How to interpret microalbumin urine?
Urine Albumin and Albumin to Creatinine Ratio
- About the Test. The purpose of a urine albumin test is to determine if there is an abnormal amount of the protein albumin in a urine sample.
- Finding a Urine Albumin or Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio Test. Testing for urine albumin levels is normally ordered by a doctor. ...
- Urine Albumin and Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio Test Results. ...
What causes microalbumin in urine?
Urine microalbumin levels can be higher than expected for a variety of reasons, including:
- Blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Certain medications
- Fever
- Recent vigorous exercise
- Urinary tract infection
- Other kidney diseases
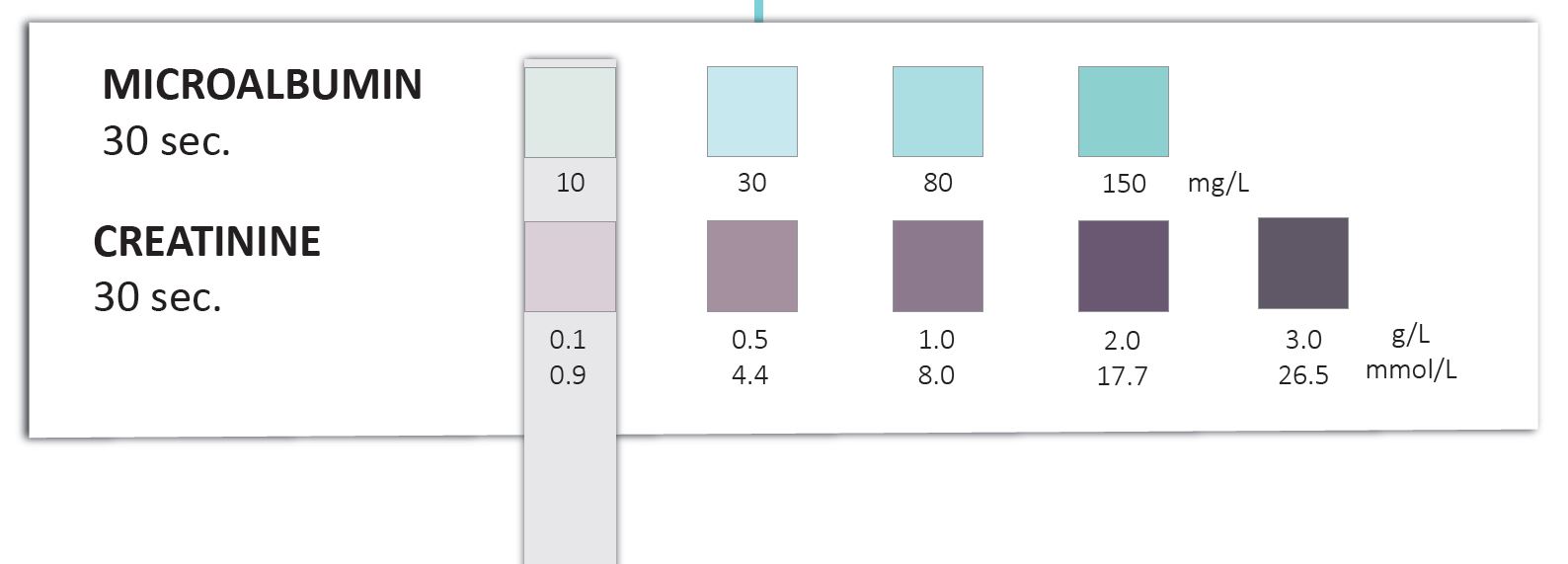
What is normal microalbumin urine?
The normal range for a random urine microalbumin test is less than 30 milligrams, says Mayo Clinic. Microalbumin is a blood protein filtered by the kidneys. The urine test measures the amount of protein unfiltered by the kidneys and is used to detect early signs of kidney damage.
How can microalbumin in my urine be reduced?
Reducing Protein In Blood Naturally
- Exercise. This should be done in a regular basis. ...
- Eating healthy. Avoiding food that are rich in sugar, fat, and salt is one of the best ways to reduce albumin levels. ...
- Sleeping adequately. This helps the body function normally.
- Avoid certain drugs that can increase albumin in blood. ...
What is the ICD 10 code Z13 89?
Code Z13. 89, encounter for screening for other disorder, is the ICD-10 code for depression screening.
