What do you need to know about uterine fibroids?
- Genetic changes. Many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typical uterine muscle cells.
- Hormones. ...
- Other growth factors. ...
- Extracellular matrix (ECM). ...
Are uterine fibroids a preexisting condition?
Fibroids or even a history of them with no current health effects were treated as a pre-existing condition. The consequence was that insurance companies either would not provide any coverage related to my uterus – including for cancer and other potential conditions completely unrelated to fibroids – or would charge me significant additional ...
How can an uterine fibroid be treated?
What Procedures Might Work?
- Fibroid embolization. Your doctor will inject polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) into the arteries that feed the fibroid. The PVA blocks the blood supply to the fibroid, which makes it shrink.
- Endometrial ablation. Myomectomy is a surgery to remove fibroids. ...
- Hysterectomy. Many women don’t need treatment that’s this drastic. ...
What are the treatments for uterine fibroids?
- Stewart E, ASRM 2020; Late-breaker abstract P-930
- Al-Hendy A, NEJM 2021; 384:630-42
- Schlaff W, NEJM 2020; 382:328-40
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for uterine fibroids?
Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified D25. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D25. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How are uterine fibroids classified?
Fibroids are generally classified by their location. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall. Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity. Subserosal fibroids project to the outside of the uterus.
What is the differential diagnosis of fibroids?
The differential diagnosis for uterine leiomyomas includes both benign and malignant diseases that cause uterine enlargement, bleeding or pelvic pain. The most common diagnoses to consider are adenomyosis, endometriosis, pregnancy, leiomyosarcoma, endometrial carcinoma and uterine carcinosarcoma [11].
What is the ICD-10 code for pedunculated fibroid?
D25. 0 - Submucous leiomyoma of uterus | ICD-10-CM.
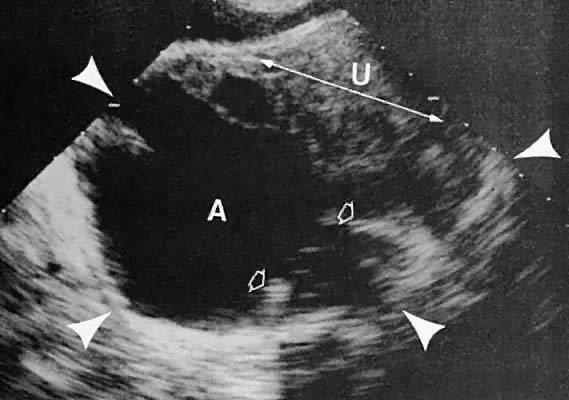
What kind of ultrasound is used for uterine fibroids?
Magnetic Resonance-guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS) is a noninvasive, incisionless technique used to treat abnormal benign growths in a woman's uterus called fibroids, or leiomyoma. Uterine fibroids are very common, occurring in approximately one in four women, and often have no symptoms.
How do fibroids appear on ultrasound?
Uterine fibroids most often appear on ultrasonograms as concentric, solid, hypoechoic masses. This appearance results from the prevailing muscle, which is observed at histologic examination. These solid masses absorb sound waves and therefore cause a variable amount of acoustic shadowing.
Can you see uterine fibroids on ultrasound?
If you have symptoms of uterine fibroids, your doctor may order these tests: Ultrasound. If confirmation is needed, your doctor may order an ultrasound. It uses sound waves to get a picture of your uterus to confirm the diagnosis and to map and measure fibroids.
What is the ICD 10 code for uterine mass?
Other benign neoplasm of uterus, unspecified D26. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D26. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the different types of fibroids?
The three main types of fibroids include:Subserosal fibroids: These are the most common fibroids. They can push outside of the uterus into the pelvis. ... Intramural fibroids: These fibroids develop in the muscular wall of the uterus.Submucosal fibroids: These fibroids are uncommon.
What is multiple fibroids in uterus?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the muscle tissue of the uterus. Fibroids can range in number and size from a single growth to multiple growths, and from very small to large. As many as 70% to 80% of all women will have fibroids by age 50. The medical term for fibroids is leiomyoma or myoma.
What is diagnosis code D25 9?
ICD-10 code: D25. 9 Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified.
What is a pedunculated fibroid?
Pedunculated fibroids are benign (noncancerous) growths in the uterus. These fibroids are attached to the uterine wall by a stalk-like growth called a peduncle. The main difference between pedunculated fibroids and other fibroids is the peduncle. These fibroids can grow both inside and outside the uterus.
What is a fibrous tumor?
Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age . Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being african-american or being overweight.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Can fibroids cause infertility?
most women with fibroids can get pregnant naturally. For those who cannot, infertility treatments may help. Treatment for uterine fibroids includes medicines that can slow or stop their growth, or surgery.
What is the code for uterine fibroids?
nih: national institute of child health and human development. Codes. D25 Leiomyoma of uterus. D25.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus.
What is a fibroid uterus?
uterine fibroid. uterine fibromyoma. uterine myoma. Clinical Information. A benign smooth muscle neoplasm arising from the body of the uterus. It is characterized by the presence of spindle cells with cigar-shaped nuclei, interlacing fascicles, and a whorled pattern. Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women ...
What is a fibrous tumor?
Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age . Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being african-american or being overweight.
Can fibroids cause a miscarriage?
Many women with uterine fibroids have no symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include. heavy or painful periods or bleeding between periods. feeling "full" in the lower abdomen. reproductive problems, such as infertility, multiple miscarriages or early labor. most women with fibroids can get pregnant naturally.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acute behavioral change due to medication
- 2. icd 10 code for infectious encephalopathy
- 3. icd 10 code for leptomeningeal mass
- 4. icd 10 code for sub carinal mass
- 5. icd 10 code for acute on chronic kidney injury
- 6. icd-10-cm code for pregnancy
- 7. icd-10 code for diarrhea
- 8. icd 10 code for absent laryngeal crepitation
- 9. icd-9 code for slipping on a slick floor without falling
- 10. icd 10 code for n stemi