What is the ICD 10 code for arteriovenous malformation?
Arteriovenous malformation, site unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Q27.30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q27.30 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 9 code for pulmonary AV malformatn?
Short description: Pulmonary AV malformatn. ICD-9-CM 747.32 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 747.32 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is arteriovenous malformation of cerebral vessels?
Arteriovenous malformation of cerebral vessels. An abnormal connection between arteries and veins characterized by the absence of intervening capillaries in the brain. Signs and symptoms include headaches, bruit upon headl examination, seizures, and bleeding. When bleeding occurs, the signs and symptoms are similar to those in stroke. Congenital...
What is the ICD 10 code for AVM with hemorrhage?
Assign code K55.21, Angiodysplasia of colon with hemorrhage, for the bleeding small bowel AVM, not stated as congenital.
What is an AVM?
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
About this website
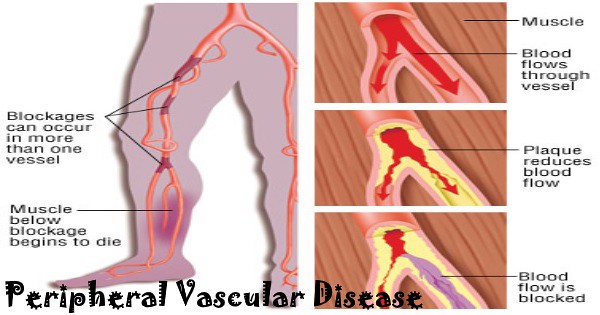
What is the ICD-10 code for AV malformation?
Q27.30ICD-10 code Q27. 30 for Arteriovenous malformation, site unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is meant by arteriovenous malformation?
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, which disrupts normal blood flow and oxygen circulation. Arteries are responsible for taking oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain.
Is arteriovenous malformation congenital or acquired?
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are high-flow malformation, characterized by direct communication between arteries and veins, lacking normal capillary network. AVMs are usually congenital. Acquired AVMs are reported to occur due to trauma or hormonal changes.
What is cerebellar arteriovenous malformation?
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth.
What is another name for arteriovenous malformation?
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system....Arteriovenous malformationOther namesAVMMicrograph of an arteriovenous malformation in the brain. HPS stain.SpecialtyNeurosurgery1 more row
Is an AVM the same as an aneurysm?
Arterial aneurysms may be present on vessels that are not AVM feeders (unrelated aneurysms) or arise from vessels that play a role in the perfusion of the nidus and, as such, are hemodynamically related to the AVM (flow-related aneurysms).
Is AVM a birth defect?
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are defects in the blood vessels of the circulatory system. A malformation is an abnormal connection between the veins and arteries. This interferes with your body's ability to circulate blood. It's usually congenital, which means the condition is present at birth.
Is AVM a neurological disorder?
AVMs also can cause a wide range of more specific neurological symptoms that vary from person to person, depending primarily upon the location of the AVM. Such symptoms may include: muscle weakness or paralysis in one part of the body. a loss of coordination (ataxia) that can lead to such problems as gait disturbances.
What causes arteriovenous malformations?
The exact cause of cerebral AVM is unknown, however growing evidence suggests a genetic cause. An AVM occurs when arteries in the brain connect directly to nearby veins without having the normal small vessels (capillaries) between them. AVMs vary in size and location in the brain.
What is an AVM in the brain NHS?
What is an arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? Normally, there is a fine network of capillaries running between the arteries and the veins throughout your brain. An AVM is the complex tangle of arteries and veins which develops when the capillaries are missing in one area.
What causes AV malformation?
The exact cause of cerebral AVM is unknown, however growing evidence suggests a genetic cause. An AVM occurs when arteries in the brain connect directly to nearby veins without having the normal small vessels (capillaries) between them. AVMs vary in size and location in the brain.
Is arteriovenous malformation life threatening?
The biggest concern related to AVMs is that they will cause uncontrolled bleeding, or hemorrhage. Fewer than 4 percent of AVMs hemorrhage, but those that do can have severe, even fatal, effects. Death as a direct result of an AVM happens in about 1 percent of people with AVMs.
Can arteriovenous malformation be cured?
Most occur in your brain and spinal cord, but they can happen anywhere in your body. Some people have symptoms; others only have symptoms after an event like a brain bleed. Surgery to remove the AVM is a cure. Other treatments can be highly successful, as well.
Is AVM serious?
What are the health consequences of AVMs? The greatest potential danger posed by AVMs is hemorrhage. Most episodes of bleeding remain undetected at the time they occur because they are not severe enough to cause significant neurological damage. But massive, even fatal, bleeding episodes do occur.
How to reduce AVM?
Embolization and sclerotherapy can reduce the size and symptoms of an AVM. They cannot make the AVM go away completely. In embolization, materials such as medical glue, metal coils or even plugs are put into the center of the AVM through a tube called a catheter, which is inserted through a blood vessel.
What is the difference between a port wine stain and an AVM?
The difference is that an AVM has fast-flowing blood in the larger blood vessels underneath the skin. The blood vessels in a CM are small and in the top layers of the skin only.
What percentage of AVMs are fatal?
The biggest concern related to AVMs is that they will cause uncontrolled bleeding, or hemorrhage. Fewer than 4 percent of AVMs hemorrhage, but those that do can have severe, even fatal, effects. Death as a direct result of an AVM happens in about 1 percent of people with AVMs.
What is the treatment for a blocked AVM?
When an AVM is blocked, blood stops flowing into it, and this helps shrink the AVM. In sclerotherapy, a liquid medicine called a sclerosant is injected into the AVM to destroy the vessels and cause scars to form. This process also leads to less or no blood flow through the AVM.
How to diagnose AVM?
Doctors can diagnose many AVMs by reviewing the patient's history and looking at the affected area (history and physical exam). In general, AVMs are not hereditary (not passed on from parent to child). AVMs can sometimes be mistaken for infantile hemangioma (IH). An AVM gets bigger when the child is no longer a baby.
Why do women have AVMs?
Women sometimes have symptoms as a result of the burden that pregnancy places on the blood vessels. Nearly 12 percent of people with AVMs do have some symptoms, however. No one knows why AVMs form. Some experts believe that the risk of developing AVMs could be genetic. AVMs can form anywhere in the body.
When do AVMs appear?
Although present at birth, an AVM may be found soon after birth or much later in life, depending on its size and location. AVMs can become apparent after an accident or as a child grows into an adult (during puberty). As a patient's body grows, the AVM grows too. AVMs grow and change over time.
What is an AVM?
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are defects in your vascular system. The vascular system includes arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart to other organs; veins carry blood back to the heart. Capillaries connect the arteries and veins. An AVM is a snarled tangle of arteries and veins. They are connected to each other, with no capillaries. That interferes with the blood circulation in an organ.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for shoulder pain
- 2. icd 10 code for urethritis
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for post op check for tooth ext
- 4. icd 10 code for squamous cell carcinoma skin
- 5. icd 10 code for cardiovasculae screening
- 6. icd 9 code for premenstrual disorder
- 7. icd 10 code for rubekka titer igg
- 8. icd 10 code for status post tracheostomy
- 9. icd 10 code for diverticulitis with pericolonic abscess
- 10. icd 10 code for fractured sternum