What is diagnosis code Z03 89?
Z03. 89 No diagnosis This diagnosis description is CHANGED from “No Diagnosis” to “Encounter for observation for other suspected diseases and conditions ruled out.” established. October 1, 2019, with the 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM.
What microalbuminuria means?
Microalbuminuria is defined as levels of albumin ranging from 30 to 300 mg in a 24-h urine collection (13). Overt albuminuria, macroalbuminuria, or proteinuria is defined as a urinary albumin excretion of ≥300 mg/24 h. Urinary albuminuria comprises 20–70% or urinary total protein excretion.
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated uric acid?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hyperuricemia without signs of inflammatory arthritis and tophaceous disease E79. 0.
When should you use the code v71 09?
09 for Observation of other suspected mental condition is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -PERSONS WITHOUT REPORTED DIAGNOSIS ENCOUNTERED DURING EXAMINATION AND INVESTIGATION.
What ICD-10 code to use for no diagnosis?
The DSM-5 Steering Committee subsequently approved the inclusion of this category, and its corresponding ICD-10-CM code, Z03. 89 "No diagnosis or condition," is available for immediate use.
What is the difference between albuminuria and microalbuminuria?
In contrast, albuminuria specifically refers to an abnormal excretion rate of albumin. Microalbuminuria refers to an abnormally increased excretion rate of albumin in the urine in the range of 30–299 mg/g creatinine.
Is Microalbumin the same as albumin creatinine ratio?
Urine albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR), also known as urine microalbumin, helps identify kidney disease that can occur as a complication of diabetes. If kidney disease is diagnosed early in people with diabetes, appropriate treatment can be given and its effects can be closely monitored.
What is the difference between microalbuminuria and clinical albuminuria?
Early of its mostly albumin because of its small size. Later on its lots of albumin but also other proteins. Microalbuminuria is now called moderately increased albuminuria while albuminuria (macroalbuminuria) or proteinuria is now called severely increased albuminuria.
What diagnosis covers uric acid?
Uric acid measurements are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of gout, renal failure, and a variety of other disorders including leukemia, psoriasis, starvation, and other wasting conditions. Patients receiving cytotoxic drugs may be monitored with uric acid measurements.
What is a gouty tophus?
A tophus (plural: tophi) happens when crystals of the compound known as sodium urate monohydrate, or uric acid, builds up around your joints. Tophi often look like swollen, bulbous growths on your joints just under your skin.
What is a tophus?
Tophi (plural of tophus, Latin for “stone”) are stone-like deposits of monosodium urate in the soft tissues, synovial tissues, or in bones near the joints. They are pathognomonic for gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis in the United States, with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 4%.
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2020 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
Article Guidance
This article contains coding that complements the Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Urine Drug Testing.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
What is the value of microalbuminuria?
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has defined microalbuminuria as a microalbumin value of 30-300 mg/g creatinine.7 A persistent microalbumin of >30 mg/g indicates a loss of kidney function and is used in the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease.8
What is the purpose of microalbumin?
Microalbumin is the quantification of small amounts of albumin, a serum protein, in urine that can be used to identify microvascular endothelial dysfunction. The presence of small amounts of albumin in the urine may suggest the presence of systemic endothelial dysfunction – an early indicator of heart disease.1 This test is more sensitive than a standard dipstick test routinely performed in an office setting.
How often should I check for microalbumin?
Microalbumin testing is determined by an individual’s medical history, but may be performed semi-annually or annually as necessary. If the initial test result is abnormal, then follow-up testing may be performed within 3-6 months following treatment.
Can microalbumin be performed on a diabetic?
Microalbumin may be performed on individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, hypertension, a family history of chronic kidney disease, those at intermediate (10-20%) risk for CVD, or those with known vascular disease.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sacrococcygeal pain
- 2. icd 10 code for right meralgia paresthetica
- 3. what is the icd 9 code for influenza b
- 4. icd 10 code for right lower end humerus fracture
- 5. icd 10 cm code for sudden onset of weaknesses
- 6. icd-10-dm code for diagnosis of reactive airway disease exacerbation
- 7. icd 10 code for intolerance to lexapro
- 8. what is icd 10 code for anemia
- 9. icd 10 code for innominate artery stenosis
- 10. icd 10 code for developmental delay children