ICD-9-CM 960.0 converts approximately to: 2022 ICD-10-CM T36.0X1A Poisoning by penicillins, accidental (unintentional), initial encounter or: 2022 ICD-10-CM T36.0X2A Poisoning by penicillins, intentional self-harm, initial encounter
Full Answer
What does ICD-9 stand for?
The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) is based on the World Health Organization's Ninth Revision, International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9). ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States.
What does additional diagnosis mean in ICD 10?
Additional Diagnosis - The secondary diagnosis code used, if available, to provide a more complete picture of the primary diagnosis. Bilateral - For bilateral sites, the final character of the codes in the ICD-10-CM indicates laterality. An unspecified side code is also provided should the side not be identified in the medical record.
What does the colon mean in ICD-9?
colon : - Punctuation found in the tabular list when a term must be modified by the addition of another term in order to qualify it for assignment of a specific code or to a category. "Excludes" as used in ICD-9-CM indicates that the code should not be used, because another code may be more appropriate.
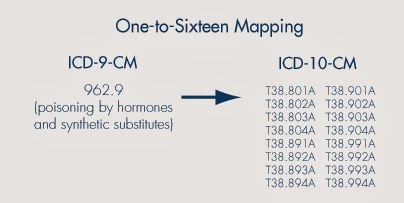
How is ICD-10-CM linked to ICD-9-CM?
The U.S. developed a Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) for medical diagnoses based on WHO's ICD-10 and CMS developed a new Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) for inpatient procedures. ICD-10-CM replaces ICD-9-CM, volumes 1 and 2, and ICD-10-PCS replaces ICD-9-CM, volume 3.
Is it possible that ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes will be used simultaneously?
However, most ICD-9-CM codes are still matched with multiple terms in ICD-10-CM, and there is still room for double billing during the period when the two systems will be activated simultaneously.
When did ICD-9 convert to ICD-10?
The last regular, annual updates to both ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 code sets were made on October 1, 2011. On October 1, 2012 and October 1, 2013 there will be only limited code updates to both the ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 code sets to capture new technologies and diseases as required by section 503(a) of Pub. L. 108–173.
What is difference between ICD-9 and ICD-10?
ICD-9 uses mostly numeric codes with only occasional E and V alphanumeric codes. Plus, only three-, four- and five-digit codes are valid. ICD-10 uses entirely alphanumeric codes and has valid codes of up to seven digits.
Why did ICD-9 change to ICD-10?
ICD-9 follows an outdated 1970's medical coding system which fails to capture detailed health care data and is inconsistent with current medical practice. By transitioning to ICD-10, providers will have: Improved operational processes by classifying detail within codes to accurately process payments and reimbursements.
What does ICD-9-CM stand for?
The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) is based on the World Health Organization's Ninth Revision, International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9).
When did ICD-10-CM replace ICD-9-CM?
October 1, 2015Objective-On October 1, 2015, the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) replaced ICD-9-CM (Ninth Revision) as the diagnosis coding scheme for the U.S. health care system.
What maps ICD-9-CM codes to ICD-10-CM codes?
The GEMs are a tool that can be used to convert data from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM and PCS and vice versa. Mapping from ICD-10-CM and PCS codes back to ICD-9-CM codes is referred to as backward mapping. Mapping from ICD-9-CM codes to ICD-10-CM and PCS codes is referred to as forward mapping.
How do you code ICD-10-CM?
ICD-10-CM is a seven-character, alphanumeric code. Each code begins with a letter, and that letter is followed by two numbers. The first three characters of ICD-10-CM are the “category.” The category describes the general type of the injury or disease. The category is followed by a decimal point and the subcategory.
What does ICD-10-CM stand for?
A: ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases -10th Version-Clinical Modification) is designed for classifying and reporting diseases in all healthcare settings.
Is ICD-10 easier than ICD-9?
With more coding space, ICD-10 adapts to changing medical practices much easier than ICD-9. Some ICD-10 databases convert ICD-9 codes into ICD-10 for you and demonstrate the additional information that longer codes include.
What is an example of an ICD-9 code?
Most ICD-9 codes are three digits to the left of a decimal point and one or two digits to the right of one. For example: 250.0 is diabetes with no complications. 530.81 is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What is the ICD-10 code for asthma?
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is a morbidity classification published by the United States for classifying diagnoses and reason for visits in all health care settings. The ICD-10-CM is based on the ICD-10, the statistical classification of disease published by the World Health Organization (WHO). Deaths have been coded using asthma diagnostic codes (ICD-9 Code: 493; or ICD-10 Codes: J45, J46) as the underlying causes of death. However, a clinical modification of the classification for morbidity purposes has been developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), the federal agency responsible for use of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD-10-CM) in the United States. 1
What is the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10?
The transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM will impact public health surveillance activities, particularly those regarding asthma morbidity and healthcare utilization. A major challenge for asthma surveillance is the difference in coding for asthma. There will also be a lag in data collection to analyze trends.
How many times is ICd 10 different from ICd 9?
The ICD-10-CM code sets have updated medical terminology and disease classifications, thus ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM are vastly different. There are nearly 5 times as many diagnosis codes in ICD-10-CM than in ICD-9-CM. The clinical modification represents significant changes from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM which include:
When did ICD-10-CM change to ICD-9-CM?
The transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM occurred on October 1, 2015. In 2015, asthma hospitalization and emergency department visits data for the first three quarters of the year were coded as ICD-9-CM (493.0-493.9) and the fourth quarter was coded as ICD-10-CM (J45.0-J45.998). If you received 2015 data with both coding schemes, you will have to differentiate ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM records to identify asthma-related hospitalization and emergency department visits. However, if your state coded the complete year (2015) using ICD-9-CM codes, then there will be no change to how data are analyzed and reported. For both scenarios, trend analysis will require a dash or other symbol indicating a coding change.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 960
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use this equivalent ICD-10-CM code, which is an exact match to ICD-9 code 960:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 960
Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail.
What is a nonessential modifier?
nonessential modifiers - Terms that may coexist with the main term but do not change the code assignment for the condition. colon : - Punctuation found in the tabular list when a term must be modified by the addition of another term in order to qualify it for assignment of a specific code or to a category.
What does "excludes" mean in ICd 9?
"Excludes" as used in ICD-9-CM indicates that the code should not be used, because another code may be more appropriate. "Excludes" notes usually include suggestions of more appropriate codes or code ranges.
What does "see" mean in coding?
see - Term used to instruct the coder to refer to another term. see also - Term used to instruct the coder to refer to another term. code also - Instruction that tells the coder that more than one code must be assigned, but it does not imply any sequencing guidance.
What does "and" mean in a sentence?
and - Means "and/or" when it appears in a title or narrative statement. with - Term used in the alphabetic index immediately following the main term, but not necessarily in alphabetic order. includes - Term that is accompanied by conditions that are examples of what may be included in a specific category.
Why should not be used in the "Excludes1" notes?
Codes/conditions listed in the "Excludes1" notes should not be used because the two conditions do not occur together. Codes/conditions listed in the "Excludes2" notes indicate that the conditions being excluded are not considered part of the subject condition, but that another code should also be assigned.
What is the term for the number of cases of a disease in a given age range?
Morbidity - Term refers to the disease rate or number of cases of a particular disease in a given age range, gender, occupation, or other relevant population based grouping. Mortality -Term refers to the death rate reflected by the population in a given region, age range, or other relevant statistical grouping.

Background
- The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is a morbidity classification published by the United States for classifying diagnoses and reason for visits in all health care settings. The ICD-10-CM is based on the ICD-10, the statistical classification of disease published by the World Health Organization (WHO). Deaths have been c…
General Changes
- The ICD-10-CM code sets have updated medical terminology and disease classifications, thus ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM are vastly different. There are nearly 5 times as many diagnosis codes in ICD-10-CM than in ICD-9-CM. The clinical modification represents significant changes from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM which include: 1. the addition of information relevant to ambulatory and mana…
Coding Changes
- The ICD-CM codes for asthma have changed from 493.00 – 493.99 in ICD-9-CM to J45.0 – J45.998 in ICD-10-CM (Table).3, 4
- Asthma codes under ICD-9-CM were stratified by extrinsic (493.00 – 493.02) and intrinsic (493.10 – 493.20)
- ICD-10-CM codes are stratified by severity
Analysis Guidance
- The transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM occurred on October 1, 2015. In 2015, asthma hospitalization and emergency department visits data for the first three quarters of the year were coded as ICD-9-CM (493.0-493.9) and the fourth quarter was coded as ICD-10-CM (J45.0-J45.998). If you received 2015 data with both coding schemes, you will have to differentiate ICD …
Challenges
- The transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM will impact public health surveillance activities, particularly those regarding asthma morbidity and healthcare utilization. A major challenge for asthma surveillance is the difference in coding for asthma. There will also be a lag in data collection to analyze trends. The coding and rule changes between ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM wil…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bilateral renal lesions
- 2. icd 10 cm code for cortisporin otic
- 3. icd 10 code for shitroy of gang greene
- 4. icd 9 code for screening for possible suspected condition
- 5. icd 9 code for htn
- 6. icd 10 code for stage dukes d colon cancer
- 7. icd 10 code for iv
- 8. icd 10 code for late effect of adverse effect of drug, medicinal or biological substance
- 9. icd 10 code for non healing ulcer
- 10. icd 9 code for prophylactic mastectomy