Is it really duct carcinoma in situ?
It is the cells lining the duct that can go “bad” in DCIS. If these abnormal cells, which are uncontrollably growing, stay inside the duct, they are referred to as Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ (DCIS). They are ductal cells that have become malignant, but they have remained in their original place (in-situ) and are thus a noninvasive cancer.
What you should know about lobular carcinoma in situ?
Treatment
- Observation. If you've been diagnosed with LCIS, your doctor may recommend more frequent exams to closely monitor your breasts for signs of cancer.
- Preventive therapy. Preventive therapy (chemoprevention) involves taking a medication to reduce your risk of breast cancer.
- Surgery. Surgery may be recommended in certain situations. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
What is papillary carcinoma in situ?
The cancer cells' finger-like appearance is what distinguishes them from cells that would be apparent in other types of breast cancer. Papillary carcinoma is often found with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), which is a type of early stage breast cancer confined to a milk duct.
How to pronounce squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
Treatments for carcinoma in situ will depend on factors, such as:
- the location of the precancerous cells
- the size and location of any benign tumor
- individual risk factors, for example, a personal or family history of cancer
- the age of the person
- other health conditions
- personal preferences
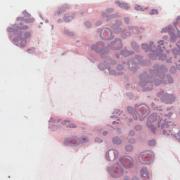
What is the ICD 10 code for ductal carcinoma in situ of right breast?
ICD-10-CM Code for Intraductal carcinoma in situ of right breast D05. 11.
How do you code ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast?
D05. 1 - Intraductal carcinoma in situ of breast | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ductal carcinoma in situ left breast?
ICD-10-CM Code for Intraductal carcinoma in situ of left breast D05. 12.
Is there a difference between ductal carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is non-invasive breast cancer that starts in the milk ducts. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is non-invasive breast cancer that starts in the milk ducts. In situ means in its original place. DCIS is non-invasive because it hasn't spread beyond the milk ducts into other healthy tissue.
What is the CPT code for ductal carcinoma in situ?
Intraductal carcinoma in situ of right breast D05. 11 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05. 11 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for intraductal carcinoma?
ICD-10-CM Code for Intraductal carcinoma in situ of unspecified breast D05. 10.
What is in situ carcinoma of the breast?
A condition in which abnormal cells are found in the tissues of the breast. There are 2 types of breast carcinoma in situ: ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and Paget disease of the nipple. DCIS is a condition in which the abnormal cells are found in the lining of a breast duct.
What is Intraductal carcinoma in situ of left breast?
Breast anatomy Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in the breast. DCIS is considered the earliest form of breast cancer. DCIS is noninvasive, meaning it hasn't spread out of the milk duct and has a low risk of becoming invasive.
What is carcinoma in situ?
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body (see left panel). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue (see right panel).
What stage is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue.
Is DCIS always Stage 0?
About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
Is carcinoma in situ considered malignant?
Carcinoma in situ refers to cancer in which abnormal cells have not spread beyond where they first formed. The words “in situ” mean “in its original place.” These in situ cells are not malignant, or cancerous. However, they can sometime become cancerous and spread to other nearby locations.
What is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Breast anatomy Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in the breast. DCIS is considered the earliest form of breast cancer. DCIS is noninvasive, meaning it hasn't spread out of the milk duct and has a low risk of becoming invasive.
What stage is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue.
What is carcinoma in situ of breast?
A condition in which abnormal cells are found in the tissues of the breast. There are 2 types of breast carcinoma in situ: ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and Paget disease of the nipple. DCIS is a condition in which the abnormal cells are found in the lining of a breast duct.
Is carcinoma in situ considered malignant?
Carcinoma in situ refers to cancer in which abnormal cells have not spread beyond where they first formed. The words “in situ” mean “in its original place.” These in situ cells are not malignant, or cancerous. However, they can sometime become cancerous and spread to other nearby locations.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D05.11 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05.11 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D05.12 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05.12 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a carcinoma of the mammary ducts?
A carcinoma entirely confined to the mammary ducts. It is also known as dcis. There is no evidence of invasion of the basement membrane. Currently, it is classified into three categories: high-grade dcis , intermediate-grade dcis and low-grade dcis.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is noninvasive carcinoma?
A noninvasive (noninfiltrating) carcinoma of the breast characterized by a proliferation of malignant epithelial cells confined to the mammary ducts or lobules, without light-microscopy evidence of invasion through the basement membrane into the surrounding stroma.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
When will the ICd 10 D05.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can ductal carcinoma spread to other tissues?
The abnormal cells have not spread outside the duct to other tissues in the breast. In some cases, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer and spread to other tissues, although it is not known at this time how to predict which lesions will become invasive. Code History.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D05.10 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05.10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is stage 0 of breast cancer?
Abnormal cells that are confined to the ducts or lobules in the breast. There are two forms, called ductal carcinoma in situ (dcis) and lobular carcinoma in situ (lcis). Stage 0 includes: tis, n0, m0. Tis: carcinoma in situ.
When will the ICd 10 D05 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D05 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is LCis in breast?
Lcis is a condition in which abnormal cells are found in the lobules (small sections of tissue involved with making milk) of the breast. This condition seldom becomes invasive cancer; however, having lcis in one breast increases the risk of developing breast cancer in either breast. Code History.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D05. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together , such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. carcinoma in situ of skin of breast (.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for tick bite
- 2. icd 10 code for depressive symptoms
- 3. icd 10 code for family history of genetic disorder
- 4. icd 10 code for left medial lower leg wound infection
- 5. icd 10 code for sprain oblique groups
- 6. icd-10 code for lab draw in office
- 7. what is the 2016 icd-10 code for o34212
- 8. icd 9 code for sarcoma of the thigh
- 9. icd 10 code for mild hearing loss
- 10. icd 10 code for sacral alar fracture