What is the American version of the ICD-10 code?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F90.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 F90.9 may differ. Codes within categories F90-F98 may be used regardless of the age of a patient.
What are the ICD-9 code edits for Medicare?
The Medicare Code Editor (MCE) detects and reports errors in the coding of claims data. The following ICD-9 Code Edits are applicable to this code: Adult diagnoses: Age range is 15–124 years inclusive. References found for the code 571.1 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
What is the ICD 10 code for F90 9?
2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. F90.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM F90.9 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F90.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 F90.9 may differ.
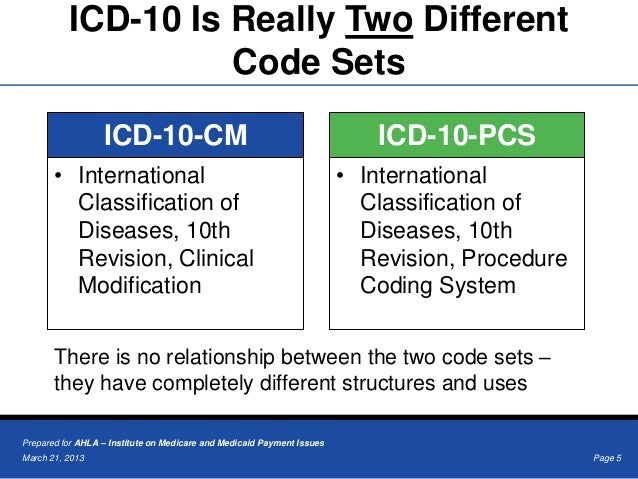
What is the ICD 10 code for AIH?
ICD-10-CM Code for Autoimmune hepatitis K75. 4.
What is the ICD 10 code for autoimmune liver disease?
K75. 4 - Autoimmune hepatitis | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 9 code for liver failure?
Short description: Liver disorder NOS. ICD-9-CM 573.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 573.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is a liver autoimmune disease?
Autoimmune liver diseases occur when the body's immune system attacks the liver, causing inflammation. If left untreated, the liver inflammation may eventually cause cirrhosis of the liver, which may lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
What is inflammatory liver disease unspecified?
Inflammation of the liver and liver disease involving degenerative or necrotic alterations of hepatocytes. Inflammation of the liver.
What is the ICD 10 code for end stage liver disease?
9 - Alcoholic liver disease, unspecified is a sample topic from the ICD-10-CM. To view other topics, please log in or purchase a subscription. ICD-10-CM 2022 Coding Guide™ from Unbound Medicine.
What is the ICD 10 code for hepatic stenosis?
Steatohepatitis K75. 81 (nonalcoholic) (NASH)
What is the ICD 9 code for hepatic encephalopathy?
572.2572.2 Hepatic encephalopathy - ICD-9-CM Vol.
What is autoimmune Cholangiopathy?
Autoimmune cholangiopathy (cholangitis; AIC) is a chronic inflammation of the liver that is considered a variant syndrome of autoimmune hepatitis.
How long does autoimmune hepatitis last?
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life.
What is liver toxicity and failure?
Acute liver failure is loss of liver function that occurs rapidly — in days or weeks — usually in a person who has no preexisting liver disease. It's most commonly caused by a hepatitis virus or drugs, such as acetaminophen. Acute liver failure is less common than chronic liver failure, which develops more slowly.
What is the ICD 10 code for hepatic steatosis?
K76. 0 - Fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified | ICD-10-CM.
Not Valid for Submission
571.1 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute alcoholic hepatitis. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
The Medicare Code Editor (MCE) detects and reports errors in the coding of claims data. The following ICD-9 Code Edits are applicable to this code:
Information for Patients
For most adults, moderate alcohol use is probably not harmful. However, about 18 million adult Americans have an alcohol use disorder. This means that their drinking causes distress and harm. It includes alcoholism and alcohol abuse.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for frr[ vs;;id vtsvl pm ypr
- 2. icd-10 code for 1. concussion and edema of thoracic spinal cord, initial encounter
- 3. icd 10 code for detached retina?
- 4. icd-10 code for influenza b
- 5. icd 10 code for hyperosmolar syndrome
- 6. icd-10 code for mood disorder
- 7. icd-10 code for urology follow-up
- 8. icd 9 code for shoulder strain
- 9. icd 10 code for low testerone level
- 10. icd 10 code for chop wound