Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for chromosomal abnormality?
Chromosomal abnormality, unspecified. Q99.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are the diagnostic groups of ICD-10-CM?
ICD-10-CM A56.2 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 727 Inflammation of the male reproductive system with mcc 728 Inflammation of the male reproductive system without mcc 742 Uterine and adnexa procedures for non-malignancy with cc/mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for chlamydia?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to A74.9: 1 Chlamydia, chlamydial A74.9 2 Disease, diseased - see also Syndrome chlamydial A74.9 3 Infection, infected, infective (opportunistic) B99.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99.9 Unspecified infectious disease 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code Chlamydia, chlamydial A74.9
What is the ICD 10 code for abnormal cytology?
R89.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Abnormal cytological findings in specimens from oth org/tiss. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R89.6 became effective on October 1, 2018.
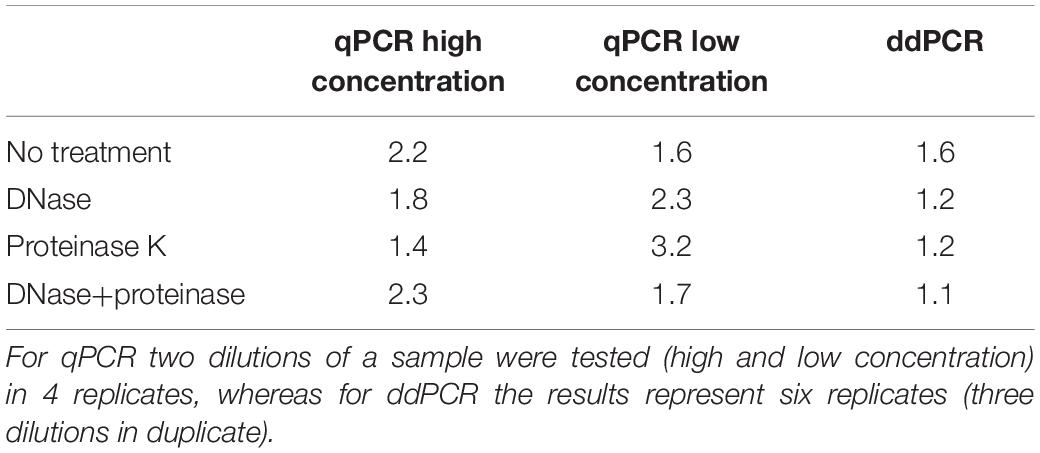
What is Gc RNA by TMA?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Urogenital - Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococci) is the causative agent of gonorrhea. In men, this disease generally results in anterior urethritis accompanied by purulent exudate. In women, the disease is most often found in the cervix, but the vagina and uterus may also be infected.
What does GC RNA mean?
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C).
What is a TMA STD test?
The preferred test is Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by Transcription-Mediated Amplification (TMA) (0060241) or if confirmation of positive results by an alternate nucleic acid target is required, refer to Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (CTNG) by Transcription-Mediated Amplification ( ...
What is CT GC RNA test?
Requisition Form. G-2B. Test Description. Target amplification nucleic acid probe test that utilizes target capture for qualitative detection and differentiation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) from Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and/or Neisseria gonorrhea (GC)
What is GC content RNA seq?
GC-content normalization is designed to reduce the dependence of gene-level read counts on sequence composition within a lane. However, other technical effects, such as between-lane differences in sequencing depth, can strongly bias differential expression results.
What does GC content indicate?
GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content), in molecular biology, is the percentage of nitrogenous bases on a DNA molecule which are either guanine or cytosine (from a possibility of four different ones, also including adenine and thymine). This may refer to a specific fragment of DNA or RNA, or that of the whole genome.
What does GC chlamydia mean?
Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) are the two most common bacterial causes of sexually transmitted diseases worldwide. In the United States CT and GC account for about 4 million and 2 million annual cases of genital infection respectively.
How do you read chlamydia test results?
Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you. Normal results are negative, meaning that no chlamydia cells were found in your sample. A positive result means that chlamydia bacteria were found and that you are likely infected with the disease.
What is Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) are the most common sexually transmitted pathogens and are the main contributors to sexually transmitted infections (STIs). CT infects approximately 5% to 10% of the population, with infection rates as high as 40% in patients with STIs [1].
What is GC DNA test?
The digene HC2CT/GC DNA Test is an in vitro nucleic microplate assay based on signal-amplified nucleic acid hybridization that uses chemiluminescence for the combined qualitative detection of DNA from Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) from cervical specimens.
What is a GC urine test?
This is a test on a urine sample to check for gonorrhea. Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). Gonorrhea can be serious if not treated. It can damage organs and cause infertility in women and men. It can even lead to a life-threatening bacterial infection.
What is GC PCR test?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (also known as Gonococcus or GC) can be detected by PCR at the same time as Chlamydia trachomatis testing. The prevalence of gonorrhoea in the population is very low, so even with a highly sensitive and specific test there is a risk of false-positive results.
Patient Preparation
Urine: Patient should not have urinated within one hour prior to collection. Female patients should not cleanse the labial area prior to providing the specimen.
Preferred Specimen (s)
1 vaginal swab in Aptima® Transport Tube or 1 endocervical or urethral swab in Aptima® Transport Tube or 2 mL urine in Aptima® Transport Tube or 1 mL liquid cytology (PreservCyt®) Preservative (ThinPrep®) in Aptima® Transfer Tube or 0.5 mL SurePath™ Preservative Fluid in Aptima® Transfer Tube
Minimum Volume
1 vaginal swab in Aptima® Transport • 1 endocervical or urethral swab in Aptima® Transport • 2 mL urine in Aptima® Transport • 1 mL PreservCyt® (ThinPrep®) in Aptima® Transfer Tube • 0.5 mL SurePath™ fluid in Aptima® Transfer Tube
Collection Instructions
Vaginal Swab: Follow instructions in the Aptima® Vaginal Swab Collection or Multitest Collection Kit (orange label).
Setup Schedule, Reject Criteria
Vaginal Swab: Follow instructions in the Aptima® Vaginal Swab Collection or Multitest Collection Kit (orange label).

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for mucus cyst finger
- 2. icd 10 code for fall off bannister
- 3. icd-9 code for cf
- 4. icd 10 code for parkinson banel
- 5. what is the icd 10 cpt code for removal of a splinter deep in the knee?
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland
- 7. icd 10 code for cystocele midline
- 8. icd 10 code for lipoma of right arm
- 9. 2020 icd 10 code for constipation
- 10. icd 10 code for lymes disease active