What causes adrenal incidentaloma?
These hormones include:
- Cortisol – Cushing syndrome or subclinical hypercortisolism are conditions caused by too much cortisol
- Aldosterone - Primary aldosteronism is a condition caused by too much aldosterone
- Adrenaline hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) - Pheochromocytomas are rare adrenal tumors that produce too much adrenaline hormone
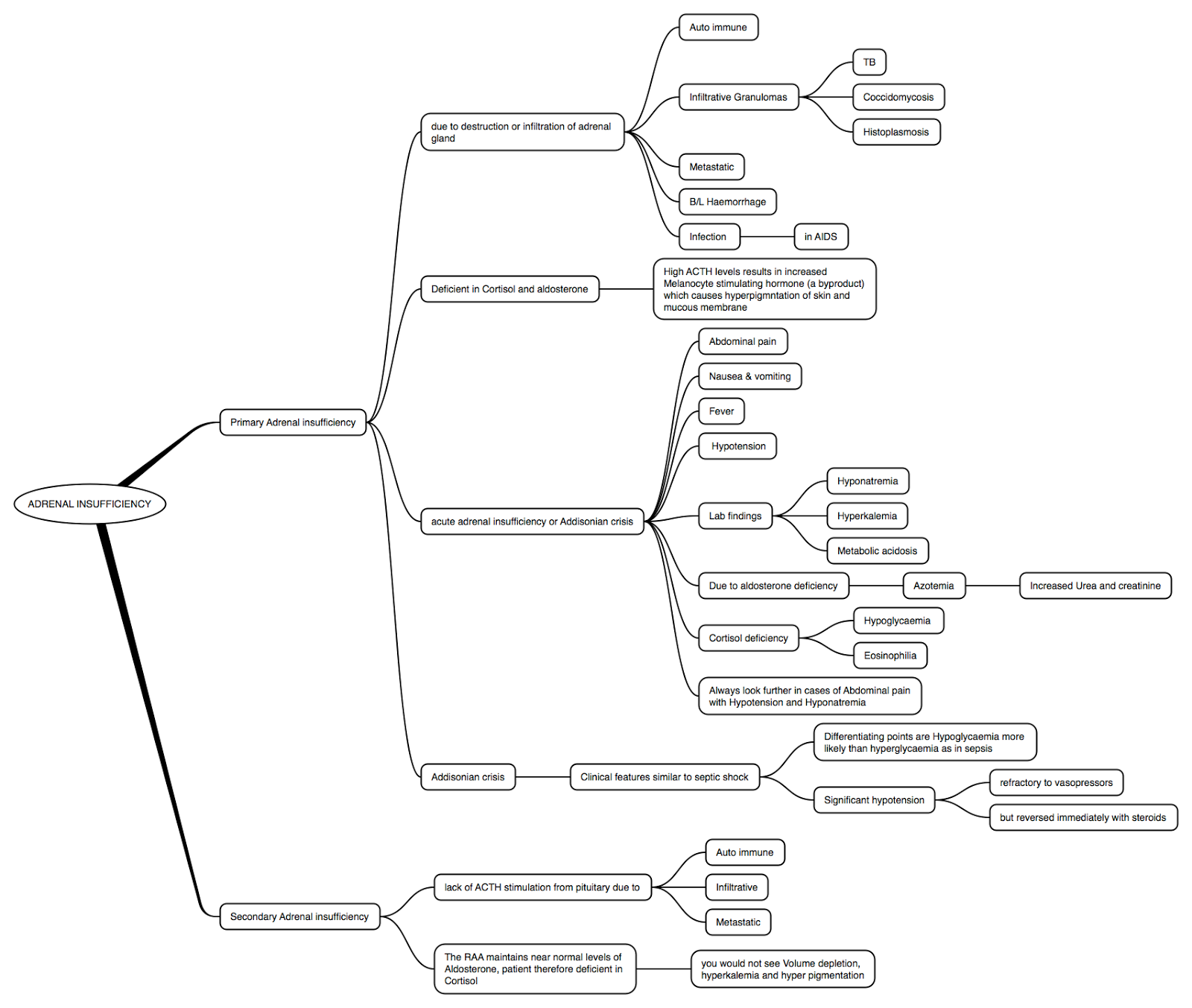
Is adrenal insufficiency a rare disease?
