What is the ICD 10 code for Centrilobular emphysema?
Centrilobular emphysema. J43.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J43.2 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J43.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 J43.2 may differ.
What is the ICD-9 code for emphysema?
: Emphysema Home> 2015 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes> Diseases Of The Respiratory System 460-519> Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease And Allied Conditions 490-496> Emphysema 492->
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 492.8 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 492.8 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
How is Centrilobular emphysema diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose centrilobular emphysema by evaluating your smoking and work histories, and performing certain tests. Your doctor may order a chest X-ray to see if your lungs are enlarged, or if you’ve developed any other physical symptoms.

What is the ICD-10 CM code for Centrilobular emphysema?
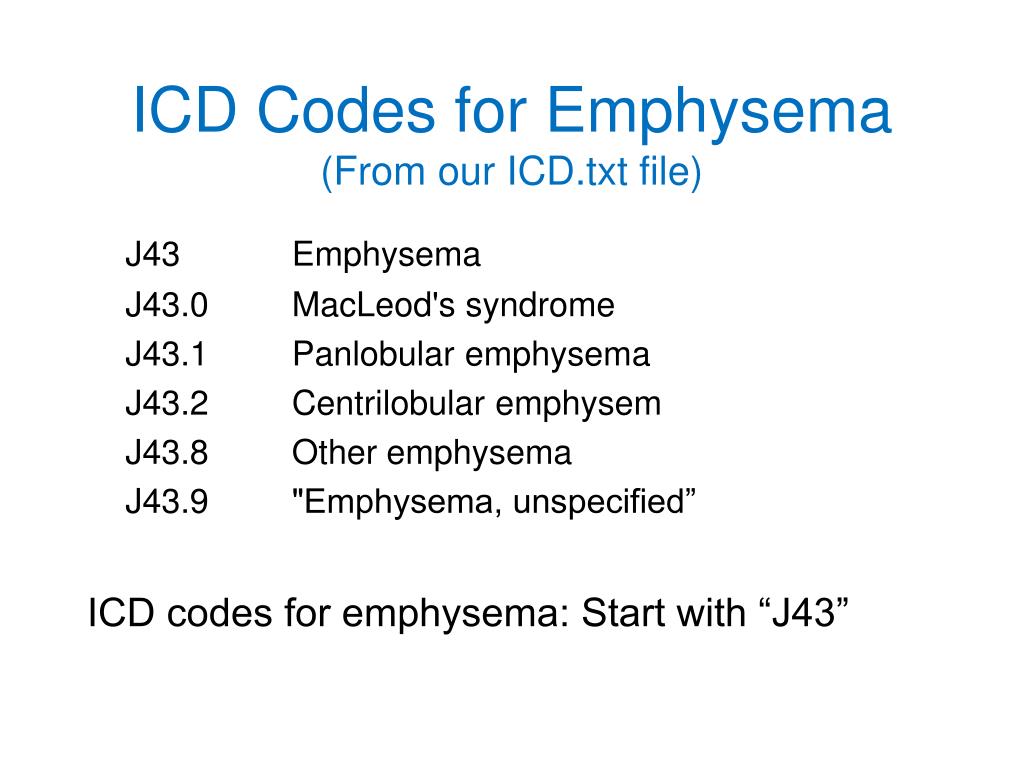
ICD-10 code J43. 2 for Centrilobular emphysema is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is centrilobular emphysema?
Centrilobular emphysema, or centriacinar emphysema, is a long-term, progressive lung disease. It's considered to be a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Centrilobular emphysema primarily affects the upper lobes of the lungs. It's characterized by damage to your respiratory passageways.
Can you code J43 9 and J44 9?
However, Coding Clinic Fourth Quarter 2017 advises to assign code J43. 9, Emphysema, unspecified, when a patient with emphysema presents with an acute exacerbation of COPD. The Excludes1 note found at category J44, Other COPD, prohibits the reporting of code J44.
What is the difference between Centrilobular and Panlobular emphysema?
Centrilobular emphysema appeared to be mainly a disease of the upper lobe and the apices within the upper and lower lobes. In contrast, panlobular emphysema was a more or less diffuse process within lobes and lungs with mild preferential involvement of the lower lobe.
Where is the Centrilobular area?
lungsThe centrilobular region, in context of the lungs and HRCT, refers to the central portion of the secondary pulmonary lobule, around the central pulmonary artery and bronchiole.
What distinguishes Centrilobular Panacinar and Localised emphysema?
Those with centrilobular emphysema appear to have more abnormalities in the small airways than those with panlobular emphysema. Panacinar emphysema appears more severe in the lower lobes, in contrast to centriacinar emphysema, which usually concentrates in the upper lobes.
Can J44 9 and J44 1 be coded together?
The advice previously published in Coding Clinic regarding COPD and emphysema was based on the current structure of the classification. Currently, codes J43. 9 and J44. 1 cannot be assigned together because of the Excludes1 note.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary emphysema?
Unilateral pulmonary emphysema [MacLeod's syndrome] J43. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J43. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the medical code for emphysema?
ICD-10-CM Code for Emphysema, unspecified J43. 9.
What are the 4 main types of emphysema?
There are four main types of emphysema, three of which are related to the anatomy of the lobules of the lung – centrilobular or centriacinar, panlobular or panacinar, and paraseptal or distal acinar and are not associated with fibrosis (scarring).
What are the two main types of emphysema?
Types of emphysemaCentriacinar – Begins in the respiratory bronchioles and spreads mainly in the upper half of the lungs. ... Panacinar – Commonly resides in the lower half of the lungs and destroys the tissue of the air sacs, causing a distinctive, uniform enlargement of air spaces.More items...
