Is Wolff Parkinson White a disability?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T75.21XA [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pneumatic hammer syndrome, initial encounter. Pneumatic hammer syndrome; Vibration white finger. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T75.21XA. Pneumatic hammer syndrome, initial encounter. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
What are the symptoms of the Wolff Parkinson White syndrome?
Oct 01, 2021 · Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome I45.6 Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Is Wolff Parkinson White syndrome misdiagnosed?
ICD10 codes matching "Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome" Codes: = Billable. I45.6 Pre-excitation syndrome
How can Wolff Parkinson White syndrome be prevented?
References in the ICD-10-CM Index to Diseases and Injuries applicable to the clinical term "wolff-parkinson-white syndrome". Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome - I45.6 Pre-excitation syndrome. Previous Term: Wolff Hirschorn Syndrome. Next Term: Wolhynian Fever.

What is the ICD 10 code for WPW?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G21 G21.
What is WPW pattern?
Some people with an extra electrical pathway don't have signs or symptoms of a fast heartbeat. This condition is called Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) pattern. It's often discovered by chance during a heart test.Jan 27, 2022
Is WPW regular or irregular?
The heart's regular pattern of electrical impulses causes the heart to fill with blood and contract in a normal fashion. WPW is an electrical abnormality in the heart that may be associated with supraventricular tachycardia (fast heart rate originating above the ventricles).Aug 14, 2019
What does pre excitation syndrome mean?
Pre-excitation describes the electrical phenomena occurring in the heart and seen on ECG in some cases due to the presence of an AP. When there is an associated tachyarrhythmia due to the presence of an AP or in patients who experience symptoms due to the AP, this disorder is termed pre-excitation syndrome (PES).
What is the difference between SVT and Wolff Parkinson White?
What is SVT? Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) refers to a group of abnormal fast heart rhythms that arise because of a problem involving the upper chambers of the heart. WPW is short for Wolf-Parkinson White syndrome which is a special form of SVT.
Is WPW Orthodromic or Antidromic?
Types of arrhythmias in WPW are AVRT (80%). There are two type of AVRT, orthodromic (90 to 95%) vs. antidromic (5%), other types are atrial fibrillation (AF) (10% to 30%), atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation [4-7].May 17, 2018
Can Wolff-Parkinson-White come back?
Abstract. Background: Although successful ablation of the accessory pathway (AP) eliminates atrial fibrillation (AF) in some of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome and paroxysmal AF, in other patients it can recur.Oct 1, 2020
Are you born with Wolff-Parkinson-White?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a type of heart condition you are born with (congenital). It causes a rapid heart rate. If you have WPW, you may have episodes of palpitations or rapid heartbeats. WPW affects less than 1 in 100 people.
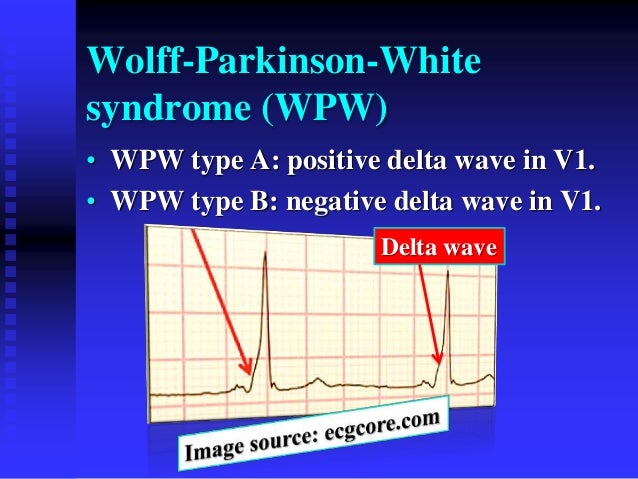
What does a WPW EKG look like?
The classic ECG morphology of WPW syndrome is described as a shortened PR interval (often <120 ms) and a slurring and slow rise of the initial upstroke of the QRS complex (delta wave; see the image below), a widened QRS complex with a total duration greater than 0.12 seconds, and secondary repolarization changes ...Jan 8, 2017
What kind of arrhythmia is pre excitation syndrome?
“Preexcitation syndrome” is a broad term delineating various conditions that can lead to several forms of SVT. Ventricular preexcitation is due to a connection of muscle fibers between the atria and the ventricles that lies outside the AV node (accessory pathway, Kent bundle).
Why is the QRS wide in WPW?
The QRS interval is widened because the ventricles are initially activated via the AP, which lies outside the normal conducting system, producing an early, albeit relatively slow, initial propagation of depolarization forces through the ventricular tissue. This produces the delta wave.Jan 8, 2017
What is Brugada syndrome?
Brugada (brew-GAH-dah) syndrome is a rare, but potentially life-threatening heart rhythm disorder that is sometimes inherited. People with Brugada syndrome have an increased risk of having irregular heart rhythms beginning in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).Mar 20, 2020
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I45.6:
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code I45.6 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is it called when your heart beats too fast?
An arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat. It means that your heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular pattern. When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia. When the heart beats too slowly, it is called bradycardia.
What causes a fast heartbeat?
The most common type of arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation, which causes an irregular and fast heart beat. Many factors can affect your heart's rhythm, such as having had a heart attack, smoking, congenital heart defects, and stress. Some substances or medicines may also cause arrhythmias.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for oral aversion
- 2. icd-10 code for ivf pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for anterior cruciate ligament tear
- 4. icd 10 code for laceration left 1st toe
- 5. icd-9 code for foot stitches
- 6. icd-10-pcs code for non excisional debridement left heel ulcer
- 7. icd 10 code for ob
- 8. icd 10 code for excision right back sarcoma
- 9. icd 9 code for nausea and vomiting in pregnancy
- 10. icd 10 code for dry eyes symptoms