Full Answer
What is the ICD 9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 403.91 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 403.91 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 9 code for Hyp Kid nos w CR Kid?
Short description: Hyp kid NOS w cr kid V. ICD-9-CM 403.91 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 403.91 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute kidney failure?
Acute kidney failure, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. N17.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-9-CM code range for infectious diseases?
ICD-9-CM Chapters Chapter Code Range Description 1 001-139 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases 2 140-239 Neoplasms 3 240-279 Endocrine, Nutritional And Metabolic Dis ... 4 280-289 Diseases Of The Blood And Blood-Forming ... 15 more rows ...
What ICD-9 codes?
ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
What is the ICD-9 code for trauma?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 958.8 : Other early complications of trauma.
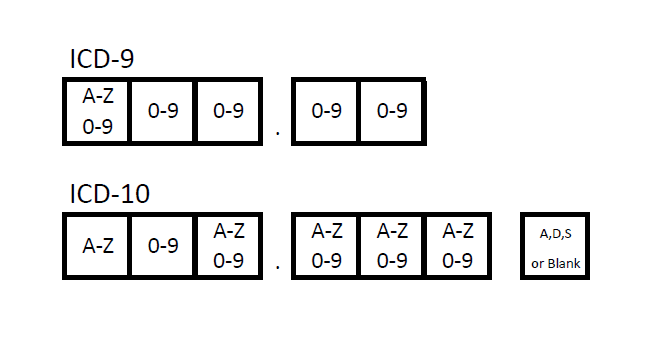
What are ICD-9 and 10 codes?
Code Structure: Comparing ICD-9 to ICD-10ICD-9-CMICD-10-CMConsists of three to five digitsConsists of three to seven charactersFirst character is numeric or alpha ( E or V)First character is alphaSecond, Third, Fourth and Fifth digits are numericAll letters used except U3 more rows•Aug 24, 2015
What is ICD-10 code for Aki?
Acute kidney failure, unspecified N17. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N17. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified cause of injury?
Y99. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is an injury code?
The injury diagnosis codes (or nature of injury codes) are the ICD codes used to classify injuries by body region (for example, head, leg, chest) and nature of injury (for example, fracture, laceration, solid organ injury, poisoning).
Are ICD-9 codes still used in 2021?
CMS will continue to maintain the ICD-9 code website with the posted files. These are the codes providers (physicians, hospitals, etc.) and suppliers must use when submitting claims to Medicare for payment.
How do you find ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10 CM Guidelines, may be found at the following website: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/icd/Comprehensive-Listing-of-ICD-10-CM-Files.htm.
What does ICD-10 stand for?
International Classification of DiseasesICD - ICD-10-CM - International Classification of Diseases,(ICD-10-CM/PCS Transition.
What is acute kidney injury N17 9?
ICD-10 code N17. 9 for Acute kidney failure, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is AKI in medical terms?
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is where your kidneys suddenly stop working properly. It can range from minor loss of kidney function to complete kidney failure. AKI normally happens as a complication of another serious illness.
Is acute kidney injury the same as kidney failure?
Acute kidney injury (AKI), also known as acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few days. AKI causes a build-up of waste products in your blood and makes it hard for your kidneys to keep the right balance of fluid in your body.
What is the ICd 9 code for symptoms?
Chapter 16 of ICD-9-CM, Symptoms, Signs, and Ill-defined conditions (codes 780.0 - 799.9) contain many, but not all codes for symptoms.
What are the conventions of ICd 9?
The conventions for the ICD-9-CM are the general rules for use of the classification independent of the guidelines. These conventions are incorporated within the index and tabular of the ICD -9-CM as instructional notes. The conventions are as follows:
What is the code for MRSA?
If a patient is documented as having both MRSA colonization and infection during a hospital admission, code V02.54, Carrier or suspected carrier, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and a code for the MRSA infection may both be assigned.
What does "with" mean in a code?
The word “with” should be interpreted to mean “associated with” or “due to” when it appears in a code title, the Alphabetic Index, or an instructional note in the Tabular List.
What is code assignment?
Code assignment is based on the provider’s documentation of the relationship between the condition and the care or procedure. The guideline extends to any complications of care, regardless of the chapter the code is located in. It is important to note that not all conditions that occur during or following medical care or surgery are classified as complications. There must be a cause-and-effect relationship between the care provided and the condition, and an indication in the documentation that it is a complication. Query the provider for clarification, if the complication is not clearly documented.
When are 760-763 codes assigned?
Codes from categories 760-763, Maternal causes of perinatal morbidity and mortality, are assigned only when the maternal condition has actually affected the fetus or newborn. The fact that the mother has an associated medical condition or experiences some complication of pregnancy, labor or delivery does not justify the routine assignment of codes from these categories to the newborn record.
When coding the birth of an infant, assign a code from categories V30-V39, according to the
When coding the birth of an infant, assign a code from categories V30-V39, according to the type of birth. A code from this series is assigned as a principal diagnosis, and assigned only once to a newborn at the time of birth.
What is the ICD-9 code for myocardial infarction?
Once again, the coder must use myocardial infarction of unspecified site, with unspecified episode ICD-9 410.90. Tamra McLain can be reached through e-mail.
Why is it important to have ICD-9 codes?
Providing the most specific ICD-9 codes is important for several reasons. For one, many hospitals use these codes to keep track of their utilization management. ICD-9 codes are also used by public health officials to track epidemics, create census reports , and for medical research purposes. While ICD-9 codes are updated every year, ...
How often are ICD-9 codes updated?
While ICD-9 codes are updated every year , the reality is that it’s all too easy for both physicians and coders to become complacent and use a narrow range of codes with which they are familiar. The good news is that when physicians provide enough detail in the medical record, coders can avoid using these codes altogether.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cellulitis of dog bite
- 2. icd 10 code for chronic kidney disease stage 3 unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for bullous keratopathy, left eye, due to cateract surgery
- 4. icd 10 diagnosis code for fall from hoverboard
- 5. icd 10 code for severe r cad
- 6. icd 10 code for dabitic foot infection
- 7. icd 10 code for onychomycosis due to dermatophyte
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for alochol use
- 9. icd 10 code for right otitis media with rupture
- 10. icd 10 code for aftercare following vertebral augmentation kyphoplasty at the t3 level