What is the ICD-10 code for hepatoblastoma?
ICD-10 | Hepatoblastoma (C22. 2)
What is the ICD-10 code for liver cancer?
Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary. C22. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C22.
How do you code primary liver cancer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant neoplasm of liver, primary, unspecified as to type C22. 8.
What is the code for hepatic cell carcinoma?
The following are types of primary liver cancer: Hepatocellular carcinoma (155.0), the most common form, starts in the hepatocytes. Cholangiocarcinoma (155.1) begins in small bile ducts in the liver. Cholangiocarcinoma combined with hepatocellular carcinoma is classified to code 155.0.
What is the meaning of hepatoblastoma?
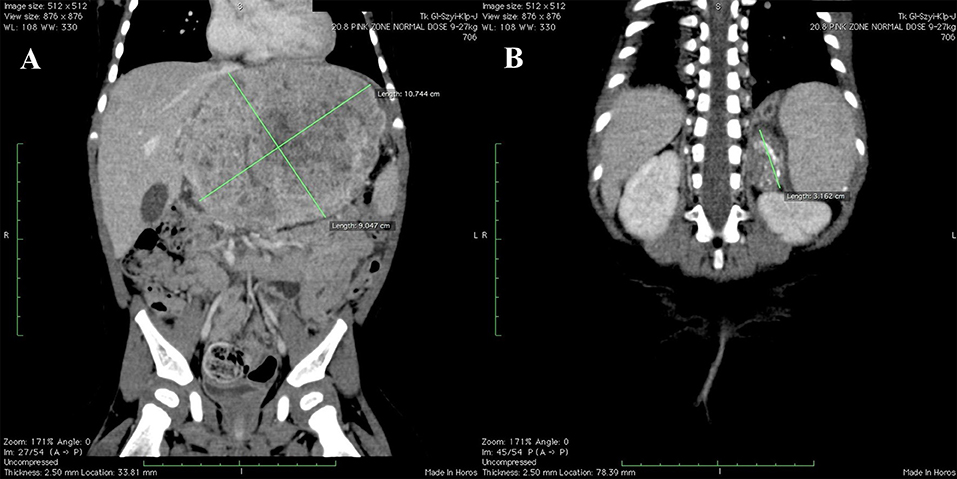
Hepatoblastoma is a rare tumor (an abnormal tissue growth) that originates in cells in the liver. It is the most common cancerous (malignant) liver tumor in early childhood. Most hepatoblastoma tumors begin in the right lobe of the liver.
What is the ICD-10 code for secondary liver cancer?
ICD-10 code: C78. 7 Secondary malignant neoplasm of liver and intrahepatic bile duct.
What is the ICD 10 code for cirrhosis of liver?
Table 1ICD-10-AM coden with codeCirrhosisK70.3 Alcoholic cirrhosis of liver193K74.4 Secondary biliary cirrhosis*12K74.5 Biliary cirrhosis, unspecified617 more rows•Sep 17, 2020
When do you code cancer history?
Cancer is considered historical when: • The cancer was successfully treated and the patient isn't receiving treatment. The cancer was excised or eradicated and there's no evidence of recurrence and further treatment isn't needed. The patient had cancer and is coming back for surveillance of recurrence.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is metastatic HCC?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide, with the highest incidence in regions with high prevalence of chronic viral hepatitis infection, especially hepatitis B infection. HCC commonly metastasises to lungs, lymph nodes, adrenal gland and bones, including the skull.
Known As
Hepatocellular carcinoma is also known as CA liver hepatocellular, cancer of the liver hepatoblastoma, cancer of the liver hepatocellular, cancer of the liver primary, hepatoblastoma, hepatoblastoma (clinical), hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer primary, liver cell carcinoma, liver cell carcinoma (clinical), and primary malignant neoplasm of liver.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Definition and Symptoms
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a type of liver tumor that occurs in infants and children. This is a malignant tumor that requires either surgical removal or liver transplantation. Symptoms include loss of appetite, a lump in the upper abdomen, weight loss, and a swollen abdomen.
What is a malignant liver neoplasm?
A malignant liver neoplasm composed of immature hepatocytic elements. A malignant liver neoplasm that occurs almost exclusively in infants, although isolated cases in older children and adults have been reported. Grossly, hepatoblastoma is solid, well circumscribed, and more often solitary than multiple.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
Is hepatoblastoma a solid tumor?
Grossly, hepatoblastoma is solid, well circumscribed, and more often solitary than multiple. Microscopically, most of the tumors are composed exclusively of immature hepatocytic elements. About a fourth of hepatoblastomas contain a stromal component that may be undifferentiated or develop into bone or cartilage.
When will the ICD-10 C22.2 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C22.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is DRG 435-437?