What is the difference between emphysema and COPD?
The main difference between emphysema and COPD is that emphysema is a progressive lung disease caused by over-inflation of the alveoli (air sacs in the lungs), and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is an umbrella term used to describe a group of lung conditions (emphysema is one of them) which are ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with emphysema?
Because most patients aren't diagnosed until stage 2 or 3, the prognosis for emphysema is often poor, and the average life expectancy is about five years.
Which type of emphysema is worse?
Panacinar emphysema seems to be more severe in the lower lobes, whereas centriacinar emphysema usually predominates in the upper lobes.
Can you live a full life with emphysema?
Early detection of the disease is key, because people with emphysema can develop life threatening conditions when the lungs and heart become damaged over time. It's important to stay healthy by eating well and getting exercise. With the aid of medications and therapies, you can live a long, healthy life with emphysema.
What are the 4 stages of emphysema?
There are four distinct stages of COPD: mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. Your physician will determine your stage based on results from a breathing test called a spirometry, which assesses lung function by measuring how much air you can breathe in and out and how quickly and easily you can exhale.
Known As
Emphysema is also known as acute vesicular emphysema, atrophic emphysema, centriacinar emphysema, centrilobular emphysema, emphysema, gas bubble disease, hemolytic anemia with emphysema AND cutis laxa, obstructive emphysema, panacinar emphysema, panlobular emphysema, paraseptal emphysema, pulmonary emphysema, pulmonary emphysema in alpha-1 PI deficiency, scar emphysema, toxic emphysema, and unilateral emphysema.
Emphysema Definition and Symptoms
Emphysema is a disease that slowly damages the air sacs in the lung (alveoli), making it progressively harder to breath. Some of the leading causes of emphysema are tobacco smoke, air pollution, dangerous fumes, and marijuana smoke. The only symptom of emphysema is shortness of breath that slowly gets worse.
How to diagnose centrilobular emphysema?
Your doctor will diagnose centrilobular emphysema by evaluating your smoking and work histories, and performing certain tests.
What are the symptoms of emphysema?
producing excess mucus, also referred to as sputum or phlegm. fatigue. blueness of lips and fingernail beds. These symptoms can worsen as the condition progresses. Lung function will decrease from above 80 percent in stage 1 of centrilobular emphysema to below 30 percent in the advanced stages of the disease.
How to measure oxygen levels in blood?
Oxygen levels. To measure oxygen levels in your blood, your doctor may perform a noninvasive pulse oximetry test. To do this, they’ ll place a clip-like device called a probe on your finger or ear lobe. The probe uses light to determine how much oxygen is present in your blood.
What is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung is an uncommon, but serious condition that can be life-threatening for people in advanced stages of emphysema. Large holes in the lungs: Holes in the lungs, known as bullae, can become as big as half of the lung.
Can secondhand smoke cause emphysema?
Contact with secondhand smoke or air pollution: Constant exposure to secondhand cigarette, cigar, or pipe smoke can increase your risk of centrilobular emphysema. Frequent exposure to air pollutants, including heating fuel fumes or car exhaust, can also cause the condition.
Can smoking cigarettes cause emphysema?
These factors include: Smoking: Cigarette smokers are at the highest risk for centrilobular emphysema. However, people who smoke pipes and cigars can also develop the condition. Your risk of developing the disease depends on how long and how much tobacco you smoke.
Can charcoal dust cause emphysema?
cause inflammation. These effects can also occur if you frequently inhale toxic fumes, such as charcoal dust. This is why centrilobular emphysema can be seen with CWP. Severe exposure to pollution and secondhand smoke can also lead to centrilobular emphysema.
What is the ICd 10 code for emphysema?
J43.2 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Centrilobular emphysema . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code?
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
When will the ICD-10 J43 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J43 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the term for enlargement of air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles?
Enlargement of air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles where gas-exchange normally takes place. This is usually due to destruction of the alveolar wall. Pulmonary emphysema can be classified by the location and distribution of the lesions.
What is the condition where the alveoli become inflated?
Pulmonary emphysema is a disorder affecting the alveoli (tiny air sacs) of the lungs. The transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs takes place in the walls of the alveoli. In emphysema, the alveoli become abnormally inflated, damaging their walls and making it harder to breathe. People who smoke or have chronic bronchitis have an increased risk of emphysema.
What is COPD in medical terms?
A subcategory of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). It occurs in people who smoke and suffer from chronic bronchitis. It is characterized by inflation of the alveoli, alveolar wall damage, and reduction in the number of alveoli, resulting in difficulty breathing. Alveoli are the vital lung structures where the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
What is the term for inhalation of chemicals, gases, fumes and vapors?
Emphysema (diffuse) (chronic) due to inhalation of chemicals, gases, fumes and vapors. Obliterative bronchiolitis (chronic) (subacute) due to inhalation of chemicals, gases, fumes and vapors. Pulmonary fibrosis (chronic) due to inhalation of chemicals, gases, fumes and vapors. Type 1 Excludes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for counseling urology
- 2. icd-10-cm code for plasma thromboplastin component deficiency
- 3. icd 9 code for benign neoplasm of skin
- 4. icd-10 code for impending stroke. patient presented with dysarthria.
- 5. icd 10 code for intra articular effusion
- 6. icd 10 code for retaining fluid
- 7. icd 9 code for borderline renal insufficiency
- 8. icd 10 code for high grade small bowel obstruction
- 9. icd 10 code for interstim placement
- 10. icd 9 code for vitamin d toxicity