What is the ICD 9 code for prostate carcinoma?
- Adenocarcinoma of prostate
- Adenocarcinoma, prostate
- CA of prostate
- CA prostate, adenoca
- CA prostate, primary
- Cancer of prostate with metastasis to eye
- Cancer of the prostate
- Cancer of the prostate with metastasis
- Cancer of the prostate, adenocarcinoma
- Cancer of the prostate, primary
What is the diagnosis code for prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is assigned to ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 185. Carcinoma in situ of the prostate is classified to code 233.4, and a benign neoplasm of the prostate goes to code 222.2. What is prostate cancer stages? Stage IIIA: The cancer has spread beyond the outer layer of the prostate into nearby tissues. It may also have spread to the seminal vesicles.
What is the survival rate of metastatic prostate cancer?
The have median time to metastatic disease in these years is about 8 years and the median survival is about 13 years. Patients with PSA doubling times of less than 3 months are at very high risk of prostate cancer related death and have a median survival of 5 to 6 years.
What is ICD 9 diagnosis?
The ICD-9-CM consists of:
- a tabular list containing a numerical list of the disease code numbers in tabular form;
- an alphabetical index to the disease entries; and
- a classification system for surgical, diagnostic, and therapeutic procedures (alphabetic index and tabular list).
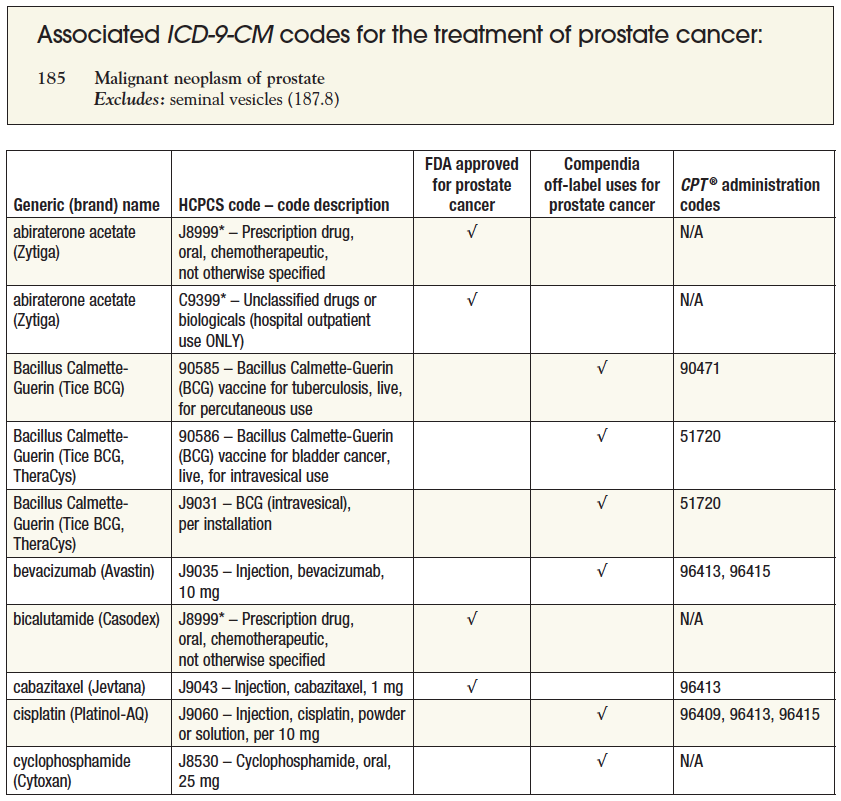
What is the ICD-9 code for prostate cancer?
ICD-9 code 185 and ICD-10 code C61 are the diagnostic codes used for malignant neoplasm of the prostate.
What is ICD-10 code for history of prostate cancer?
ICD-10 code Z85. 46 for Personal history of malignant neoplasm of prostate is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What ICD-10 code covers PSA screening?
Report HCPCS Level II code G0102 Prostate cancer screening; digital rectal examination or G0103 Prostate cancer screening; prostate specific antigen test (PSA), total, as appropriate, with ICD-10-CM diagnosis code Z12. 5 Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of prostate (ICD-9-CM V76.
What is diagnosis code C61?
C61: Malignant neoplasm of prostate.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for prostate cancer?
ICD-10 code C61 for Malignant neoplasm of prostate is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Malignant neoplasms .
What is the ICD-10 code for prostate?
Disorder of prostate, unspecified N42. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N42. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for prostate screening?
ICD-10 code Z12. 5 for Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of prostate is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What diagnosis codes will cover PSA?
. Medicare coverage for screening PSAs is limited to once every 12 months Diagnostic PSAs CPT codes for diagnostic PSA tests are 84153: EPIC: LAB4427 TIP: Free and Total PSA is a diagnostic PSA and should be coded as such.
What diagnosis covers PSA screening?
Screening prostate specific antigen tests (PSA) means a test to detect the marker for adenocarcinoma of prostate. PSA is a reliable immunocytochemical marker for primary and metastatic adenocarcinoma of prostate.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is malignant neoplasm of prostate?
Prostate cancer occurs when the uncontrolled cell growth happens in the prostate, a walnut-sized gland found in reproductive system in males. It's caused by specific changes in the DNA of prostate cells that can be inherited or acquired over time.
What is a neoplasm of the prostate?
