Breast Cancer Screening ICD 9
ICD-9-CM Volume 3
ICD-9-CM Volume 3 is a system of procedural codes. It is a subset of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) 9-CM. Volumes 1 and 2 are used for diagnostic codes.
Card security code
A card security code (CSC), card verification data (CVD), card verification number, card verification value (CVV), card verification value code, card verification code (CVC), verification code (V-code or V code), or signature panel code (SPC) is a security feature for "card not present" payment c…
What is the diagnosis code for breast cancer?
- 174.0, Nipple and areola;
- 174.1, Central portion;
- 174.2, Upper-inner quadrant;
- 174.3, Lower-inner quadrant;
- 174.4, Upper-outer quadrant;
- 174.5, Lower-outer quadrant;
- 174.6, Axillary tail;
What is the ICD - 9 code for benign breast?
subareolar duct (M8506/0) 217. Trichoepithelioma (M8100/0) - see also Neoplasm, skin, benign. breast 217. 216.9. ICD9Data.com. 218. ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 217 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
What is the CPT code for breast cancer?
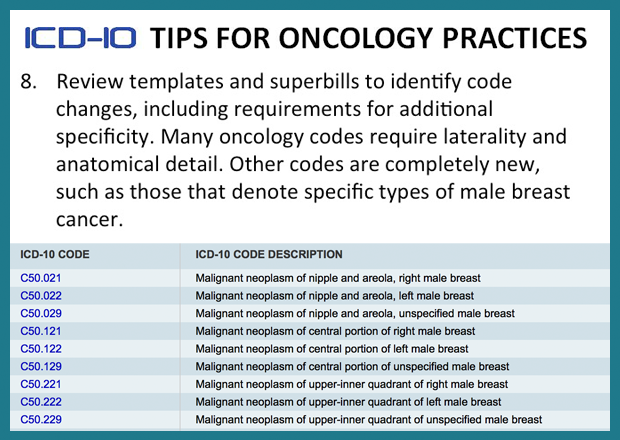
Breast Cancer ICD-10 Code Reference Sheet. FEMALE. Right. C50.011. Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola, right female breast. C50.111. Malignant neoplasm of central portion, right female breast. C50.211. Malignant neoplasm of upper-inner quadrant, right female breast.
What is the ICD 9 code for history of cancer?
- accessory sinus V10.22
- adrenal V10.88
- anus V10.06
- bile duct V10.09
- bladder V10.51
- bone V10.81
- brain V10.85
- breast V10.3
- bronchus V10.11
- cervix uteri V10.41
What is the diagnosis code for preventive mammogram?
An ICD-10-CM diagnosis code(s) should be linked to the appropriate CPT mammography code reported. The proper diagnosis code to report would be Z12. 31, Encounter for screening mammogram for malignant neoplasm of breast.
What is the difference between Z12 31 and Z12 39?
Z12. 31 (Encounter for screening mammogram for malignant neoplasm of breast) is reported for screening mammograms while Z12. 39 (Encounter for other screening for malignant neoplasm of breast) has been established for reporting screening studies for breast cancer outside the scope of mammograms.
What is code Z12 39?
39 (Encounter for other screening for malignant neoplasm of breast). Z12. 39 is the correct code to use when employing any other breast cancer screening technique (besides mammogram) and is generally used with breast MRIs.
What is the ICD-9 code for screening mammogram?
ICD-9 Code V76. 12 -Other screening mammogram- Codify by AAPC.
What does code Z12 11 mean?
A screening colonoscopy should be reported with the following International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD-10) codes: Z12. 11: Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of the colon.
Can you code Z12 31 and R92 2 together?
Per the ICD-10-CM classification, R92. 2 cannot be assigned with Z12. 31 because of an Excludes1 note under Z12. 31.
What is code R92 8?
ICD-10 code R92. 8 for Other abnormal and inconclusive findings on diagnostic imaging of breast is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is Z00 01?
ICD-10 code Z00. 01 for Encounter for general adult medical examination with abnormal findings is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is diagnosis code N64 4?
ICD-10 code N64. 4 for Mastodynia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the CPT code for breast exam?
What are insurance billing codes for additional breast screening tests?TestCPT Code2D Mammogram (screening)77067 (both breasts, 2-views of each)2D Mammogram (diagnostic)77065 (one breast) 77066 (both breasts)3D Mammogram /tomosynthesis (screening)77067 (2D both breasts) + 77063 (3D both breasts )6 more rows•Nov 3, 2021
What is the CPT code for bilateral diagnostic mammography?
CPT/HCPCS Codes for Diagnostic Mammography * 77056 (in conjunction with 77051 for computer-aided detection applied to a diagnostic mammogram): Mammography; bilateral.
What is the Hcpcs modifier for diagnostic mammogram left breast?
When modifier 52 is appended to the screening mammography codes 77057 or G0202 and 77052, it would be assumed that the service rendered was a unilateral mammography. The unilateral mammography would be paid at a reduced rate.
What is the ICd 9 code for breast cancer?
Breast Cancer is coded under “Neoplasms (ICD 9 Code 140 - 239)”. Then, as cancer is the malignant form of neoplasm, look under Malignant Neoplasm of Bone, Connective Tissue, Skin, and Breast (ICD 9 Code 170 - 176) to find Breast Cancer ICD 9 Diagnosis Codes. Cancer of the female breast is coded differently from cancer of the male breast.
What is the ICd 9 code for malignant neoplasm of central portion of female breast?
ICD 9 Code 174.1 for malignant neoplasm of central portion of female breast.
What is the ICd 9 code for malignant neoplasm of upper-outer quadrant of?
ICD 9 Code 174.4 for malignant neoplasm of upper-outer quadrant of female breast.
