What is anaphylaxis really like?
The first visible symptom of anaphylaxis usually appears on the skin, which gets red. Often, this occurs in the cheeks, and may look like flushing, though it will not include any sweating. Redness can also occur on the chest and neck, or other areas of the body. Next, the person may develop hives.
What is the correct definition of anaphylaxis?
define anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially fatal systemic allergic reaction that occurs suddenly (minutes to hours) after contact with an allergy-causing substance Pre-formed granules in anaphylactic reactions Histamine (causes itch, mucus, sneeze, urticaria, bronchospasm)
What are the two most common signs of anaphylaxis?
What are two signs of anaphylaxis?
- abdominal cramps.
- heart palpitations.
- nausea and vomiting.
- swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
- skin reactions such as hives, itching, or peeling.
- breathing problems.
- dizziness or fainting.
- weak and rapid pulse.
How to emotionally heal after anaphylaxis?
Steps to take for signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis:
- Immediately give 1 shot of epinephrine only into the outer thigh muscle. Even if your allergic reaction seems mild, it can quickly become anaphylaxis. ...
- Leave the shot in place as directed. ...
- Call 911 and go to the emergency department, even if the shot improved symptoms. ...
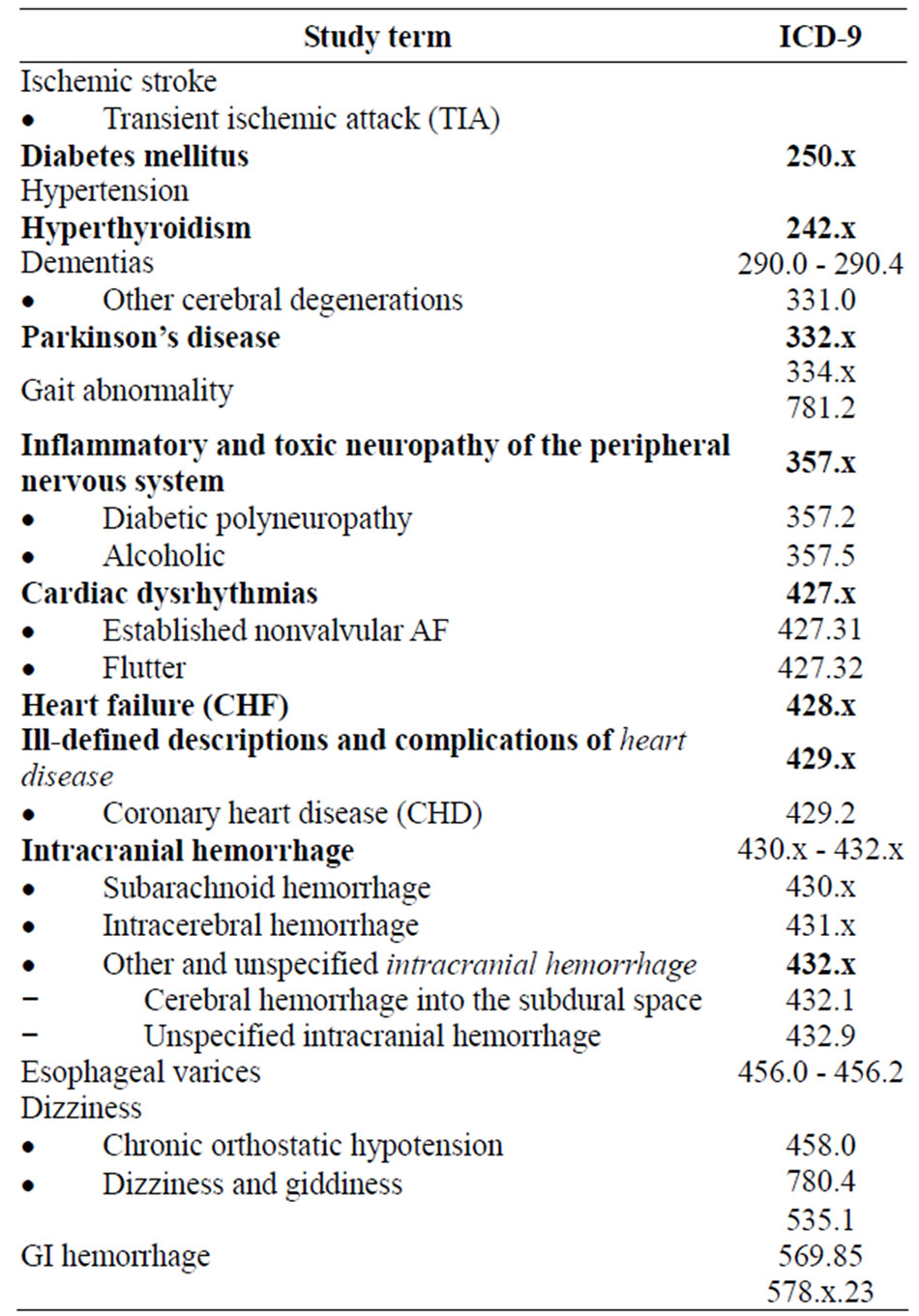
What is the ICD 10 code for acute allergic reaction?
ICD-10 code T78. 40XA for Allergy, unspecified, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is anaphylaxis diagnosis?
The diagnosis of anaphylaxis is typically made when symptoms occur within one hour of exposure to a specific antigen. Confirmatory testing using serum histamine and tryptase levels is difficult, because blood samples must be drawn with strict time considerations.
What is the ICD 10 code for anaphylactic shock from peanuts?
T78.01XAICD-10-CM Code for Anaphylactic reaction due to peanuts, initial encounter T78. 01XA.
What is the medical term for anaphylactic reaction?
Anaphylactic shock: A widespread and very serious allergic reaction.
Is anaphylaxis the same as an allergic reaction?
