What is the ICD 10 code for wound care?
Z48.0 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z48.0. Encounter for attention to dressings, sutures and drains 2016 2017 2018 2019 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. Type 1 Excludes encounter for planned postprocedural wound closure (Z48.1) Encounter for attention to dressings, sutures and drains.
How do you code an open wound for follow up?
You would never code the open wound for a follow up and you would not a scar unless specifically documented. Code only the V code for follow up Do Medicare and/or commercial payers cover V67.59?
What is the ICD 10 code for follow-up examination?
Encounter for follow-up examination after completed treatment for conditions other than malignant neoplasm. Z09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM Z09 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the ICD 10 code for surgical aftercare?
Z48.81 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z48.81. Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems 2016 2017 2018 2019 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. Applicable To These codes identify the body system requiring aftercare.
What is the ICD-10 index for wounds?
What is an open wound?
What causes a laceration in a wound?
What is a penetrating wound?
Is an incision a life threatening wound?
Can a puncture wound be gaping?
See more
About this website
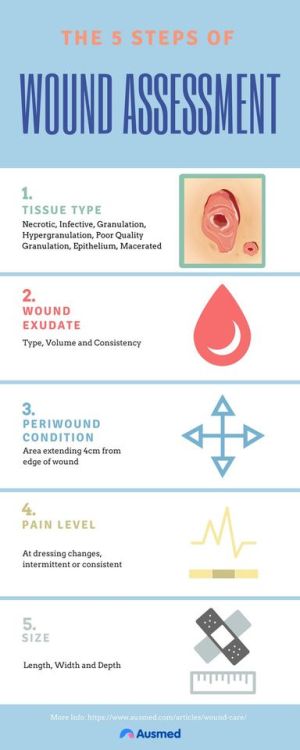
What is ICD-10 code for wound care?
This article addresses the CPT/HCPCS and ICD-10 codes associated with L37228 Wound Care policy.
What is the ICD-10 code for attention to surgical wound?
Z48. 0 - Encounter for attention to dressings, sutures and drains. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for wound dressing?
ICD-10 Code for Encounter for change or removal of surgical wound dressing- Z48. 01- Codify by AAPC.
How do you code surgical aftercare?
Use Z codes to code for surgical aftercare. Z47. 89, Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare, and. Z47.
What is the ICD 10 code for aftercare following surgery?
81: Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems.
What is the CPT code for wound care?
Dressings applied to the wound are part of the services for CPT codes 97597, 97598 and 97602 and they may not be billed separately. It is not appropriate to report CPT code 97602 in addition to CPT code 97597 and/or 97598 for wound care performed on the same wound on the same date of service.
What is the CPT code for wound cleaning and dressing?
CPT codes 97597 and 97598 are used for wet-to-dry dressings, application of medications with enzymes to dissolve dead tissue, whirlpool baths, minor removal of loose fragments with scissors, scraping away tissue with sharp instruments, debridement with pulse lavage, high-pressure irrigation, incision, and drainage.
What is the ICD-10 code for wound infection?
ICD-10 Code for Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified- L08. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for post operative wound infection?
4-, a post-procedural wound infection and post-procedural sepsis were assigned to the same ICD-10-CM code T81. 4-, Infection following a procedure with a code for the infection (sepsis, cellulitis, etc.)
What is the difference between follow-up and aftercare?
Follow-up. The difference between aftercare and follow-up is the type of care the physician renders. Aftercare implies the physician is providing related treatment for the patient after a surgery or procedure. Follow-up, on the other hand, is surveillance of the patient to make sure all is going well.
What is follow-up coding?
Follow-up codes are used to explain continuing surveillance following completed treatment of a disease, condition, or injury. They imply that the condition has been fully treated and no longer exists.
Billing and Coding Guidelines for Wound Care
Billing and Coding Guidelines for Wound Care LCD ID L34587 Billing Guidelines Wound Care (CPT Codes 97597, 97598 and 11042-11047) 1. Active wound care procedures are performed to remove devitalized and/or necrotic tissue to
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes S31.1*: Open wound of abdominal wall without ...
