What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified head injury?
- S06.9X9A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Unsp intracranial injury w LOC of unsp duration, init
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S06.9X9A became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can ultrasound diagnose spina bifida?
Ultrasound is the gold standard diagnostic tool for spina bifida. Three-dimensional ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are also beginning to play a role in the characterisation of the open spina bifida spinal lesion.
Is spina bifida an inherited disease?
Spina bifida is a complex condition that in most cases, is likely caused by the interaction of multiple genetic and environmental factors (called multifactorial inheritance). Some of these factors have been identified, but many remain unknown. Changes in any of many genes may influence the risk of spina bifida.
Can spina bifida be misdiagnosed?
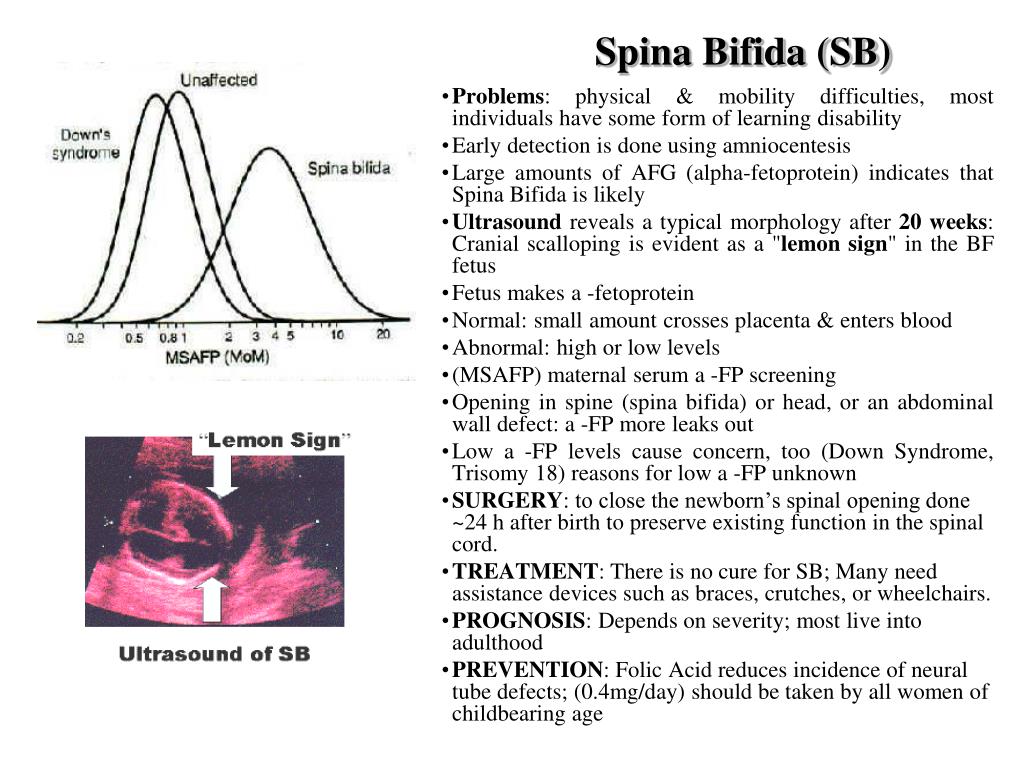
Spina bifida can be accurately diagnosed during the second trimester ultrasound scan. Therefore, this examination is crucial to identify and rule out congenital anomalies such as spina bifida. An advanced ultrasound also can detect signs of spina bifida, such as an open spine or particular features in your baby's brain that indicate spina bifida.
What is spina bifida unspecified?
It is a type of neural tube defect, which is a problem with the spinal cord or its coverings. It happens if the fetal spinal column doesn't close completely during the first month of pregnancy. There is usually nerve damage that causes at least some paralysis of the legs.
What is the DX code for spina bifida?
What is the ICD-10 Code for Spina Bifida? The ICD-10 Code for spina bifida is Q05. 9.
What are ICD-9 diagnosis codes?
ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
What is the difference between ICD-10 and 9?
ICD-9-CM codes are very different than ICD-10-CM/PCS code sets: There are nearly 19 times as many procedure codes in ICD-10-PCS than in ICD-9-CM volume 3. There are nearly 5 times as many diagnosis codes in ICD-10-CM than in ICD-9-CM. ICD-10 has alphanumeric categories instead of numeric ones.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for spina bifida occulta?
ICD-10 code Q76. 0 for Spina bifida occulta is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
Which of the following conditions would be reported with Code Q65 81?
