What is the default code for urosepsis?
Dec 20, 2019 · What is the ICD 10 code for Urosepsis? Sepsis, unspecified organism. A41. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a …
How to Code Sepsis ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2019 · What is the ICD 10 code for Urosepsis? A41. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM A41. 9 became effective on October 1, 2019. Read rest of the answer. Just so, what is the default code for Urosepsis? Urosepsis Is No Longer Coded Considered in ICD-10-CM as a …
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Septicemia NOS. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Urinary tract infection, site not specified. ; Urinary tract infection, recurrent; Urinary tract infectious disease; Urosepsis; Uti (urinary tract. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39.0.
What is the diagnosis code for urosepsis?
May 27, 2020 · Urosepsis Is No Longer Coded. Considered in ICD-10-CM as a nonspecific term and not associated with sepsis, the default code for this condition in ICD-9-CM (599.0 Urinary tract infection, site not specified) is not carried forward in ICD-10-CM. Find out everything you need to know about it here.

How do you code Urosepsis in ICD-10?
Urosepsis is actually coded urinary tract infection (599.0) in ICD 9. But, in ICD 10 is has no diagnosis code for urosepsis. ICD 10 does not consider urosepsis as disease or disorder. Hence urosepsis should not be coded in ICD 10, only sepsis should be reported with ICD 10 diagnosis codes.Aug 2, 2019
How do you code Urosepsis?
Urosepsis Is No Longer Coded Considered in ICD-10-CM as a nonspecific term and not associated with sepsis, the default code for this condition in ICD-9-CM (599.0 Urinary tract infection, site not specified) is not carried forward in ICD-10-CM.Apr 8, 2011
What is the ICD-10 code for sepsis due to UTI?
The ED coder would assign the following ICD-10 diagnosis codes:R65.21Severe sepsis with shockN39.0UTI, site not specifiedR30.0DysuriaR50.81Fever presenting with conditions classified elsewhereN17.9Acute kidney failure, unspecified2 more rows
Is Urosepsis coded as sepsis?
Urosepsis isn't sepsis—not from a coding standpoint, at least. Unless you want a query, don't document it. If it was a urinary tract infection (UTI), then document that. If it was sepsis due to a UTI, please say that in your documentation.May 30, 2019
What is urosepsis?
Urosepsis is sepsis caused by infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis, or lower urinary tract and bladder infections, and pyelonephritis, or upper urinary tract and kidney infections. Nearly 25 percent of sepsis cases originate from the urogenital tract.Feb 9, 2022
What is the ICD 10 code for obstructive uropathy?
Obstructive and reflux uropathy, unspecified N13. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the default code for urosepsis?
There is no default code for urosepsis in ICD-10-CM, and the provider must be queried for clarification when this term is documented.Apr 8, 2013
Is urosepsis serious?
In serious cases, urosepsis can progress into a condition called septic shock. If you go into septic shock, your blood pressure drops to dangerously low levels and your body's organs begin shutting down. This is a medical emergency. You should call 911 or seek emergency medical attention right away.
Can sepsis be coded as primary diagnosis?
According to the guidelines above, sepsis would be the appropriate principal diagnosis if it is the reason the patient is admitted, and meets the definition of principal diagnosis.Dec 5, 2016
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary retention?
ICD-10 | Retention of urine, unspecified (R33. 9)
How do you code sepsis and severe sepsis?
Chapter-specific guidelines state, “First code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code R65. 20, Severe sepsis. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41. 9, Sepsis, unspecified organism, for the infection.
When do you code sepsis?
Coding sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: a code for the systemic infection (e.g., 038. xx) and the code 995.91, SIRS due to infectious process without organ dysfunction. If no causal organism is documented within the medical record, query the physician or assign code 038.9, Unspecified septicemia.
What is post-procedural sepsis?