What is the difference between ICd 9 and ICd 10?
ICD 9 uses only numbers for the codes, but ICD 10 uses a letter and numbers. Breast Cancer Symptoms are often in the forms of abnormal lumps, weight loss, abnormal bleeding, etc. Cancer can be hereditary, but it can also develop from infections, radiations, pollutants, or chemicals in instant food.
What is the ICD code?
ICD (International Classification of Diseases) are a series of codes created by WHO (World Health Organization) to make it easier to diagnose diseases, make health statistics, compare international health statistics, including morbidity and mortality statistics, from various countries across the world, synchronize various information, including signs, symptoms, causes, abnormalities, and statistics, of each disease.
Is cancer malignant or malignant?
That is why the term cancer is always malignant. Cancer can grow on any parts of the body, including breast.
What is the report code for breast cancer?
Report code V76.12 (Screening for malignant neoplasms, other screening mammogram) for all other screening mammography. If the patient has a personal history of breast cancer, has completed active treatment and is back to annual mammographic screening, report V76.11.
Why is mammogram not recommended for women?
In general, screening mammograms are not recommended for women under 40 years of age, in part because breast tissue tends to be more dense in younger women, making mammograms as a screening tool less effective.
What is mammography screening?
Screening Mammography: Screenings are performed on otherwise healthy individuals to look for cancer or precursors to cancer of the breasts.
What is a diagnostic mammogram?
Diagnostic Mammography: Diagnostic mammography includes additional x-ray views of each breast, taken from different angles and if performed digitally, may be manipulated, enlarged, or enhanced for better visualization of the abnormality found during screening mammography.
When to report modifier 52?
As a screening mammogram is inherently bilateral in nature, report modifier -52 when screening mammogram is performed on a patient with a history of mastectomy where only one breast is imaged.
Can breast implants be seen?
Patient's with breast implants should still undergo screening mammograms; however, the implants can make it more difficult to see the breast tissue clearly. There is a technique that technicians should be trained in that allows them to better visualize breast tissue surrounding the implants called 'implant displacement views.' Patients with implants after mastectomy should have orders that clarify if the physician wants the reconstructed breast to be screened as well.
Is CAD a good tool for mammograms?
While the ACR (American College of Radiology) feels that CAD, when used with screening and diagnostic mammography, is a *valuable tool that aids in the detection of early breast cancer, there are other professional organizations that, after studying the results of mammograms performed with CAD, believe that it may instead make readings less accurate*.
What is the code for breast MRI?
As shown in Table C, codes 77046 and 77047 are reported for breast MRI without contrast.
What is a screening mammogram?
Screening mammography is performed for a person without signs or symptoms of breast disease.
What are the modifiers for Medicare?
Modifiers that can be used with CPT® codes 76641 or 76642 include: 1 50 – Bilateral procedure. This modifier is used to bill bilateral procedures that are performed at the same operative session. Under the Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS), payments are adjusted to 150 percent of the unilateral payment when a service has a bilateral payment indicator assigned. 2 26 – Professional component. A physician who performs the interpretation of an ultrasound exam in the hospital outpatient setting may submit a charge for the professional component of the ultrasound service by appending this modifier to the ultrasound code. 3 TC – Technical component. This modifier is used to bill for services by the owner of the equipment to report the technical component of the service. This modifier is commonly used when the service is performed in an independent diagnostic testing facility (IDTF).
Is breast ultrasound a good screening tool?
When mammography reveals an abnormal finding, a breast ultrasound may be used during a needle biopsy or as a follow-up test. A breast ultrasound alone is not considered a good breast cancer screening tool.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICD-10 C50.919 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C50.919 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a tumor that is not palpable?
When tumor is found in one lobe, both lobes or in prostatic apex by needle biopsy but is not palpable or visible by imaging, use code 15. C. CODES 20 to 24 are used only for clinically/radiographically apparent tumor, i.e., that which is palpable or visible by imaging.
What is the largest group of breast cancers?
Duct carcinoma, NOS (8500): The largest group of breast cancers. Duct carcinoma, NOS is not a specific histologic type because it lacks specific features that can be used to better classify the tumor. See Table 1 and Table 2 for intraductal and duct types.
What is an invasive tumor?
Invasive: A tumor that penetrates beyond the ductal basement membrane into the adjacent stroma of the breast parenchyma.
What is 8035 in cancer?
Carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells (8035): This is a specific type of duct carcinoma. The carcinomatous part of the lesion is most commonly an infiltrating duct carcinoma.
What is the position of a tumor in the breast?
The position of the tumor in the breast may be described as the positions on a clock
When to code C508?
1. Code the primary site to C508 when there is a single tumor that overlaps two or more subsites, and the subsite in which the tumor originated is unknown 2. Code the primary site to C508 when there is a single tumor located at the 12, 3, 6, or 9 o’clock position on the breast . 3.
Is sarcoma rare in breast cancer?
Sarcoma of breast: Primary sarcomas of the breast are rare accounting for less than 0.1% of all malignant tumors of the breast. Diagnoses may include fibrosarcoma, angiosarcoma, pleomorphic sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, myxofibrosarcoma, hemangio- pericytoma, and osteosarcoma (extra-osseous osteosarcoma of breast).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for parkinson's with dementia
- 2. 2015 icd 9 code for arteriovenous fistula
- 3. icd 10 cm code for unstagable ischial decubitis ulcer
- 4. icd 10 code for room and board
- 5. icd 10 code for l hip pain
- 6. icd 10 code for lipectomy for right and left thighs
- 7. icd 10 code for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures
- 8. 2016 icd 10 code for maxillary sinusitis
- 9. icd 10 code for right breast mass.
- 10. icd 10 code for v65