How do you code acute on chronic?
· Whenever separate subentries for acute (subacute) and chronic are listed, code both and sequence the acute condition first. · When there are no subentries for acute (subacute) or chronic, disregard these modifiers in coding the particular condition. · When the Index does not provide a subentry for a condition described as subacute, code the condition as acute. Examples
What does acute on chronic mean?
- Week 1 = 1400 AU
- Week 2 = 1200 AU
- Week 3 = 1800 AU
- Week 4 = 1600 AU
How does acute pain become chronic?
Post-procedural pain
- Nerve damage (complicated aetiology likely than just nerve injury alone)
- Factors predisposing to prolonged inflammatory states (foreign materials)
- Volume of surgeries performed per year for given operation
- Recurrence of operation
- Type of surgery
- Length of surgery
How to improve time to diagnosis in acute heart failure?
What You Can Do
- Exercise. People who are diagnosed with heart disease have no reduced mortality risk linked to weight loss, but ongoing and sustained physical activity are associated with considerable risk reduction.
- Diabetes Control. Diabetes is associated with the risk of developing heart failure. ...
- Medications. ...
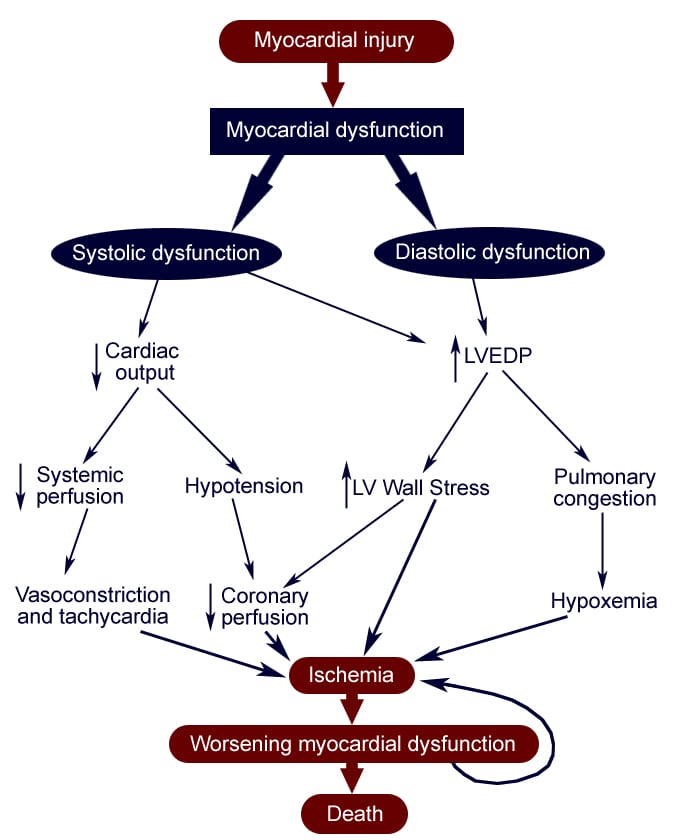
How do you code Acute on chronic heart failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 23.
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute on chronic systolic CHF?
I50. 23 - Acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure | ICD-10-CM.
What is Acute on chronic systolic congestive heart failure?
What is acute heart failure? Heart failure means your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's demands. This can be chronic, meaning it happens slowly over time. Or it can be acute, meaning it happens suddenly.
What is the correct code for Acute systolic heart failure?
ICD-10 Code for Acute systolic (congestive) heart failure- I50. 21- Codify by AAPC.
What are ICD-10 codes for heart failure?
9 – Heart Failure, Unspecified. Code I50. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Heart Failure, Unspecified.
What is the diagnosis code for congestive heart failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Systolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 2.
Is systolic heart failure acute or chronic?
Chronic systolic heart failure occurs over a period of time, typically caused by other heart conditions such as high blood pressure, a damaged heart, or coronary artery disease.
What is the difference between acute heart failure and chronic heart failure?
Q: What is the difference between acute and chronic heart failure? A: Chronic heart failure is generally a condition that develops gradually over time, whereas acute heart failure, in most cases, occurs very suddenly and should be considered a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.
Is systolic heart failure the same as CHF?
Systolic CHF - Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly. Diastolic CHF - Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff.
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute decompensated heart failure?
Assign code I50. 9, heart failure NOS for a diagnosis of congestive heart failure. “Exacerbated” or “Decompensated” heart failure – Coding guidelines advise that “exacerbation” and “decompensation” indicate an acute flare-up of a chronic condition.
What does diagnosis code 150.9 mean?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 150.9 : Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified site.
What is the difference between congestive heart failure and decompensated heart failure?
When heart failure becomes severe enough to cause symptoms requiring immediate medical treatment, it is called decompensated heart failure (DHF). On the other hand, if you have heart failure but your heart is still functioning well enough that you don't have symptoms, you have compensated heart failure.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of renal dysfunction
- 2. icd 10 code for prolonged fever
- 3. icd 10 cm code for rhogam injection first
- 4. icd 10 code for paratubal cyst in pregnancy
- 5. icd 9 code for med refill
- 6. icd 10 code for shivers adn shaking
- 7. icd-10 code for acute cystitis with hematuria
- 8. icd 10 code for carpal tunnel syndrome right wrist
- 9. icd 10 code for pre procedure testing
- 10. icd 10 code for postoperative pelvic fluid collection