DRG Group #435-437 - Malignancy of hepatobiliary system or pancreas without CC or MCC.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code C22.2 and a single ICD9 code, 155.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICD code for hepatoblastoma?
C22.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of hepatoblastoma. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is liver cancer?
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, is a cancer that originates in the liver. Liver tumors are discovered on medical imaging equipment (often by accident) or present themselves symptomatically as an abdominal mass, abdominal pain, yellow skin, nausea or liver dysfunction. Specialty:
How rare are liver tumors?
They make up between 1 and 2% of all pediatric tumors. They are rare in childhood, and about two-thirds of primary liver tumors are malignant. It has been estimated that about 37% of primary liver tumors are hepatoblastomas (1). Hepatoblastoma typically occurs in infants and toddlers.
What is the role of EpCAM in cellular signaling?
EpCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein mediating calcium-independent homotypic cell-cell adhesion in the epithelium. This molecule is also involved in cellular signaling, migration, proliferation, and differentiation. It plays a role in the event-free survival outcome of patients harboring hepatoblastoma (18, 20–23).
How long does hepatoblastoma last?
Hepatoblastoma can remain asymptomatic for months. Babies born prematurely and newborns with low birth weight should be screened. In affected children, painless swelling in the upper right abdominal area occasionally occurs in the early stages. When sick children begin to suffer from symptoms, it is almost always when the disease has reached an advanced stage. Overall, the complaints are nonspecific, including nausea, vomiting, weight loss and increasing general weakness, which can delay development. In this context, osteopenia can develop. Children with hepatoblastoma can become conspicuous due to osteopenia, and resultant pathological fractures (34). Very rarely, obstructive jaundice can occur when the tumor occludes the intrahepatic biliary tract (2). Spontaneous tumor rupture with extensive intra- or extra-tumor bleeding is extremely rare (35). Precocious puberty can occur in boys due to the increased formation of human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) caused by hepatoblastoma (36). Further symptoms can occur depending on the site of metastasis. The lungs are most commonly affected, with breathing difficulties, coughing fits, and occasional hemoptysis (2, 3).
What is the mixed hepatoblastoma type?
In addition to epithelial components, the mixed hepatoblastoma type contains mesenchymal stroma such as osteoid, collagen fibers, and rarely, cartilage and skeletal muscle cells (17). Liver progenitor cells harbor the ability to express of keratin 19 (CK19) and/or the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) (18–21).
What is the most common liver cancer in children?
Hepatoblastoma is the most common liver cancer in children aged 3 years and younger. The differential diagnosis of this neoplasm is crucial for the proper management. Recent additions to protocols of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology and Children’s Oncology Group have been key in tackling this oncological disease.
Why do boys have puberty?
Precocious puberty can occur in boys due to the increased formation of human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) caused by hepatoblastoma (36) . Further symptoms can occur depending on the site of metastasis. The lungs are most commonly affected, with breathing difficulties, coughing fits, and occasional hemoptysis (2, 3).
What are the two types of hepatoblastoma?
Histologically, hepatoblastoma are broadly classified into two types: epithelial and mixed. Depending on the degree of differentiation, hepatoblastoma cells can be distinguished into two subtypes: embryonic and fetal. In some cases, both cell types are present. Embryonic tumor cells are less differentiated whereas the fetal cells are well-differentiated. Small-cell anaplastic hepatoblastoma is a unique subtype; it mainly infiltrates the bile ducts and is considered prognostically unfavorable (16). In addition to epithelial components, the mixed hepatoblastoma type contains mesenchymal stroma such as osteoid, collagen fibers, and rarely, cartilage and skeletal muscle cells (17). Liver progenitor cells harbor the ability to express of keratin 19 (CK19) and/or the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) (18–21). EpCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein mediating calcium-independent homotypic cell-cell adhesion in the epithelium. This molecule is also involved in cellular signaling, migration, proliferation, and differentiation. It plays a role in the event-free survival outcome of patients harboring hepatoblastoma (18, 20–23). CK19 expression has been correlated with aggressive behavior in hepatoblastoma [20] and hepatocellular carcinoma (24). Of tremendous importance is that EpCAM expression is independent of previous cisplatin-based chemotherapy and can be utilized as a tumor marker and potential target for immunotherapy (18, 19). Kiruthiga et al.found that more than 90% of tumors with strong expression of EpCAM showed viable tumor after chemotherapy (19).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for psoas muscle strain unspecified
- 2. what is the icd 10 code cm for displaced fractured base, left first metacarpal
- 3. icd 10 code for burn right second digit
- 4. icd 10 code for thyroid biopsy
- 5. icd 10 code for emergency cesarean section
- 6. icd 10 code for cinv
- 7. icd 9 code for mass
- 8. icd 9 code for history of cervical polyp
- 9. icd 10 code for decreased wbcs
- 10. icd 10 code for strabismus left eye