Cancer of the prostate is the most commonly diagnosed neoplasm in men in the United States, after skin cancer. Many controversies exist regarding the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer, especially in the areas of screening and the choice of therapy once a diagnosis is made.
How to diagnose prostate cancer?
your doctor will diagnose prostate cancer by feeling the prostate through the wall of the rectum or doing a blood test for prostate-specific antigen (psa). Other tests include ultrasound, x-rays, or a biopsy.treatment often depends on the stage of the cancer.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
Risk factors for developing prostate cancer include being over 65 years of age, family history, being african-american, and some genetic changes.symp toms of prostate cancer may include. problems passing urine, such as pain, difficulty starting or stopping the stream, or dribbling. low back pain. pain with ejaculation.
What is the ICd 9 code for prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer (ICD-9-CM code 185) occurs when cells within the prostate grow uncontrollably, creating small tumors. Adenocarcinoma is the most common type (85%) and arises from the glandular tissue within the prostate.
How do you know if you have prostate cancer?
Symptoms. Common symptoms of prostate cancer include bloody semen; difficulty initiating or stopping urination; frequency of urination (especially nocturnal); hematuria; pain or burning during urination; pain in the lower back, hips, or upper thighs; and a stuttering or weak urine flow. Diagnosis.
What is the ICD-10 CM for neoplasms?
The ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting for neoplasms is similar to the ICD-9-CM official coding guidelines with a few exceptions. Here is a summary of the ICD-10-CM neoplasm coding guidelines:
What are some examples of prostate cancer?
Other medications include antiandrogens, which prevent testosterone from reaching cancer cells. Examples include bicalutamide (Casodex) and nilutamide (Nilandron). Coding and sequencing for prostate cancer are dependent on the physician documentation in the medical record and application of the Official Coding Guidelines for inpatient care.
What is the normal PSA level?
Normal PSA levels are dependent on age and race, but broad ranges are less than 2.5 ng/mL for ages 40 to 49, less than 4 ng/mL for ages 50 to 59, less than 4.5 ng/mL for ages 60 to 69, and less than 6.5 ng/mL for ages 70 to 79. Grading. Grading is used to determine how aggressive the cancer is.
What is the secretion of PSA?
PSA is secreted exclusively by prostatic epithelial cells. PSA levels can be helpful in detecting prostate cancer, but the PSA level may be elevated due to other conditions such as benign prostatic hypertrophy, infection (including prostatitis), or inflammation.
What is the code for prostate cancer?
Once the patient is found to be cancer-free, a code of Z85.46, Personal history of malignant neoplasm of prostate is reported. When a primary malignancy has been previously excised or eradicated from its site and there is no further treatment directed to that site and there is no evidence of any existing primary malignancy, a code from category Z85, Personal history of malignant neoplasm, should be used to indicate the former site of the malignancy.
What is the CPT code for prostate removal?
Treatment of prostate cancer may also require surgical removal of the prostate. CPT codes for prostatectomy include: 55801. Prostatectomy, perineal, subtotal (including control of postoperative bleeding, vasectomy, meatotomy, urethral calibration, and /or dilation, and internal urethrotomy) 55812.
What is the N40 code for prostate?
Screening may detect nodules or other abnormalities of the prostate. Benign prostatic hyperplasia or hypertrophy, enlarged prostate , or nodular prostate are common conditions code in category N40. The 4 th digit is used to describe the condition and/or the presence of associated lower urinary tract symptoms as follows:
What drugs lower PSA?
Factors which might lower PSA level – even if the man has prostate cancer: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: Certain drugs used to treat BPH or urinary symptoms, such as finasteride (Proscar or Propecia) or dutasteride (Avodart), can lower PSA levels.
How to treat prostate cancer early stage?
Treatment. Conventional treatments for early-stage prostate cancer include surgery and radiation . Hormonal therapy, which can reduce levels of the male hormones (androgens like testosterone) that lead to tumor growth, is also used to treat early-stage tumors.
How long does prostate cancer last?
In its early stages, prostate cancer is highly treatable, with five-year survival rates close to 100%. Once prostate cancer has metastasized, however, the 5-year survival rate falls to less than 30%, highlighting a significant need for more effective treatment of advanced stage disease. Because prostate cancer is highly curable when detected in ...
How many people die from prostate cancer each year?
It affects roughly 1.3 million people and kills more than 360,000 people each year, which represents about 4% of all cancer deaths worldwide. In its early stages, prostate cancer is highly treatable, with five-year survival rates close ...
How to diagnose prostate cancer?
your doctor will diagnose prostate cancer by feeling the prostate through the wall of the rectum or doing a blood test for prostate-specific antigen (psa). Other tests include ultrasound, x-rays, or a biopsy.treatment often depends on the stage of the cancer.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
Risk factors for developing prostate cancer include being over 65 years of age, family history, being african-american, and some genetic changes.symptom s of prostate cancer may include. problems passing urine, such as pain, difficulty starting or stopping the stream, or dribbling. low back pain.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for psa screen
- 2. icd 10 cm code for bipolar disorder manic type
- 3. icd 10 code for opiate addiction
- 4. icd 10 code for cervical and lumbar radiculopathy
- 5. icd 10 code for occlusion saphenous vein grafts
- 6. 2015 icd 10 code for crushed by a horse
- 7. icd 10 code for transient arrhythmia
- 8. icd code for scaphoid proximal pole fracture
- 9. icd 10 code for congenital dysplasia with renal failure
- 10. icd 10 code for administrative encounter