Allergic reactions are common in children. Most reactions are mild. A severe allergic reaction (i.e. anaphylaxis) involves a person's breathing and/or circulation. Anaphylaxis is the most severe form of an allergic reaction and is life threatening.
What are the three diagnostic criteria for anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis is considered likely to be present if any 1 of the 3 following clinical criteria is satisfied within minutes to hours: Acute symptoms involving skin, mucosal surface, or both, as well as at least one of the following: respiratory compromise, hypotension, or end-organ dysfunction.
What is the ICD-10 code for angioedema?
T78.3XXAICD-10-CM Code for Angioneurotic edema, initial encounter T78. 3XXA.
What is the ICD-10 code for food allergies?
ICD-10 code Z91. 01 for Food allergy status is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for environmental allergies?
J30. 2 - Other seasonal allergic rhinitis. ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock?
The terms "anaphylaxis" and "anaphylactic shock" are often used to mean the same thing. They both refer to a severe allergic reaction. Shock is when your blood pressure drops so low that your cells (and organs) don't get enough oxygen. Anaphylactic shock is shock that's caused by anaphylaxis.
What is anaphylaxis allergy?
Anaphylaxis is when you get severe allergic reactions. Examples include reactions to certain foods or particular insect stings. Going into anaphylactic shock can be life-threatening. If you notice symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as having trouble breathing, use an epinephrine injector.
What are the 4 types of allergic reactions?
Four different types of allergic reactions are immediate, cytotoxic, immune-complex mediated and delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hepititis c
- 2. icd 10 cm code for anxiety state
- 3. icd 10 code for nondisplaced fracture left superior pubic ramus
- 4. icd-9 code for hypoechoic mass
- 5. icd 10 code for multiple insect bites all over body
- 6. icd-10 code for left upper eyelid stye
- 7. what is the icd 10 cm code for fecal lith
- 8. icd 10 code for right lung contusion
- 9. 2016 icd 10 code for right groin hernia
- 10. icd 9 cm code for congestive heart failure?