ICD-10-CM Codes › S00-T88 Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes ; S30-S39 Injuries to the abdomen, lower back, lumbar spine, pelvis and external genitals ; S31-Open wound of abdomen, lower back, pelvis and external genitals Open wound of abdominal wall without penetration into peritoneal cavity S31.1
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S81.802A
Approximate Synonyms. Gunshot wound of left lower leg; Open wound of left lower leg; ICD-10-CM S81.802A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0):. 604 Trauma to the skin, subcutaneous tissue and breast with mcc; 605 Trauma to the skin, subcutaneous tissue and breast without mcc; 963 Other multiple significant trauma with mcc; 964 Other multiple significant trauma with cc
ICD-10 Coding Help Sheet
B12 Deficiency NOS – D51.9 . Blood Loss –D62 (acute) D50.0 (chronic) Chemotherapy – D64.81 . Note: Use additional code, T45.1X5+ Chronic Kidney Disease –D63.1
What is the ICD-10 index for wounds?
Main term entries in the ICD-10-CM index for open wounds can be either the type of wound (e.g., puncture), or the term wound, open. Using either term will allow the coder to find the correct type of wound and anatomical location by using the indented subterms. For example, if you look up puncture wound of the abdomen in the index using the main term Wound, open and then go to the subterms Abdomen, wall, puncture, an instructional note will guide you to “see” Puncture, abdomen, wall.#N#Example 1:
What is an open wound?
Type of wound — Open wounds include: Abrasions: Shallow, irregular wounds of the upper layers of skin. Caused by skin brushing with either a rough surface or a smooth surface at high speed. Usually present with minor to no bleeding, with some pain that subsides shortly after initial injury.
What causes a laceration in a wound?
Lacerations are generally caused by trauma or contact with an object. Incisions: Typically the result of a sharp object such as a scalpel, knife, or scissors.
What is a penetrating wound?
Penetrating wounds can be life threatening, causing serious injury, especially if involving vital organs, major blood vessels, or nerves. Gunshot wounds: These are considered to be penetrating wounds that are exclusively caused by bullets from firearms (guns, rifles, etc.).
Is an incision a life threatening wound?
Depending on the depth and site of the wound, an incision can be life threatening, especially if it involves vital organs, major blood vessels, or nerves. Punctures: Small, rounded wounds that result from needles, nails, teeth (bites), or other tapered objects.
Can a puncture wound be gaping?
The puncture wounds on the patient’s hands are not gaping and I think the risks outweigh the benefits of any type of suture closure. The wounds are quite small and I think suturing them would likely increase their risk of infection. IMPRESSION: Dog bite.
What is the ICD-10 index for wounds?
Main term entries in the ICD-10-CM index for open wounds can be either the type of wound (e.g., puncture), or the term wound, open. Using either term will allow the coder to find the correct type of wound and anatomical location by using the indented subterms. For example, if you look up puncture wound of the abdomen in the index using the main term Wound, open and then go to the subterms Abdomen, wall, puncture, an instructional note will guide you to “see” Puncture, abdomen, wall.#N#Example 1:
What is an open wound?
Type of wound — Open wounds include: Abrasions: Shallow, irregular wounds of the upper layers of skin. Caused by skin brushing with either a rough surface or a smooth surface at high speed. Usually present with minor to no bleeding, with some pain that subsides shortly after initial injury.
What causes a laceration in a wound?
Lacerations are generally caused by trauma or contact with an object. Incisions: Typically the result of a sharp object such as a scalpel, knife, or scissors.
What is a penetrating wound?
Penetrating wounds can be life threatening, causing serious injury, especially if involving vital organs, major blood vessels, or nerves. Gunshot wounds: These are considered to be penetrating wounds that are exclusively caused by bullets from firearms (guns, rifles, etc.).
Is an incision a life threatening wound?
Depending on the depth and site of the wound, an incision can be life threatening, especially if it involves vital organs, major blood vessels, or nerves. Punctures: Small, rounded wounds that result from needles, nails, teeth (bites), or other tapered objects.
Can a puncture wound be gaping?
The puncture wounds on the patient’s hands are not gaping and I think the risks outweigh the benefits of any type of suture closure. The wounds are quite small and I think suturing them would likely increase their risk of infection. IMPRESSION: Dog bite.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for m43.10
- 2. icd 10 cm code for compression fracture
- 3. billable icd 10 code for hypothyroidism
- 4. icd code for depression screening
- 5. icd 10 code for mucositis due to chemotherapy
- 6. what is the icd 10 code cm for intrauterine pregnancy, 39 weeks, previous cesarean section
- 7. icd 9 code for schizophreniform disorder
- 8. icd-10 code for chronic ear infection left ear
- 9. icd-10-cm code for encounter for blood typetesting prior to surgery
- 10. 2019 icd 10 code for breast ultrasound post op due to implants