How do we diagnose acute myeloid leukemia?
Types of samples used to test for AML
- Blood samples. Blood tests are generally the first tests done to look for leukemia. Blood is taken from a vein in the arm.
- Bone marrow samples. Leukemia starts in the bone marrow, so checking the bone marrow for leukemia cells is a key part of testing for it.
- Spinal fluid. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain and spinal cord. ...
What do you need to know about acute myeloid leukemia?
What causes AML?
- Certain changes in your DNA
- A bone marrow disease in the past
- Exposure to high amounts of radiation, or medicines such as chemotherapy
- Exposure to chemicals such as pesticides or benzene (in tobacco, some paints and glues)
- Age older than 60 years
How to pronounce acute myeloid leukemia?
- Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)
- Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)
- Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
How is acute myeloid leukemia classified?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer. It starts in your bone marrow, the soft inner parts of bones. AML usually begins in cells that turn into white blood cells, but it can start in other blood-forming cells, as well. With acute types of leukemia such as AML, bone marrow cells don't grow the way they're supposed to.
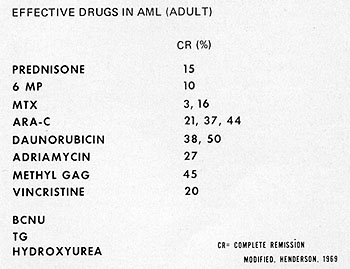
What is the ICD 9 code for leukemia?
ICD-9-CM Codes 204.0 (lymphoid leukemia, acute…) C91. 1 (chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B- cell type…) 204.1 (lymphoid leukemia, chronic…)
What is the most significant symptom of acute myelocytic leukemia?
Bruises (or small red or purple spots) on the skin. Excess bleeding. Frequent or severe nosebleeds. Bleeding gums.
What is the code for acute leukemia?
Acute leukemia of unspecified cell type, in remission C95. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C95. 01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is acute myeloid leukemia the same as acute myeloblastic leukemia?
Acute myelogenous leukemia is also known as acute myeloid leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, acute granulocytic leukemia and acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.
Which type of leukemia is most fatal?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most fatal type of leukemia. The five-year survival rate (how many people will be alive five years after diagnosis) for AML is 29.5%.
What is the life expectancy of someone with acute myeloid leukemia?
The 5-year survival rate tells you what percent of people live at least 5 years after the cancer is found. Percent means how many out of 100. The 5-year survival rate for people 20 and older with AML is 27%. For people younger than 20, the survival rate is 69%.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute lymphocytic leukemia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute lymphoblastic leukemia [ALL] C91. 0.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for acute promyelocytic leukemia?
C92.40ICD-10 Code for Acute promyelocytic leukemia, not having achieved remission- C92. 40- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of leukemia?
ICD-10 code Z85. 6 for Personal history of leukemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What are the two types of acute leukemia?
Types of leukemiaAcute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). This is the most common type of leukemia in young children. ... Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). AML is a common type of leukemia. ... Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). ... Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). ... Other types.
What are the types of acute myeloid leukemia?
The types of acute myelogenous leukemia include:Myeloblastic (M0) - on special analysis.Myeloblastic (M1) - without maturation.Myeloblastic (M2) - with maturation.Promyeloctic (M3)Myelomonocytic (M4)Monocytic (M5)Erythroleukemia (M6)Megakaryocytic (M7)
What is the difference between acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is cancer that affects the myeloid cells, which are cells that give rise to certain types of white blood cells. Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is cancer that affects the lymphocytes, which are one of the primary white blood cells in the immune response.
Which type of anemia is usually present in a patient with acute leukemia?
More than 75% of the patients presents with anemia, which is usually normochromic and normocytic and associated with a normal to low reticulocyte count.
Which type of anemia is usually present in a patient with acute leukemia *?
Chemotherapy, radiation, and some drugs doctors use to treat leukemia may cause aplastic anemia. This is because some cancer therapies prevent bone marrow from making new, healthy blood cells.
Which diagnostic finding is a hallmark of chronic myelogenous leukemia CML?
The presence of BCR/ABL rearrangement is the hallmark of CML, although this rearrangement has also been described in other diseases. It is considered diagnostic when present in a patient with clinical manifestations of CML.
How is acute lymphocytic leukemia ALL classified for adults?
Subtypes of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) Different systems have been used to classify ALL into subtypes. In the 1970s, a group of French, American, and British (FAB) leukemia experts divided ALL into 3 subtypes (L1, L2, and L3), based on the way the leukemia cells looked under the microscope after routine staining.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for cardioemboli stroke
- 2. icd 10 code for lisinopril cause cough
- 3. icd 9 code for redness under breast
- 4. icd 10 code for status post mesenteric stent
- 5. icd-10 code for ankle bimalleolar fracture
- 6. icd 10 code for carotid artery stenosi
- 7. 2019 icd 10 code for osteoarthritis right leg
- 8. icd 10 code for fall same level
- 9. icd 10 code for svt unspecified
- 10. icd 10 cm code for nose sore