Why impacted wisdom teeth are so dangerous?
Since impacted wisdom teeth are partially up, bacteria and food particles get easily lodged in these teeth which increases the chances of teeth decay. An impacted wisdom tooth is very difficult to clean. So pericoronitis, a very painful inflammatory gum disease will occur.
How to tell if wisdom tooth infected?
- If you experience pain when eating, you may have a tooth infection. ...
- Your tooth has turned a darker color compared to your other teeth.
- You’re experiencing swelling of your jaw, face, and surrounding lymph nodes. ...
- Your gum is swollen and filled with pus. ...
- A bad taste in your mouth or bad breath may also be an indicator of an infection.
When to consider bone graft for Impacted wisdom teeth?
When to Consider Bone Graft for Impacted Wisdom Teeth? During wisdom teeth extraction, bone grafting may be indicated if there is significant bone loss due to infection, cysts, gum disease, or proximity of the…
How to prepare for Impacted wisdom teeth removal?
- Eat soft foods like yogurt, apple sauce, and ice cream for the first 24–48 hours 9
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Brush your teeth starting the second day (avoid blood clots)
- Take the drugs prescribed by your doctor
- Call your doctor if you have a fever, or if your pain or swelling doesn’t improve
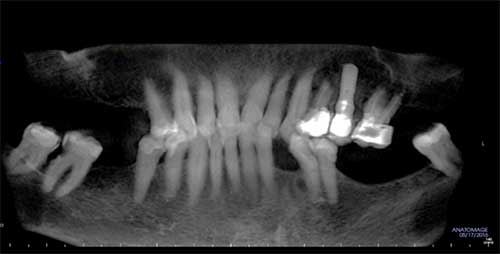
What is the ICD-10 code for impacted wisdom tooth?
ICD-10-CM Code for Impacted teeth K01. 1.
What is the CPT code for impacted wisdom teeth?
D7230 and D7240 – Guidance on Coding for Impacted Teeth Removal Procedure as seen above is also available at no cost for you to download.
What is the ICD-10 code for status post tooth extraction?
Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on the teeth or oral cavity. Z48. 814 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What's an impacted molar?
An impacted tooth remains stuck in gum tissue or bone for various reasons. The area may be overcrowded, leaving no room for the teeth to emerge. For example, the jaw may be too small to fit the wisdom teeth. Teeth may also become twisted, tilted, or displaced as they try to emerge. This results in impacted teeth.
What is the difference between D7140 and D7210?
The removal of the root portion of the tooth through elevation and forceps should be coded as a D7140 (extraction, erupted tooth or exposed root). If a flap, bone removal and/or root sectioning is required to remove the root, the correct code is D7210.
What is a soft tissue impacted wisdom tooth?
You might hear your dentist use the terms “soft tissue impaction” and “hard tissue impaction.” Soft tissue impaction means your tooth has erupted from your jawbone but hasn't broken through your gums. Hard tissue impaction means your tooth is still completely covered by your gums and jawbone.
Are ICD-10 codes used for dental?
Use of ICD-10 codes is supported by the American Dental Association. The ADA now includes both dental- and medical-related ICD-10 codes in its “CDT Code Book.” Dental schools have included the use of ICD-10 codes in their curricula to prepare graduating dentists for their use in practice.
What is the ICD-10 code for dental disease?
Disorder of teeth and supporting structures, unspecified K08. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K08. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Do dentists have to use ICD-10 codes?
ICD and CDT Coding Examples Dentists, by virtue of their clinical education, experience and professional ethics, are the individuals responsible for diagnosis. As such, a dentist is also obligated to select the appropriate diagnosis code for patient records and claim submission.
What is an impacted wisdom tooth?
Sometimes a wisdom tooth becomes stuck below the surface of your gums (impacted), and grows at an odd angle, possibly causing complications. Impacted wisdom teeth are third molars at the back of the mouth that don't have enough room to emerge or develop normally.
What is a wisdom tooth called?
A third molar, commonly called a wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through (erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties.
What is a non impacted wisdom tooth?
Non-impacted wisdom teeth are those that are fully erupted and are above the gum line. This is opposed to impacted wisdom teeth which still remain in the jaw and often can lead to complications down the road.
What does CPT code 41899 mean?
Because of this, the unlisted dental procedure code of 41899 is used for dental diagnostic and/or preventive procedures, dental restorations of fillings, tooth replacements, endodontic procedures such as root canals, and many other dental procedures when performed in an ambulatory center setting.
What is CPT code D7140?
D7140 – extraction, erupted tooth or exposed root (ele- vation, and/or forcep removal). The descriptor of this code includes routine removal of tooth structure, minor smoothing of socket bone and closure as necessary.
What is dental code D7953?
D7953 bone replacement graft for ridge preservation – per site.
What is dental code D7280?
D7280. surgical access of an unerupted tooth.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 520.6
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use the following three equivalent ICD-10-CM codes, which are an approximate match to ICD-9 code 520.6:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 520.6
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What is impaction in teeth?
A condition in which a tooth is so crowded in its socket that it cannot erupt normally. A tooth that is prevented from erupting by a physical barrier, usually other teeth. Impaction may also result from orientation of the tooth in an other than vertical position in the periodontal structures.
When will the ICD-10-CM K01.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K01.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for tooth eruption?
520.9 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified disorder of tooth development and eruption. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What are the symptoms of a tooth problem?
The most familiar symptom of a tooth problem is a toothache. Others include worn-down or loose teeth. It's important that you see a dentist if you have any problems with your teeth. Fortunately, you can prevent many tooth disorders by taking care of your teeth and keeping them clean.
What is a code also note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction.
What are teeth made of?
Your teeth are made of a hard, bonelike material. Inside the tooth are nerves and blood vessels. You need your teeth for many activities you may take for granted. These include eating, speaking and even smiling. But tooth disorders are nothing to smile about. They include problems such as cavities (also known as tooth decay), infections, and injuries.
What happens when you impact your teeth?
Impacted teeth are extremely troublesome. They not only impact the tooth by trajecting at an angle and interfering with adjacent teeth but also cause an infection.
Is D7241 a bone or bone crown?
D7241 removal of the impacted tooth which is completely bony with unusual surgical complications. Most or all of the crown is covered by bone making the procedure unusually difficult or complicated due to factors such as requirement of nerve dissection, separate closure of maxillary sinus required or aberrant tooth position.
Why do my wisdom teeth hurt?
impacted wisdom teeth (or impacted third molars) are wisdom teeth which do not fully erupt into the mouth because of blockage from other teeth. if the wisdom teeth do not have an open connection to the mouth, pain can develop with the onset of inflammation or infection or damage to the adjacent teeth.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for laceration to right eyebrow
- 2. icd-10 code for major neurocognitive disorder
- 3. icd 10 code for status post gastric bypass
- 4. icd 10 code for diabetes mellitus type 2
- 5. icd code for major depressive disorder single episode
- 6. icd 10 cm code for scratched legs
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for cervical myelopathy
- 8. icd 10 cm code for arm skin lesions
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral pleural effusions with atelectasis
- 10. icd 10 code for venomous spider bite right thigh