Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
- M35.00 (Sjogren syndrome, unspecified)
- M35.01 (Sjogren syndrome with keratoconjunctivitis)
- M35.02 (Sjogren syndrome with lung involvement)
- M35.03 (Sjogren syndrome with myopathy)
- M35.04 (Sjogren syndrome with tubulo-interstitial nephropathy)
- M35.05 (Sjogren syndrome with inflammatory arthritis)
What is the ICD 10 code for persistent diarrhea?
You would select the following codes:
- R10.823, Rebound abdominal tenderness, right lower quadrant,
- R11.0, Nausea without vomiting,
- R19.7, Diarrhea, unspecified,
- R19.11, Absent bowel sounds,
- D72.820, Lymphocytosis (symptomatic).
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations. Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations.
What is the ICd 10 code for diarrhea?
What does diarrhea mean?
What is a code also note?
About this website
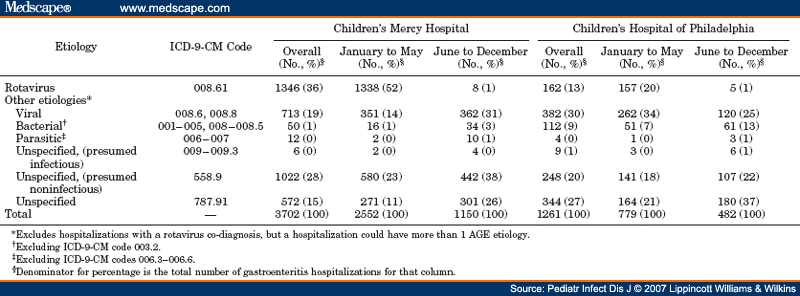
What is the correct code for infectious diarrhea?
"009.3 - Diarrhea of Presumed Infectious Origin." ICD-10-CM, 10th ed., Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the National Center for Health Statistics, 2018. ICD-10, www.unboundmedicine.com/icd/view/ICD-10-CM/961976/all/009_3___Diarrhea_of_presumed_infectious_origin.
What is the ICD-10 code for diarrhea of presumed infectious origin?
Infectious gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified A09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for infectious disease?
B99. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B99.
What is the ICD-9 code for infection?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 041.84 : Other specified bacterial infections in conditions classified elsewhere and of unspecified site, other anaerobes.
What is diarrhea of presumed infectious origin?
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur.
What is the ICD 10 code for infectious gastroenteritis?
ICD-10 code A09 for Infectious gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
Which chapters of the ICD-10-CM code book includes certain infectious and parasitic diseases?
Certain infectious and parasitic diseases ICD-10-CM Code range A00-B99A00-A09. Intestinal infectious diseases.A15-A19. Tuberculosis.A20-A28. Certain zoonotic bacterial diseases.A30-A49. Other bacterial diseases.A50-A64. Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission.A65-A69. ... A70-A74. ... A75-A79.More items...
Which ICD code has been related to the carrier of infectious disease?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z22: Carrier of infectious disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial infection?
ICD-10 code: A49. 9 Bacterial infection, unspecified.
What are ICD-9 diagnosis codes?
ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
Where can I find ICD-9 codes?
ICD9Data.com takes the current ICD-9-CM and HCPCS medical billing codes and adds 5.3+ million links between them. Combine that with a Google-powered search engine, drill-down navigation system and instant coding notes and it's easier than ever to quickly find the medical coding information you need.
What is ICD-9 and ICD-10 difference?
ICD-9 uses mostly numeric codes with only occasional E and V alphanumeric codes. Plus, only three-, four- and five-digit codes are valid. ICD-10 uses entirely alphanumeric codes and has valid codes of up to seven digits.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
How long does diarrhea last in children?
You should talk to your doctor if you have a strong pain in your abdomen or rectum, a fever, blood in your stools, severe diarrhea for more than three days or symptoms of dehydration. If your child has diarrhea, do not hesitate to call the doctor for advice.
What causes diarrhea in the colon?
Causes of diarrhea include bacteria, viruses or parasites, certain medicines, food intolerances and diseases that affect the stomach, small intestine or colon. In many cases, no cause can be found. Although usually not harmful, diarrhea can become dangerous or signal a more serious problem.
What is fecal consistency?
Fecal consistency is related to the ratio of water-holding capacity of insoluble solids to total water, rather than the amount of water present. Diarrhea is not hyperdefecation or increased fecal weight. Diarrhea means that you have loose, watery stools more than three times in one day.
What is the ICd 10 code for diarrhea?
009.2 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of infectious diarrhea. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What does diarrhea mean?
Diarrhea means that you have loose, watery stools more than three times in one day. You may also have cramps, bloating, nausea and an urgent need to have a bowel movement.
What is a code also note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cast discomfort
- 2. icd 9 code for pruitis
- 3. icd 10 code for injury while skateboarding
- 4. icd 10 cm code for protonix
- 5. icd 10 code for anemia of chronic disease
- 6. icd 10 cm code for trichomonas exposure
- 7. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm right arm
- 8. icd 10 code for elevated hemidiaphragm
- 9. icd-10 code for undesired fertility
- 10. icd code for extreme prematurity (birthweight of 999 grams or less)