How is a dilated aortic root repaired?
Your surgeon will remove the bulging weak area and sew a man-made substitute, called a graft, into place. If the aortic valve is not healthy, your surgeon may repair it or replace it with an artificial valve. After your surgeon does all of the repairs, normal blood flow through your heart and your aorta will resume.
What are the symptoms of dilated aorta?
- Chest and back pain (most common)
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Intense fast heart beat
- Numbness
- Chilling sensation
- Loss of consciousness
- Light headed feeling
What is the ICD 10 code for aortic root replacement?
The procedure code 02RX0KZ is in the medical and surgical section and is part of the heart and great vessels body system, classified under the replacement operation. The applicable bodypart is thoracic aorta, ascending/arch. 02RX0KZ replaces the following previously assigned ICD-10-PCS code (s):
What is dilated ascending aorta?
Dilatation of the ascending aorta is a very indolent process as it takes many years to develop and it is asymptomatic initially. In patients who develop an ascending aortic aneurysm secondarily to a systemic disorder, signs of the primary disease are the ones who lead the clinician to look for the dilatation such as in Marfan syndrome.
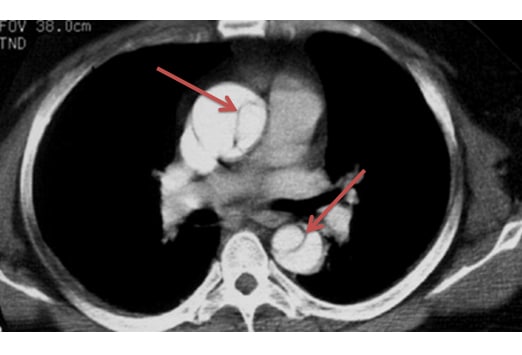
What does it mean to have a dilated aortic root?
Otherwise known as an aortic root aneurysm, a dilated aortic root is when the first section of the aorta, where the aortic valve resides, becomes enlarged. When this enlargement reaches a critical size, there is a risk of it rupturing or tearing, leading to a life-threatening situation.
Is aortic root dilation the same as aortic aneurysm?
An aortic root aneurysm occurs in the beginning, or root, of the aorta. The aorta is the body's largest blood vessel. It transports blood to the body from the heart. Doctors also call an aortic root aneurysm a dilated aortic root.
What is diagnosis code i71 2?
2 Thoracic aortic aneurysm, without rupture.
How is aortic root dilation diagnosed?
Aortic root dilation is typically first identified on echocardiography in 60–80% of Marfan patients [18]. Therefore, surveillance echocardiography has been routinely used to serially monitor aortic dimensions.
What is dilated aortic root and ascending aorta?
Abstract. Background: The aorta is considered pathologically dilated if the diameters of the ascending aorta and the aortic root exceed the norms for a given age and body size. A 50% increase over the normal diameter is considered aneurysmal dilatation.
Is aortic root dilation common?
Dilated aortic root (DAR) is a relatively common finding, with a reported prevalence of about 4% measured at the level of the sinuses of Valsalva in the general population.
What is the ICD-10 code for aortic root aneurysm?
Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site, without rupture I71. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I71. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does diagnosis code 150.9 mean?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 150.9 : Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified site.
Is aortic root part of thoracic aorta?
The Thoracic Aorta has 4 distinct parts: Aortic Root – Lies in the front portion of the chest below the sternum. It starts at the level of the heart and includes the aortic valve and the portion where the coronary arteries arise called the Sinus of Valsalva.
How do you fix a dilated aortic root?
In aortic valve and root replacement (composite aortic root replacement), your surgeon removes a section of the body's largest blood vessel (aorta) your aortic valve. The section of your aorta is replaced with an artificial tube (graft), and your aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
Is aortic root dilation congenital?
Aortic dilation at the level of the aortic root can be caused by a variety of congenital or acquired conditions that lead to weakening of the aortic wall.
Can you live with a dilated aortic root?
Yes, you can live with an aortic aneurysm, and there are many ways to prevent dissection (splitting of the blood vessel wall that causes blood to leak) or worse, a rupture (a burst aneurysm).
How do you fix a dilated aortic root?
In aortic valve and root replacement (composite aortic root replacement), your surgeon removes a section of the body's largest blood vessel (aorta) your aortic valve. The section of your aorta is replaced with an artificial tube (graft), and your aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
Can you live with a dilated aortic root?
Yes, you can live with an aortic aneurysm, and there are many ways to prevent dissection (splitting of the blood vessel wall that causes blood to leak) or worse, a rupture (a burst aneurysm).
Is a dilated aorta serious?
Also known as an aortic aneurysm, this condition can be deadly if left undiagnosed. Learn more about who is at risk for enlarged aorta. Each year in the United States, aortic aneurysms contribute to nearly 20,000 deaths.
What is the treatment for a dilated aorta?
The most common type of surgery is open abdominal or chest repair, where the doctor opens up your chest or abdomen, depending on where the problem is, removes the bulge in your aorta, and replaces it with a fabric tube called a graft.
What is the ICd 10 code for aorta dilation?
Congenital dilation of aorta 1 Q25.44 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q25.44 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q25.44 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q25.44 may differ.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q25.44 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q25.44 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for a dilated aortic valve?
027F04Z is a valid billable ICD-10 procedure code for Dilation of Aortic Valve with Drug-eluting Intraluminal Device, Open Approach . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (PCS) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What is DRG 216?
DRG 216 - CARDIAC VALVE AND OTHER MAJOR CARDIOTHORACIC PROCEDURES WITH CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION WITH MCC

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for follow up hospitalization for fever
- 2. icd 10 code for hepatitis c chronic
- 3. icd 10 cm code for juvenle onset diabeticsecond trimester
- 4. assign the icd-10-cm code for dirofilariasis
- 5. icd 10 code for louti
- 6. icd-10-cm code for allergy to morphine
- 7. icd-10 code for foot enjury
- 8. icd 10 code for constipation nos
- 9. icd 10 code for personal history of brain tumor
- 10. icd 10 code for eating less