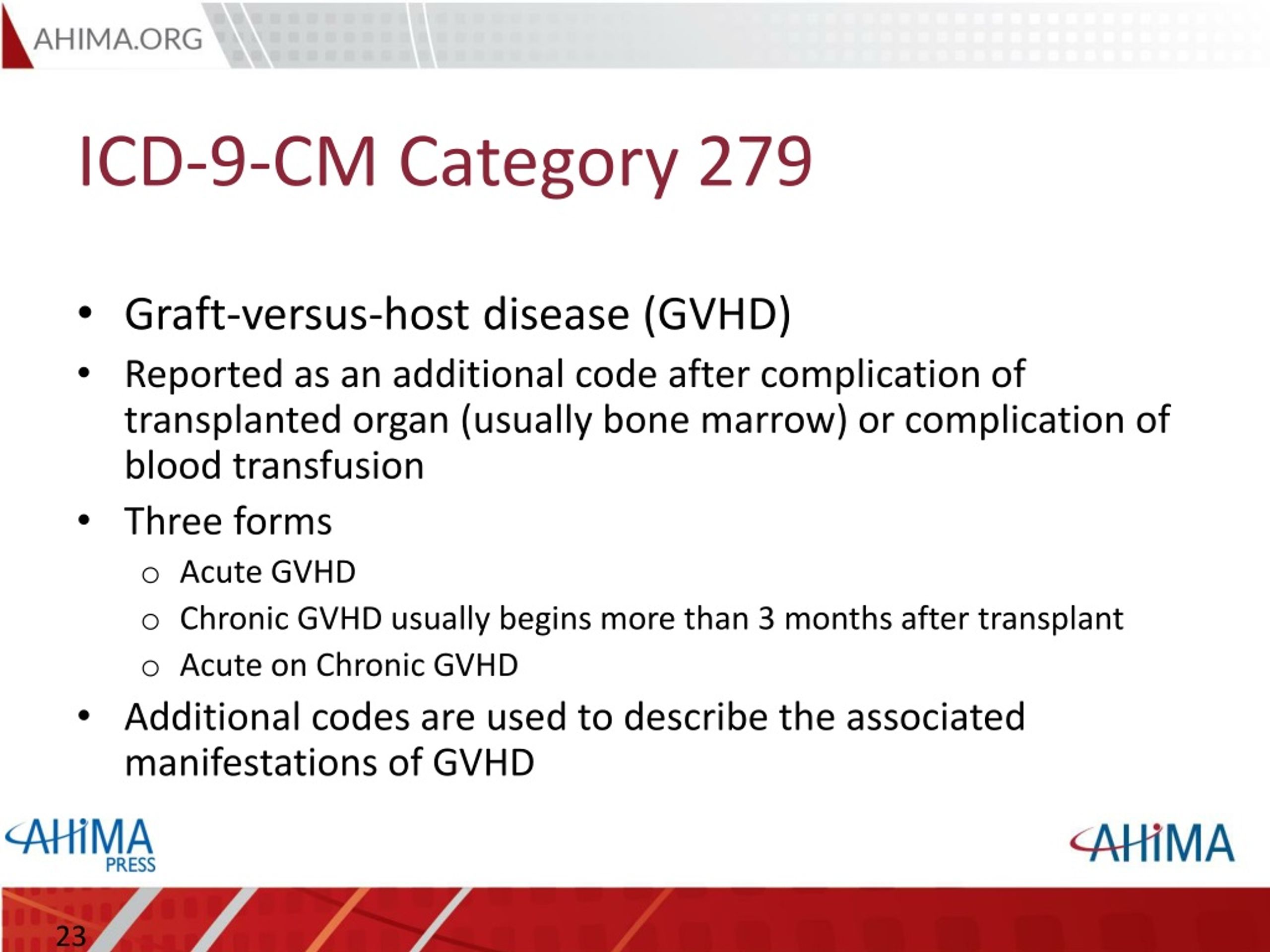
What is ICD 9 diagnosis?
The ICD-9-CM consists of:
- a tabular list containing a numerical list of the disease code numbers in tabular form;
- an alphabetical index to the disease entries; and
- a classification system for surgical, diagnostic, and therapeutic procedures (alphabetic index and tabular list).
What is the ICD 9 code for pre diabetes?
Prediabetes is defined as an abnormal blood glucose level, an elevated A1c level, or an abnormal glucose tolerance test. Thus R73.01, R73.02 or R73.09 would all be appropriate depending on which test is being used to justify the diagnosis of prediabetes.
What are the ICD 10 codes for diabetes?
