15 minutes, and may be relieved with rest or nitroglycerin, which relax the blood vessels and lower blood pressure. Unstable angina (I20.0 Unstable angina) results in severe symptoms that do not occur on a regular basis or predictable manner.
Can angina pectoris cause chest pain?
The spasms lead to angina, and may lead to myocardial infarction. Other forms of angina pectoris include: Angina equivalent – A group of symptoms heralding angina pectoris that does not include chest pain (for example, dyspnea, diaphoresis, profuse vomiting in a diabetic patient, or arm or jaw pain) Angina of effort – Defined as angina pectoris ...
What is the I20 code?
There is an instructional note under category I20 that states to use and additional code to identify exposure to environmental tobacco smoke, history of tobacco use, occupational exposure to environmental tobacco smoke, tobacco dependence, or tobacco use. Author. Recent Posts.
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code procedure code for an egd is performed and a biopsy of the stomach was taken.
- 2. icd 10 code for osteonecrosis of palate
- 3. icd 10 code for gangrene left foot
- 4. icd 10 code for biceps tendinosis
- 5. icd 10 code for attention and concentration deficit
- 6. icd 10 code for kidney infection
- 7. icd 10 code for t wave abnormality
- 8. icd 10 code for protein
- 9. icd 10 code for gbs negative in pregnancy
- 10. icd 10 code for lennox gastaut syndrome and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia