What to do if you have Achilles tendinitis?
- Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training.
- Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. ...
- Choose your shoes carefully. ...
- Stretch daily. ...
- Strengthen your calf muscles. ...
- Cross-train. ...
What is best treatment for Achilles tendonitis?
What is the initial treatment for Achilles tendinopathy?
- Rest. Rest and time off from sporting activities are important if you have Achilles tendinopathy. ...
- Painkillers. Painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen may help to relieve pain. ...
- Ice packs. ...
- Achilles tendon exercises. ...
- Orthotics. ...
- A note about steroid injections. ...
How to heal and prevent Achilles tendonitis?
- Ice the tendon.
- Massage the tendon to activate the blood flow to promote healing.
- Foam roll the calf muscle, hamstrings.
- Massage the plantar fascia by using a golf ball.
- Stretch the Achilles tendon and calf muscles by pressing your foot against the wall, hands against the wall, move up and forward- hold for 30secs.
What do you need to know about Achilles tendonitis?
What causes Achilles tendinitis?
- Overuse of your leg muscles
- A sudden increase in the amount or intensity of an activity
- Jumping or running on hard or uneven surfaces
- Wearing shoes that do not fit or support your foot and ankle
- Tight calf muscles
- A bone spur where your Achilles tendon attaches to your heel
- Medicines such as steroids or antibiotics
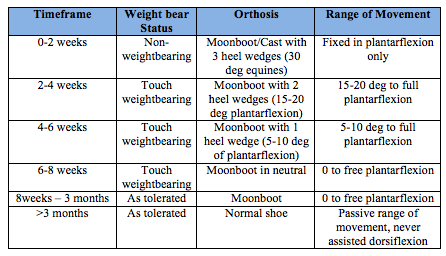
What is the ICD-10 code for Achilles tendonitis?
M76. 60 - Achilles tendinitis, unspecified leg | ICD-10-CM.
What is meant by Achilles tendonitis?
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles (uh-KILL-eez) tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs.
What is the ICD-10 code for Achilles tendon rupture?
ICD-10 code S86. 0 for Injury of Achilles tendon is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What causes Achilles tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy is usually caused by overuse – this means repeated stress on your Achilles tendon over time. This can cause changes to the structure of your tendon and sometimes tiny tears, making it weaker. Any sports or activities that put stress on your Achilles tendon can lead to Achilles tendinopathy.
What is the best way to treat Achilles tendonitis?
How are Achilles tendon injuries treated?Rest.Ice.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief (such as, ibuprofen or naproxen)Specific exercises to strengthen your calf muscles.Physical therapy.More items...
What do you do for Achilles tendonitis?
Ice. To decrease pain or swelling, apply an ice pack to the tendon for about 15 minutes after exercising or when you experience pain. Compression. Wraps or compressive elastic bandages can help reduce swelling and reduce movement of the tendon.
What is the CPT code for Achilles tendon repair?
27650: Repair, primary, open or percutaneous, ruptured Achilles tendon; Lay Description (Code): The physician repairs a ruptured Achilles tendon.
What is the name of the test to indicate Achilles tendonitis?
The Thompson testDefinition/Description The Thompson test examines the integrity of the Achilles tendon by squeezing the calf. It is performed as a clinical test to identify the presence of a complete Achilles rupture.
Is Achilles tendon flexor or extensor?
Function. Through the action of the triceps surae, which raises the heel and lowers the forefoot, the Achilles tendon is involved in plantar flexion of the foot (approximately 93% of the plantar flexion force).
What is the difference between Achilles tendonitis and Achilles tendinopathy?
While the two have almost identical symptoms, they're different conditions. Tendinopathy is a degeneration of the collagen protein that forms the tendon. Tendonitis, on the other hand, is just inflammation of the tendon.
What kind of physical therapy is used for Achilles tendonitis?
Self-stretching and manual therapy techniques (massage and movement) applied to the lower body to help restore and normalize motion in the foot, ankle, knee, and hip can decrease this tension and restore full range of motion.
Does stretching help Achilles tendonitis?
If you have Achilles tendonitis or other Achilles tendon issues, you can do stretches to help recovery. These moves improve mobility by loosening up the tendon. Strengthening exercises can also tone the calf and heel muscles attached to the tendon.
Does Achilles tendonitis go away?
It is important to remember that it may take at least two to three months for the pain of Achilles tendonitis to go away. If your pain does not improve, you may need surgery to remove inflamed tissue and abnormal areas of the tendon. If there is a bone spur irritating the tendon, surgery can be used to remove the spur.
Is it OK to walk with Achilles tendonitis?
At the moment, your tendon may not be able to cope with all the walking you want to do, but it will likely be able to tolerate some. You can help your Achilles tendon to recover by staying active but limiting your walking and other activities to a level that doesn't aggravate your symptoms too much.
What causes tendonitis?
What causes tendonitis and tenosynovitis? The cause of tendonitis and tenosynovitis is often not known. They may be caused by strain, overuse, injury, or too much exercise. Tendonitis may also be related to a disease such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or infection.
Is Achilles tendonitis permanent?
The structural changes that occur in the tendon due to degeneration are largely irreversible, but the symptoms may resolve and thus the athlete may be able to return to play. However, symptoms sometimes recur after activities are resumed.
What is the ICd 10 code for Achilles bursitis?
726.71 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of achilles bursitis or tendinitis. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
How to treat tendinitis?
Doctors diagnose tendinitis with your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. The first step in treatment is to reduce pain and swelling. Rest, wrapping or elevating the affected area, and medicines can help. Ice is helpful for recent, severe injuries. Other treatments include ultrasound, physical therapy, steroid injections, and surgery.
What is the term for the swelling of a tendon?
Tendons are flexible bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones. They help your muscles move your bones. Tendinitis is the severe swelling of a tendon.
How to tell if you have bursitis?
Symptoms of bursitis include pain and swelling. Your doctor will diagnose bursitis with a physical exam and tests such as x-rays and MRIs. He or she may also take fluid from the swollen area to be sure the problem isn't an infection.
When is the ICd 10 code for Achilles tendinitis effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.6 became effective on October 1, 2020.
When will the ICd 10-CM M76.6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is tendon inflammation?
Disorder occurring at the site of insertion of tendons or ligaments into bones or joint capsules. Inflammation of a tendon, usually resulting from an overuse injury. It is characterized by swelling of the tendon, tenderness around the inflamed tendon, and pain while moving the affected area of the body.
When will the ICd 10-CM M77.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M77.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is Tendinitis a clinical diagnosis?
It is characterized by the degeneration of tendons accompanied by an inflammatory repair response, fibroblastic proliferation, and formation of granulation tissue. Tendinitis is not a clinical diagnosis and can be confirmed only by histopathological findings.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for baker's cyst
- 2. icd 10 code for comt gene mutation
- 3. icd 10 code for cellulitis back
- 4. what is the icd code for invasive ductal carcinoma right breast
- 5. icd 10 code for laparoscopy, conversion to open, appendectomy
- 6. icd 10 code for celiac supplement
- 7. icd 10 code for feared condition not found
- 8. icd 10 code for cva of basilar artery
- 9. icd 10 pcs code for coronary angiography using high osmolar contrast
- 10. icd 10 code for 4% 3rd degree burn to calf icd 10