What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale?
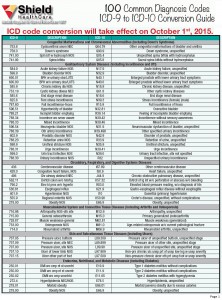
Other pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale. I26.99 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.99 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for uremia?
2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. I26.99 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.99 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I26.99 - other international versions of ICD-10 I26.99 may differ.
What is the J85 code for pulmonary embolism?
embolism complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O88.-) lung abscess ( J85.-) code to identify the site of the embolism ( I74.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery.
What are ICD-9-CM codes?
ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 415.1 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare. Although ICD-9-CM and CPT codes are largely numeric, they differ in that CPT codes describe medical procedures and services.

What is the ICD-9 code for pulmonary embolism?
415.1xVTE codes were categorized as pulmonary embolism (ICD-9 code 415.1x), lower extremity DVT (451.1x, 451.2, 451.81, 453.4x, 453.5x), upper extremity DVT (451.83, 451.84, 451.89, 453.72, 453.73, 453.74, 453.75, 453.76, 453.77, 453.82, 453.83, 453.84, 453.85, 453.86, 453.87), and other venous thrombosis (451, 451.9, 452, ...
What is the ICD-9 code for an annual physical?
V70. 0 Routine medical exam - ICD-9-CM Vol.
What is the ICD-10 code for PE?
ICD-10 code I26. 9 for Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What are ICD-9 procedure codes?
ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
How do you code an annual physical exam?
Physical Exam CPT Codes For Established Patients CPT 99393: Established patient annual preventive exam (5-11 years). CPT 99394: Established patient annual preventive exam (12-17 years). CPT 99395 Established patient annual preventive exam (18-39 years).
How do I code an annual wellness exam?
The two CPT codes used to report AWV services are:G0438 initial visit.G0439 subsequent visit.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of pulmonary embolism?
ICD-10 code Z86. 711 for Personal history of pulmonary embolism is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for recurrent PE?
ICD-10 Code for Chronic pulmonary embolism- I27. 82- Codify by AAPC.
What is a segmental PE?
Small segmental or subsegmental PE are of importance in patients with limited cardiopulmonary reserve and for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary hypertension. They may be an indicator of silent deep venous thrombosis, which may predispose patients to more severe embolic events.
Are ICD-9 codes still used in 2021?
Currently, the U.S. is the only industrialized nation still utilizing ICD-9-CM codes for morbidity data, though we have already transitioned to ICD-10 for mortality.
What are ICD-9 10 and CPT codes?
ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes provide the reason for seeking health care; ICD-10-PCS procedure codes tell what inpatient treatment and services the patient got; CPT (HCPCS Level I) codes describe outpatient services and procedures; and providers generally use HCPCS (Level II) codes for equipment, drugs, and supplies for ...
What is ICD-9 and ICD-10 difference?
ICD-9 uses mostly numeric codes with only occasional E and V alphanumeric codes. Plus, only three-, four- and five-digit codes are valid. ICD-10 uses entirely alphanumeric codes and has valid codes of up to seven digits.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
When will ICD-10-CM I26.99 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.99 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is the term for the closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches?
The closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 362.36
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use this equivalent ICD-10-CM code, which is an approximate match to ICD-9 code 362.36:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 362.36
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What is the ICD code for a lung embolism?
The ICD code I26 is used to code Pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of the lung's main artery or one of its branches by a substance that has traveled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). PE results from a deep vein thrombosis (commonly a blood clot in a leg) that breaks off and migrates to the lung, ...
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code I26 is a non-billable code.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for von willebrands disease
- 2. icd 10 code for right eye haze
- 3. icd 10 code for history of brain tumor
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for hypotensive
- 5. icd 10 code for a fibrillation
- 6. icd 10 code for cancer of stomach
- 7. icd 10 code for antinuclear antibody
- 8. icd 10 code for left quadriceps tendon rupture
- 9. 2015 icd 10 code for eminese
- 10. icd 9 code for labor