Nonspecific urethritis. N34.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N34.1 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for urethral syndrome?
Oct 01, 2021 · Nonspecific urethritis N00-N99 2022 ICD-10-CM Range N00-N99 Diseases of the genitourinary system Type 2 Excludes certain conditions originating... N30-N39 2022 ICD-10 …
What is the ICD-10 code for gonococcal cystitis and urethritis?
ICD-10 code N34.3 for Urethral syndrome, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system . Subscribe to Codify and get the …
What is the ICD 10 code for urinalysis?
N34.3 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of urethral syndrome, unspecified. The code N34.3 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through …
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary incontinence?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified abnormal findings in urine. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R82.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to …
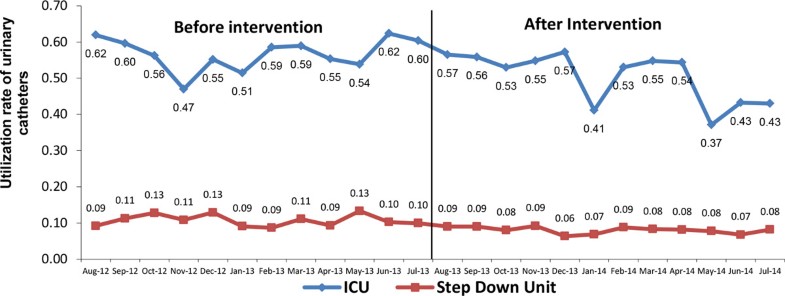
What is the ICD-10 code for recurrent urethritis?
What is ICD-10 code N39?
What is unspecified urethral stricture?
What is the ICD-10 code for urethral stricture?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N35. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for UTI with E coli?
A04. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute UTI?
How is urethral stricture diagnosis?
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary retention?
What is the CPT code for urethral dilation?
What is a pendulous urethral stricture?
Do urethral strictures hurt?
What is a fossa Navicularis stricture?
What is the code for urethral syndrome?
N34.3 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of urethral syndrome, unspecified. The code N34.3 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the name of the test that a doctor uses to diagnose urethral problems?
Doctors diagnose urethral problems using different tests. These include urine tests, x-rays and an examination of the urethra with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatment depends on the cause of the problem. It may include medicines and, in severe cases, surgery.
What is the term for a narrowing of the opening of the urethra?
Urethral stricture - a narrowing of the opening of the urethra. Urethritis - inflammation of the urethra, sometimes caused by infection. Urethral problems may cause pain or difficulty passing urine. You may also have bleeding or discharge from the urethra.
Can a urethra cause pain?
Urethral problems may cause pain or difficulty passing urine. You may also have bleeding or discharge from the urethra. Doctors diagnose urethral problems using different tests. These include urine tests, x-rays and an examination of the urethra with a scope called a cystoscope.
What is the name of the test to check for urethral problems?
You may also have bleeding or discharge from the urethra. Doctors diagnose urethral problems using different tests. These include urine tests, x-rays and an examination of the urethra with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatment depends on the cause of the problem.
When to use N34.3?
Unspecified diagnosis codes like N34.3 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition.
Coding Guidelines
The appropriate 7th character is to be added to each code from block Injury of urinary and pelvic organs (S37). Use the following options for the aplicable episode of care:
Specific Coding for Unspecified injury of urethra
Non-specific codes like S37.30 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for unspecified injury of urethra:
Index to Diseases and Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code (s). The following references for the code S37.30 are found in the index:
Information for Patients
The urethra is the tube that allows urine to pass out of the body. In men, it's a long tube that runs through the penis. It also carries semen in men. In women, it's short and is just above the vagina. Urethral problems may happen due to aging, illness, or injury. They include
What is the urinary system?
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Infections of the urinary tract (utis) are the second most common type of infection in the body. You may have a uti if you notice. pain or burning when you use the bathroom.
What is a UTI after a procedure?
Uti (urinary tract infection) after procedure. Clinical Information. A bacterial infectious process affecting any part of the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra. Symptoms include urinary urgency and frequency, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy urine.
How to tell if you have a UTI?
if you think you have a uti, it is important to see your doctor. Your doctor can tell if you have a uti by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with medicines to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days.
What are the symptoms of a swollen bladder?
Symptoms include urinary urgency and frequency, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy urine. A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra.
Is enuresis a symptom of incontinence?
Involuntary loss of urine, such as leaking of urine. It is a symptom of various underlying pathological processes. Major types of incontinence include urinary urge incontinence and urinary stress incontinence.
What is discharge of urine after completion of urinary control?
Involuntary discharge of urine after expected age of completed development of urinary control. This can happen during the daytime (diurnal enuresis) while one is awake or during sleep (nocturnal enuresis). Enuresis can be in children or in adults (as persistent primary enuresis and secondary adult-onset enuresis).

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for aortic aneurysm
- 2. what is the icd 10 code for hearing loss
- 3. icd 10 code for aftercare following cardiac catheterization
- 4. icd 10 code for eoe
- 5. icd 10 code for loose body left knee
- 6. icd 10 code for flutter
- 7. icd 10 code for raccoon bite left lower leg
- 8. icd 10 code for fall off bicycle
- 9. icd 10 code for right toe injury
- 10. icd 10 code for prerenal azotemia unspecified