How to code nonischemic cardiomyopathy?
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Edema or swelling
- Fatigue, especially with exertion
- Unexplained weight gain
- Shortness of breath when lying down
How to code medical diagnosis?
- Point out the tests that were already performed to show the reason for the problem.
- Explain how these evaluations confirmed your diagnosis and show conclusive evidence.
- Use factual information, such as test result quotes, to back up your identification of the patient's issue.
What is diagnosis for code 90862?
must be submitted with a covered diagnosis. F. CPT code 90862: CPT code 90862 is intended to refer to a visit that is focused on the monitoring and prescribing of psychopharmacologic agents. Relevant history is obtained, a mental status examination is performed, and medical decision making (i.e., assessment of treatment response and ongoing
How bad is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Rarely, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause heart-related sudden death in people of all ages. Because many people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy don't realize they have it, sudden cardiac death may be the first sign of a problem. It can happen in seemingly healthy young people, including high school athletes and other young, active adults.
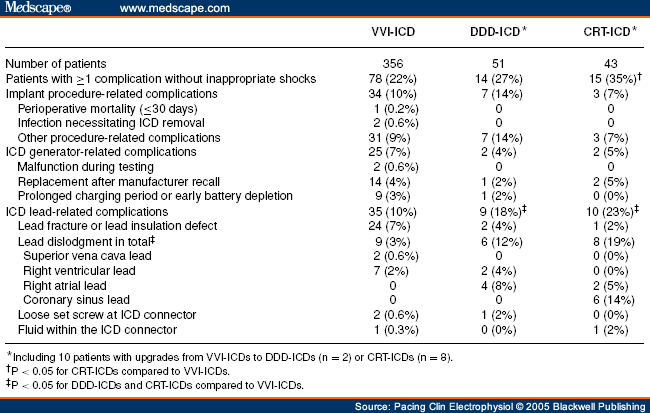
How do you code cardiomyopathy?
ischemic and dilated cardiomyopathy, code I25. 5, Ischemic cardiomyopathy, is advised. Dilated cardiomyopathy is most commonly the result of ischemic cardiomyopathy; the underlying disease should be reported. "congestive dilated cardiomyopathy," should be reported with I42.
What is the ICD 10 code for cardiomyopathy unspecified?
ICD-10 code I42. 9 for Cardiomyopathy, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the CPT code for cardiomyopathy?
Code 425.4 is assigned for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy unless the condition is documented as obstructive, which is classified to code 425.1. Congenital hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy is assigned to code 746.84.
Do you code CHF and cardiomyopathy?
When a patient presents with CHF and cardiomyopathy, treatment is typically focused on the CHF management. Therefore, sequence code 428.0 as the principal diagnosis, with code 425.4 added as a secondary diagnosis (AHA Coding Clinic for ICD-9-CM, 1990, second quarter, page 19).
What does cardiomyopathy unspecified mean?
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. The various types of the disease have many causes, signs and symptoms as well as treatments. In most cases, cardiomyopathy causes the heart muscle to become enlarged, thick or rigid.
How do you code cardiomyopathy and hypertension?
First, report code I11. 0, hypertensive heart disease with heart failure as instructed by the note at category I50, heart failure. Report an additional code from category I50- heart failure to specify the type of heart failure.
How do you code nonischemic cardiomyopathy?
Hence, most of the coder are using unspecified code I42. 9, for nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
How do you code non ischemic cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy, unspecifiednewborn I42.8.non-ischemic I42.8 - see also by cause.obscure of Africa I42.8.specified NEC I42.8.
Is dilated cardiomyopathy heart disease?
Dilated cardiomyopathy causes the chambers of the heart to grow larger. Untreated, dilated cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a type of heart muscle disease that causes the heart chambers (ventricles) to thin and stretch, growing larger.
Is cardiomyopathy the same as heart failure?
Overview. Cardiomyopathy (kahr-dee-o-my-OP-uh-thee) is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure. The main types of cardiomyopathy include dilated, hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
Is non ischemic cardiomyopathy the same as heart failure?
Many epidemiological and clinical studies simply classify patients as having NICM if heart failure is present but there is no clinical or electrocardiographic evidence of coronary disease.
Is nonischemic cardiomyopathy the same as dilated cardiomyopathy?
Dilated cardiomyopathy, also sometimes referred to as dilated, non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, is a type of heart muscle disease that causes the left ventricle of the heart to stretch abnormally. This prevents your heart from pumping blood effectively.
Known As
Ischemic caridomyopathy is also known as cardiomyopathy ischemic, chronic myocardial ischemia, coronary insufficiency chronic, generalized ischemic myocardial dysfunction, hibernationg myocardium, ischemic cardiomyopathy, ischemic cardiomyopathy (heart condition), ischemic congestive cardiomyopathy, myocardial ischemia, silent myocardial ischemia, and stunned myocardium.
Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Definition and Symptoms
Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a heart condition that occurs when the heart muscles are weakened. The left ventricle is typically enlarged.
What is the ICd 9 code for cardiomyopathy?
There are three types of cardiomyopathy: • Dilated cardiomyopathy (ICD-9-CM code 425.4) is the most common type in which the left ventricle becomes enlarged and can no longer pump blood throughout the body. This type generally occurs in middle-aged people.
What is cardiomyopathy?
For The Record. Vol. 23 No. 10 P. 27. Cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of the heart muscle with no known etiology. The condition makes it difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Although it may develop secondarily to a disease elsewhere in the body, such as coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease, ...
What is the term for ventricular dilation?
This type of cardiomyopathy usually affects older people. Physicians may use the term “congestive cardiomyopathy, ” which is also referred to as dilated cardiomyopathy and is characterized by ventricular dilation, contractile dysfunction, and symptoms of chronic heart failure (CHF).
Can cardiomyopathy cause heart failure?
Although it may develop secondarily to a disease elsewhere in the body, such as coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease, the underlying cause may never be identified. Cardiomyopathy may lead to heart failure, blood clots, a heart murmur, and cardiac arrest.
What is the ICd 10 code for cardiomyopathy?
I42.9 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Cardiomyopathy, unspecified . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2020 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
Article Guidance
Medicare covers cardiac rehabilitation (CR) services to beneficiaries as per Sections 1861 (s) (2) (CC) and 1861 (eee) (1) of the Social Security Act and 42CFR410.49 which defines key terms and the cardiac conditions that would enable a beneficiary to obtain CR services. This article provides coding requirements for outpatient cardiac rehabilitation services..
ICD-10-CM Codes that Support Medical Necessity
The following diagnoses support cardiac rehabilitation: *Use Z48.812 only to describe cardiac valvular repair for dates of service October 1, 2015 and after.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
Not Valid for Submission
425.4 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other primary cardiomyopathies. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Patients
Cardiomyopathy is the name for diseases of the heart muscle. These diseases enlarge your heart muscle or make it thicker and more rigid than normal. In rare cases, scar tissue replaces the muscle tissue.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for nevis
- 2. icd 9 code for ingrown toenail great toe
- 3. icd 10 code for low flui
- 4. icd 10 code for lymphoid aggregate of colon
- 5. icd 10 code for calcification of left parietal lobe
- 6. icd-10-cm code for vascular dementia
- 7. icd 10 code for carpal tunnel syndrome left side
- 8. icd 10 pcs code for denervation
- 9. icd 10 cm code for epigastric pain
- 10. icd 10 code for screening b12 deficiency