- N18.3: Chronic kidney disease, stage 3 (moderate).
- 024: Diabetes in pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium.
- L97.4 or L97.5: To designate site, laterality, and depth of non-pressure skin ulcer.
- O24.011: Pre-existing diabetes mellitus, type 1, in pregnancy, first trimester.
- O24.12: Pre-existing diabetes mellitus, type 2, in childbirth.
What is the icd9-cm code for diabetes?
Coding in ICD-9-CM
- 250.0, diabetes mellitus without mention of complication
- 250.1, diabetes with ketoacidosis
- 250.2, diabetes with hyperosmolarity
- 250.3, diabetes with other coma
- 250.4, diabetes with renal manifestations
- 250.5, diabetes with ophthalmic manifestations
- 250.6, diabetes with neurological manifestations
- 250.7, diabetes with peripheral circulatory disorders

What is the ICD-9 code for diabetes mellitus?
Table 5ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes defining diabetesDescriptionICD-9-CM codeDiabetes mellitus without mention of complications250.0xDiabetes with ketoacidosis250.1xDiabetes with hyperosmolarity250.2xDiabetes with other coma250.3x8 more rows
What is the ICD-9 code for diabetes type 2?
Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. It is a disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make large amounts of urine.
What is the ICD-9 code for type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes codes were considered to be: ICD-9 250. x1, ICD-9 250. x3, and ICD-10 E10.
What is the ICD code for diabetes?
E08. 3531 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition... E08. 3532 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition...
What is the ICD-10 code for each type of diabetes?
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Codes for Diabetes Conversion TableICD-9ICD-10249.00E08.9 or E09.9 or E13.9249.01Aug 7, 2016
What is ICD-10 code for uncontrolled diabetes mellitus?
ICD-10 code E11. 65 represents the appropriate diagnosis code for uncontrolled type 2 diabetes without complications.
What is the proper ICD-10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple complications?
E11. 69 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication. ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes). Z79.
What is the CPT code for Type 2 diabetes?
ICD-10 code E11. 9 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
Is diabetes mellitus type 1 or type 2?
The main difference between the type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that type 1 diabetes is a genetic condition that often shows up early in life, and type 2 is mainly lifestyle-related and develops over time. With type 1 diabetes, your immune system is attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas.
What is the ICd 9 code for diabetes?
Resistin is thus a hormone that potentially links obesity to diabetes. ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions.
How to control diabetes?
Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your glucose level and take medicine if prescribed. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases. Diabetes mellitus.
What is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance?
A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high.
How does diabetes affect your body?
Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes.a blood test can show if you have diabetes. Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your glucose level and take medicine if prescribed. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases
Which group of disorders share glucose intolerance in common?
Heterogeneous group of disorders that share glucose intolerance in common. Type 2 diabetes, characterized by target-tissue resistance to insulin, is epidemic in industrialized societies and is strongly associated with obesity; however, the mechanism by which increased adiposity causes insulin resistance is unclear.
Can diabetes cause heart disease?
It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes.a blood test can show if you have diabetes.
Does diabetes make insulin?
With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
What is the ICD code for diabetes mellitus?
The ICD code E11 is used to code Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) is a complication of diabetes mellitus (predominantly type 2) in which high blood sugars cause severe dehydration, increases in osmolarity (relative concentration of solute) and a high risk of complications, coma and death.
Is maternal obesity a risk factor for diabetes?
Maternal obesity as a risk factor for early childhood type 1 diabetes: a nationwide, prospective, population-based case–control study. NZ case study; A citizen scientist controls autoimmune diabetes without insulin, with a low carb diet, a glucose meter, and metformin.
Is there a default code for uncontrolled diabetes?
First, coders will need to have further documentation of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia as there is no default code for uncontrolled diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes is classified by type and whether it is hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. The term uncontrolled is not synonymous with hyperglycemia.
Can high blood glucose cause heart problems?
Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. You have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise. Having prediabetes also increases your risk.
Is DKA a complication of diabetes?
It is related to diabetic ketoacidosis ( DKA), another complication of diabetes more often (but not exclusively) encountered in people with type 1 diabetes; they are differentiated with measurement of ketone bodies, organic molecules that are the underlying driver for DKA but are usually not detectable in HHS.
Is there more than one type of diabetes?