Post-procedural Sepsis and Sepsis Due to a Device, Implant, or Graft. A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to wound infection, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
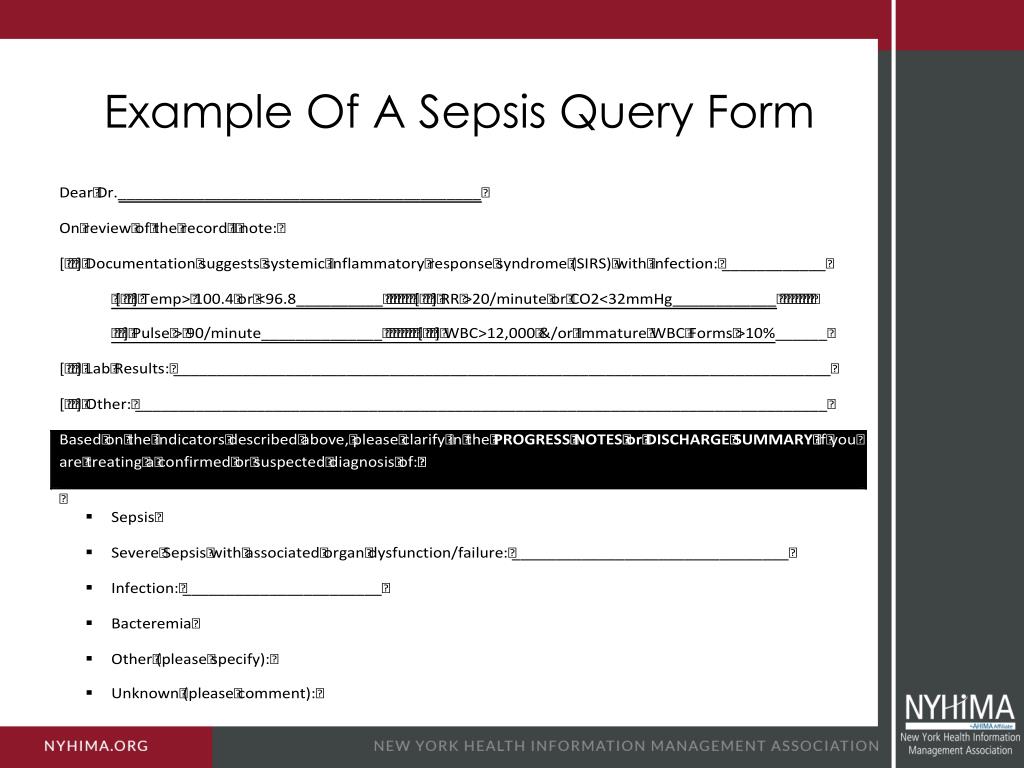
When to query a physician for sepsis?
You must query the physician when the term “sepsis syndrome” is documented as a final diagnosis. Know when to Query. Sepsis is a complicated condition to code, and it is often necessary to query the physician to code the case correctly.
What is the A41.51?
A41.51 Sepsis due to Escherichia coli [E. coli] N39.0. SIR S. SIRS is the body’s clinical cascading response to infection or trauma that triggers an acute inflammatory reaction and progresses to coagulation of the blood, impaired fibrinolysis, and organ failure.
What is the term for a lab finding of infectious organisms in the blood?
Bacteremia . Bacteremia is a lab finding of infectious organisms in the blood. The patient has no clinical signs of sepsis or SIRS. Bacteremia may be transient, or may lead to sepsis. When a patient’s blood cultures are positive and not believed to be a contaminant, the patient is usually treated with antibiotics.
What are the symptoms of SIRS?
SIRS is manifested by two or more of the following symptoms: fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, leukocytosis, or leukopenia. Documentation issues: When SIRS is documented on the chart, determine if it’s due to an infectious or non-infectious cause. SIRS due to a localized infection can no longer be coded as sepsis in.
What are the discharge diagnoses?
The discharge diagnoses were influenza with pneumonia bacterial superinfection, positive for pseudomonas, as well as acidosis, asthma exacerbation, hypoxemia, and chronic bronchitis. Sepsis and SIRS were not mentioned on the discharge summary, and are mentioned only sporadically throughout the progress notes.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if severe sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
What is systemic disease?
Systemic disease associated with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream causing a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock. Symptoms include fever, chills, tachycardia, and increased respiratory rate.
What is the term for the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues?
Urosepsis . Clinical Information. (sep-sis) the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues. A disorder characterized by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream that cause a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for late effects cva dysarthria
- 2. icd 10 code for pathological left hip fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for occlusion of distal right radial artery
- 4. icd-10-cm code for precordial chest pain
- 5. icd 10 code for sacral alar fracture
- 6. icd 10 code for abnormal weioght gain
- 7. 2015 icd 9 code for severly delayed gastric emptying
- 8. icd-10 code for endocardial fibroelastosis
- 9. icd 10 code for salivary gland swelling
- 10. icd 10 code for left fifth digit fracutre