Adrenal insufficiency occurs when the adrenal glands don’t make enough of the hormone cortisol. The primary kind is known as Addison’s disease. It is rare. It is when the adrenal glands don’t make enough of the hormones cortisol and aldosterone.
What does adrenal insufficiency stand for?
You have two adrenal glands, one above each kidney. They make important hormones that your body uses for some of its most basic functions. When they don’t make enough of those hormones, you have a condition called adrenal insufficiency, also called adrenocortical insufficiency or hypocortisolism. What Do These Hormones Do?
What does adrenal adenoma mean?
An adrenal gland adenoma is a tumor on your adrenal gland that isn’t cancer, but can still cause problems. Learn what causes them, how to know if you might have one, and how they’re treated.

What is the ICD 10 code for right adrenal mass?
ICD-10-CM Code for Benign neoplasm of right adrenal gland D35. 01.
What is adrenal mass?
An adrenal mass is an abnormal growth that develops in the adrenal gland. It's unclear why these masses form. They can develop in anyone of any age, but they are more common in older individuals.!
What is a functional adrenal mass?
Adrenal tumors that produce hormones are called "functional" adrenal tumors. That means they are functional as intended to produce hormones--but they just produce too much of the hormone. It is important to understand that most functional adrenal tumors are benign (non-cancerous).
WHO do you refer to for adrenal mass?
If the history or exam are concerning for adrenal disease, or if the laboratory work- up reveals abnormal findings, refer to Endocrinology or Endocrine Surgery. referral to Endocrinology or Endocrine Surgery is advised. 5.
Where is an adrenal mass?
An adrenal mass, or tumor, is a benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growth that develops on an adrenal gland. There are two adrenal glands in the body, one situated above each kidney.
What are the different types of adrenal tumors?
Types of tumors that start in the adrenal glands include:Adenoma. This is the most common kind of adrenal gland tumor. ... Adrenal cortex cancer (adrenal cortical carcinoma). This kind of tumor is rare. ... Pheochromocytoma. This is a tumor that makes hormones inside the adrenal glands (in the medulla). ... Neuroblastoma.
Is an adrenal nodule a tumor?
A benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) nodule, also called a tumor or mass, may develop in one of the adrenal glands that sit atop each kidney.
How do you diagnose adrenal tumors?
Your doctor will thoroughly examine your abdomen for evidence of a tumor (or mass). Your blood and urine will likely be tested to look for high levels of the hormones made by some adrenal tumors. If an adrenal tumor is suspected, imaging tests will be done to look for it. These tests can also help see if it has spread.
Are adrenal masses cancerous?
Adrenal tumors can be malignant (cancer) or benign (not cancerous). Even benign adrenal tumors can be dangerous or cause uncomfortable symptoms. The adrenal glands are part of the endocrine system, which releases hormones into the blood system.
What causes adrenal mass?
Risk Factors of Adrenal Masses The only known risk factors for adrenal masses and cancer are certain genetic syndromes and mutations. The most common of these are: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome types 2A and 2B (MEN 2A and 2B), von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome (VHL), Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1)).
What is the ICD code for acute care?
D35.0. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code D35.0 is a non-billable code.
What is an adenoma?
An adenoma (from Greek αδένας, adeno-, "gland" + -ώμα, -oma, "tumor") (/ˌædᵻˈnoʊmə/; plural adenomas or adenomata /ˌædᵻˈnoʊmᵻtə/) is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, over time they may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. But even while benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.
Where do adenomas grow?
Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli).
Do adenomas transform?
Most adenomas do not transform. But even while benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for general inhalation anesthesia.
- 2. icd 10 code for renal lesions
- 3. icd 9 code for metastatic ca of ovary
- 4. icd 10 code for blisters on multiple sites
- 5. icd 10 code for mild hepatomegaly
- 6. icd 10 cm code for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis with infarction
- 7. icd 10 code for dysfunctional mediport
- 8. what icd 10 code would i use for pain over aicd pocket
- 9. icd 10 code for syphilis screen
- 10. icd 10 cm code for status post cholecystectomy