What is the ICD-9 code for chronic pulmonary heart disease?
ICD-9 code 416 for Chronic pulmonary heart disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISEASES OF PULMONARY CIRCULATION (415-417). Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic pulmonary embolism (CPE)?
Chronic pulmonary embolism 1 I27.82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I27.82 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I27.82 - other international versions of ICD-10 I27.82 may differ. More ...
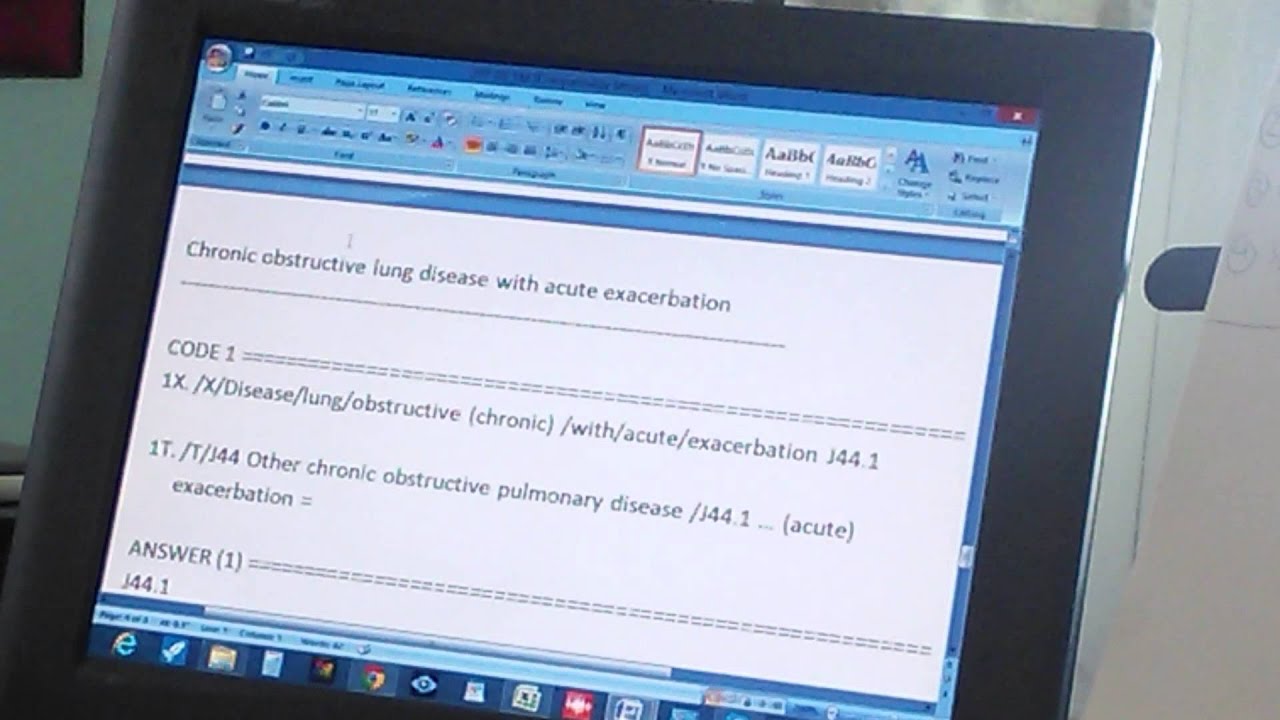
What is the ICD 9 code for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 490-496?
The ICD-9 code range CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE AND ALLIED CONDITIONS for 490-496 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary edema?
ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. J00-J99 Diseases of the respiratory system. ›. J80-J84 Other respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium. ›. J81- Pulmonary edema. ›. 2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J81.1.

How do you code chronic pulmonary embolism?
ICD-10 Code for Chronic pulmonary embolism- I27. 82- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic pulmonary embolism?
I27. 82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-9 code for primary pulmonary hypertension?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 416.0 : Primary pulmonary hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic pulmonary heart disease?
Pulmonary heart disease, unspecified I27. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I27. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD code for pulmonary embolism?
We used ICD-10 codes (I26. 9: pulmonary embolism without cor pulmonale, and I26. 0: pulmonary embolism with cor pulmonale) to identify patients diagnosed with PE; we refer to these identified patients as the coded PE group (Fig.
Can pulmonary embolism be chronic?
Types of Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary emboli can present as acute PE or chronic PE. Acute PE is a new obstruction causing acute onset heart strain.
What is the ICD-10 code for severe pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension due to lung diseases and hypoxia I27. 23 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I27. 23 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 | Fever, unspecified (R50. 9)
How do you code CKD and hypertension?
If chronic kidney disease is documented with hypertension, a combination code from I12 — hypertensive chronic kidney disease — should be reported. Documentation needs to identify the stage as 1-5 or end stage renal disease (ESRD) in order to report an additional code from category N18 — chronic kidney disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic respiratory failure?
10 for Chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
Is cor pulmonale chronic?
Chronic cor pulmonale is defined as right heart hypertrophy and/or chronic right heart failure. There are many etiologies, but the common cause is increased right heart work from pulmonary hypertension.
What is a cardiopulmonary disease?
Cardiopulmonary disease is the medical term used to describe a range of serious disorders that affect the heart (“cardio-”) and lungs (“-pulmonary”). The two primary tobacco-related cardiopulmonary diseases are Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD).
What are the symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Signs and symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, productive cough, and chest tightness. The two main types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are chronic obstructive bronchitis and emphysema. A disease of chronic diffuse irreversible airflow obstruction. Subcategories of copd include chronic bronchitis and pulmonary emphysema.
What is a chronic lung disorder?
A chronic and progressive lung disorder characterized by the loss of elasticity of the bronchial tree and the air sacs, destruction of the air sacs wall, thickening of the bronchial wall, and mucous accumulation in the bronchial tree.
What is the name of the disease that makes it hard to breathe?
A type of lung disease marked by permanent damage to tissues in the lungs, making it hard to breathe. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease includes chronic bronchitis, in which the bronchi (large air passages) are inflamed and scarred, and emphysema, in which the alveoli (tiny air sacs) are damaged.
What is the disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that
A disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure. Accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues causing disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure.
What is excessive accumulation of fluid in the lung?
Excessive accumulation of extravascular fluid in the lung, an indication of a serious underlying disease or disorder. Pulmonary edema prevents efficient pulmonary gas exchange in the pulmonary alveoli, and can be life-threatening. Extravascular accumulation of fluid in the pulmonary tissue and air spaces.
What causes pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary edema is usually caused by heart problems, but it can also be caused by high blood pressure, pneumonia, certain toxins and medicines, or living at a high altitude. Symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, and trouble exercising.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lymph nodes exhibiting metastatis
- 2. icd-10 code for burn of second degree left hand second finger
- 3. icd 10 code for limb pain lower extremity
- 4. icd 10 code for primary osteoarthritis of rt knee.
- 5. icd 10 code for punctate keratitis
- 6. icd-10 code for abdominal cramping in pregnancy
- 7. icd 10 code for acute on chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure
- 8. assign the icd-10-cm external cause code for case-2
- 9. icd 10 code for recurrent right inguinal hernia with gangrene.+
- 10. 2018 icd 10 code for sleep apnea