I'm pretty sure all of you who made it thus far in this article are familiar with the fact that there are at least two major types of diabetes: type I, or juvenile, and type II, with usual (though not mandatory) adult onset. Just like ICD-9, ICD-10 has different chapters for the different types of diabetes. The table below presents the major types of diabetes, by chapters, in both ICD coding versions. Diabetes Coding Comparison ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM 249._ - Secondary diabetes mellitus E08._ - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition E09._ - Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus E13._ - Other specified diabetes mellitus 250._ - Diabetes mellitus E10._ - Type 1 diabetes mellitus E11._ - Type 2 diabetes mellitus 648._ - Diabetes mellitus of mother, complicating pregnancy, childbirth, or the puerperium O24._ - Gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnancy 775.1 - Neonatal diabetes mellitus P70.2 - Neonatal diabetes mellitus This coding structure for diabetes in ICD-10 is very important to understand and remember, as it is virtually always the starting point in assigning codes for all patient encounters seen and treated for diabetes. How To Code in ICD-10 For Diabetes 1. Determine Diabetes Category Again, "category" here refers to the four major groups above (not just to type 1 or 2 diabetes): E08 - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition E09 - Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus E10 - Type 1 diabetes mellitus E11 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus E13 - Other specified diabetes mellitus Note that, for some reason, E12 has been skipped. Instructions on Diabetes Categories Here are some basic instructions on how to code for each of the diabetes categories above: E08 - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition. Here, it is Continue reading >>
What is the code for gestational diabetes?
Codes for gestational diabetes are in subcategory O24.4. These codes include treatment modality — diet alone, oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin — so you do not need to use an additional code to specify medication management. Do not assign any other codes from category O24 with the O24.4 subcategory codes.
What is the ICd 10 code for secondary diabetes?
Follow the instructions in the Tabular List of ICD-10-CM for proper sequencing of these diagnosis codes. For example, if a patient has secondary diabetes as a result of Cushing’s syndrome and no other manifestations, report code E24.9 Cushing’s syndrome, unspecified, followed by E08.9 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition without manifestations. If a patient is diagnosed with secondary diabetes due to the adverse effects of steroids, report codes E09.9 Drug or chemical induced diabetes without complications and T38.0X5A Adverse effect of glucocorticoids and synthetic analogues, initial encounter.
How does diabetes affect blood sugar?
In patients with type 2 diabetes, problems begin when the cells in their body start to not respond to insulin as well as they should. This is called insulin resistance, which causes high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). The pancreas responds by making more insulin to try and manage the hyperglycemia, but eventually, the pancreas can’t keep up and blood sugar levels rise. Left uncontrolled, the disease progresses into prediabetes and, eventually, type 2 diabetes. This is the most common type of diabetes and is initially treated with lifestyle modification including a healthy diet and exercise. If these measures are not effective, treatment generally starts with an oral hypoglycemic agent. If better control is needed, injectable medications or insulin may be initiated to help manage blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
What chapter do you report diabetes?
Report encounters related to pregnancy and diabetes using codes in Chapter 15 Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium. If a pregnant woman has pre-existing diabetes that complicates the pregnancy, Chapter 15 guidelines instruct us to assign a code from O24 first, followed by the appropriate diabetes code (s) from Chapter 4 (E08–E13). Report codes Z79.4 or Z79.84 if applicable.
What is secondary diabetes?
Secondary diabetes — DM that results as a consequence of another medical condition — is addressed in Chapter 4 guidelines. These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
What is type 1.5 diabetes?
Type 1.5 diabetes is a form of diabetes in which an adult has features of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. These patients have also been described with the terms “latent autoimmune diabetes of adults” (LADA), and “slow-progressing type 1 diabetes.” The condition has also been called “double” diabetes, because individuals demonstrate both the autoimmune destruction of beta cells of type 1 diabetes and the insulin resistance characteristic of type 2 diabetes. People with type 1.5 diabetes have autoantibodies to insulin-producing beta cells and gradually lose their insulin-producing capability, requiring insulin within 5–10 years of diagnosis.
What is the most common type of diabetes?
Left uncontrolled, the disease progresses into prediabetes and, eventually, type 2 diabetes. This is the most common type of diabetes and is initially treated with lifestyle modification including a healthy diet and exercise. If these measures are not effective, treatment generally starts with an oral hypoglycemic agent.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abnormal finding brain mri
- 2. icd 10 cm code for sinus tachycardia
- 3. icd-10 code for abcess of bursa, left knee due to streptococus a
- 4. icd code for j0585
- 5. icd 10 code for asthma with bronchitis
- 6. icd 10 code for t1dm
- 7. icd 10 cm code for primary biliary cirrhosis
- 8. icd-10 code for moderate anxiety
- 9. icd 10 code for prediabetes non clinical diabetes
- 10. icd 10 code for rib cramping