What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations. Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations.
What is the ICD 10 code for early onset dementia?
What is the ICD 10 code for early onset dementia? ICD-10 code G30. 0 for Alzheimer's disease with early onset is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system . How do you code Alzheimer's dementia? Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's dementia requires two ICD-9-CM codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for general anxiety disorder?
What are the types of anxiety disorders?
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). People with GAD worry about ordinary issues such as health, money, work, and family. ...
- Panic disorder. People with panic disorder have panic attacks. ...
- Phobias. People with phobias have an intense fear of something that poses little or no actual danger. ...
Who is at risk for a psychotic disorder?
Risk factors for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders include: Chronic psychotic disorders are much more likely to arise in people with inherited brain differences or in those whose brains were changed by physical or chemical events early in their lives. Psychosis can lead to changes in emotions.
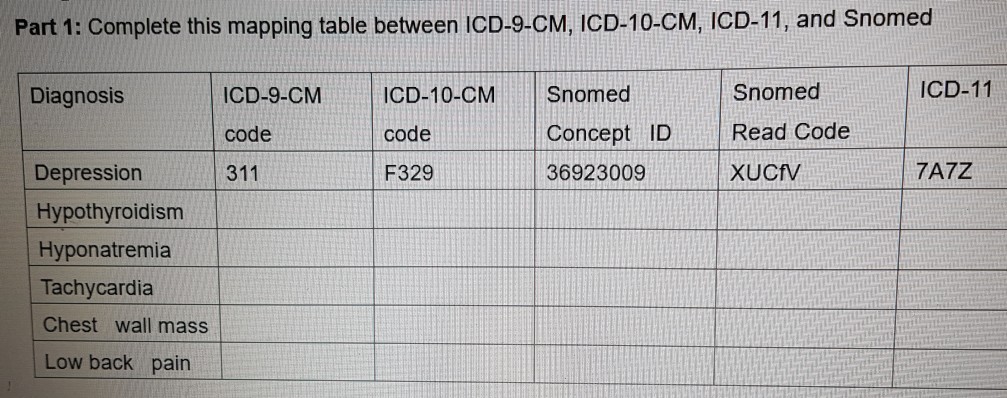
What is the diagnosis code for psychosis?
psychosis, psychogenic (F23. 3)
Is acute psychosis a diagnosis?
The term "acute psychosis" is commonly used as a provisional diagnosis in psychiatric acute settings, especially in emergency, when there is not sufficient information available to give a specific categorical diagnosis.
Is acute psychosis a DSM-5 diagnosis?
Brief psychotic disorder is defined in the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) as the presence of one or more psychotic symptoms with a sudden onset and full remission within one month [1].
What is acute psychosis?
Also known as Brief Psychotic Disorder, this is an acute mental health condition when there is a loss of contact with reality. This is characteristised by one or more of following features. A reduced level of social functioning. Blunted or inappropriate affect. Changes in perception due to hallucination.
What are the differential diagnosis of psychosis?
Differential Diagnosis of Acute PsychosisDiagnosisTestsHuman immunodeficiency virus26CT, serum antibody testingNeurosyphilis27CT or MRI, lumbar puncture, treponemal antibody testing (e.g., fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test)Metabolic conditionsAcute intermittent porphyria28Urine porphyrins testing44 more rows•Jun 15, 2015
What causes acute psychosis?
Psychosis can be caused by a mental (psychological) condition, a general medical condition, or alcohol or drug misuse.
What is the DSM-5 code for psychosis?
Unspecified Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorder DSM-5 298.9 (298.9) (298.9)
What is difference between DSM 4 and DSM-5?
In the DSM-IV, patients only needed one symptom present to be diagnosed with substance abuse, while the DSM-5 requires two or more symptoms in order to be diagnosed with substance use disorder. The DSM-5 eliminated the physiological subtype and the diagnosis of polysubstance dependence.
What mental disorders are listed in the DSM-5?
Download fact sheets that cover changes to disorders in the DSM–5.Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)Autism Spectrum Disorder.Conduct Disorder.Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder.Eating Disorders.Gender Dysphoria.Intellectual Disability.Internet Gaming Disorder.More items...
Is acute psychosis a schizophrenic?
The sudden onset of severe psychotic symptoms may be considered “acute” schizophrenia, but not always. Onset can occur at any time, though typically individuals are diagnosed between their teen years and their early thirties. It is very rare for a diagnosis to be made earlier or later in one's life.
What is acute and transient psychosis?
acute and transient psychotic disorder (ATPD) defined by ICD-10 (World Health Organization) characterized by acute onset (no greater than 2 weeks from first appearance of symptoms to full disorder) of hallucinations, delusions, and/or incomprehensible or incoherent speech.
What's the difference between delirium and psychosis?
Psychotic patients tend not to have visual hallucinations They have auditory hallucinations. They hear voices....Is this patient psychotic? Or Delirious?DeliriumPsychosisSudden OnsetNo sudden onsetDisorientedOrientedVisual hallucinationsNo visual hallucinationsSick (abnormal vital signs, sweaty, look sick)Not sickFeb 6, 2012
Is acute psychosis a schizophrenic?
The sudden onset of severe psychotic symptoms may be considered “acute” schizophrenia, but not always. Onset can occur at any time, though typically individuals are diagnosed between their teen years and their early thirties. It is very rare for a diagnosis to be made earlier or later in one's life.
How are psychotic disorders classified?
There are five such domains: hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thought (speech), disorganized or abnormal motor behavior (including catatonia), and negative symptoms.
What is the DSM-5 code for psychosis?
Unspecified Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorder DSM-5 298.9 (298.9) (298.9)
How many symptoms does it take to diagnose psychosis?
According to the DSM-5, a schizophrenia diagnosis requires the following: At least two of five main symptoms. Those symptoms, explained above, are delusions, hallucinations, disorganized or incoherent speaking, disorganized or unusual movements and negative symptoms.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bphcolon cancer
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for mri brain
- 3. icd-10 code for viral syndrome
- 4. icd 10 code for perihilar mass
- 5. icd 10 code for conjunctivitis bilateral
- 6. icd 10 code for insect bite right chin
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral pedal edema
- 8. icd 10 code for fracture left wrist
- 9. icd 10 code for urinary tract infection serrtia marrescens
- 10. icd 10 code for mucopurultent rhinitis