Which of the following conditions would be reported with code Q65. 81? Imaging of the renal area reveals congenital left renal agenesis and right renal hypoplasia.
What is the difference between ICD-9 and ICD-9-CM?
The current ICD used in the United States, the ICD-9, is based on a version that was first discussed in 1975. The United States adapted the ICD-9 as the ICD-9-Clinical Modification or ICD-9-CM. The ICD-9-CM contains more than 15,000 codes for diseases and disorders. The ICD-9-CM is used by government agencies.
What does an ICD-9 code look like?
Most ICD-9 codes are three digits to the left of a decimal point and one or two digits to the right of one. For example: 250.0 is diabetes with no complications. 530.81 is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What does ICD-9 code mean in medical terms?
The International Classification of Diseases Clinical Modification, 9th Revision (ICD-9 CM) is a list of codes intended for the classification of diseases and a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease.
How many codes does ICD-9 have?
13,000 codesThe current ICD-9-CM system consists of ∼13,000 codes and is running out of numbers.
When did ICD-9 stop?
No updates have been made to ICD-9 since October 1, 2013, as the code set is no longer being maintained.
When did ICD-9 change to ICD-10?
On October 1, 2013, the ICD-9 code sets will be replaced by ICD-10 code sets. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services issued a final rule on January 16, 2009, adopting ICD-10-CM (clinical modifier) and ICD-10-PCS (procedure coding) system.
What is spina bifida myelomeningocele?
Myelomeningocele is the most serious type of spina bifida. With this condition, a sac of fluid comes through an opening in the baby's back. Part of the spinal cord and nerves are in this sac and are damaged.
What is the ICD-10 code for myelomeningocele?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q05. 7 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q05.
What is Lipomeningocele?
Lipomeningocele. This type of spina bifida is associated with an overlying fatty tumor. At birth, the skin is intact over the underlying spinal cord and vertebral anomaly. There is associated muscle weakness and decreased sensation, relevant to the level of the spinal cord involved.
Are myelomeningocele and Meningomyelocele the same?
Meningomyelocele, also commonly known as myelomeningocele, is a type of spina bifida. Spina bifida is a birth defect in which the spinal canal and the backbone don't close before the baby is born. This type of birth defect is also called a neural tube defect.
What is the open form of spina bifida?
The open form is called spina bifida cystica and the closed form is spina bifida occulta. (from Joynt, Clinical Neurology, 1992, ch55, p34) Developmental anomaly characterized by defective closure of the bony encasement of the spinal cord, through which the cord and meninges may protrude.
What is Spina Bifida Aperta?
Spina bifida aperta. Spina bifida without hydrocephalus. Clinical Information. Birth defect involving inadequate closure of the bony casement of the spinal cord, through which the spinal membranes, with or without spinal cord tissue, may protrude.
Can Spina Bifida be cured?
They may have learning difficulties, urinary and bowel problems or hydrocephalus, a buildup of fluid in the brain. There is no cure.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is the term for the buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain?
Hydrocephalus is the buildup of too much cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Normally, this fluid cushions your brain. When you have too much, though, it puts harmful pressure on your brain.
What is the ICD-10 code for spina bifida?
741.00 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of spina bifida with hydrocephalus, unspecified region. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the most common birth defect in the United States?
Herniation of spinal cord tissue and meninges through a defect in a region of the vertebral column. Spina bifida is the most common disabling birth defect in the United States. It is a type of neural tube defect, which is a problem with the spinal cord or its coverings.
What is the open form of Spinal Dysraphism?
Spinal dysraphism includes all forms of spina bifida. The open form is called spina bifida cystica and the closed form is spina bifida occulta. (from Joynt, Clinical Neurology, 1992, ch55, p34) Congenital, or rarely acquired, herniation of meningeal and spinal cord tissue through a bony defect in the vertebral column.
What does a type 1 exclude note mean?
They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as Q05.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
Can Spina Bifida be cured?
They may have learning difficulties, urinary and bowel problems or hydrocephalus, a buildup of fluid in the brain. There is no cure.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cerebral palsy to replace 343.9
- 2. icd 10 code for mild global hypokinesis
- 3. icd 10 code for sprain of thyroid nodule
- 4. icd 10 cm code for allergic reaction.
- 5. icd 10 code for candidiasis throat.
- 6. icd 10 cm code for open occipital condyle fracture type 1
- 7. icd=10- code for infection ^\viral
- 8. icd-9 diagnosis code for rib pain
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral osteoarthritis knee
- 10. icd 10 code for injury of right great toe