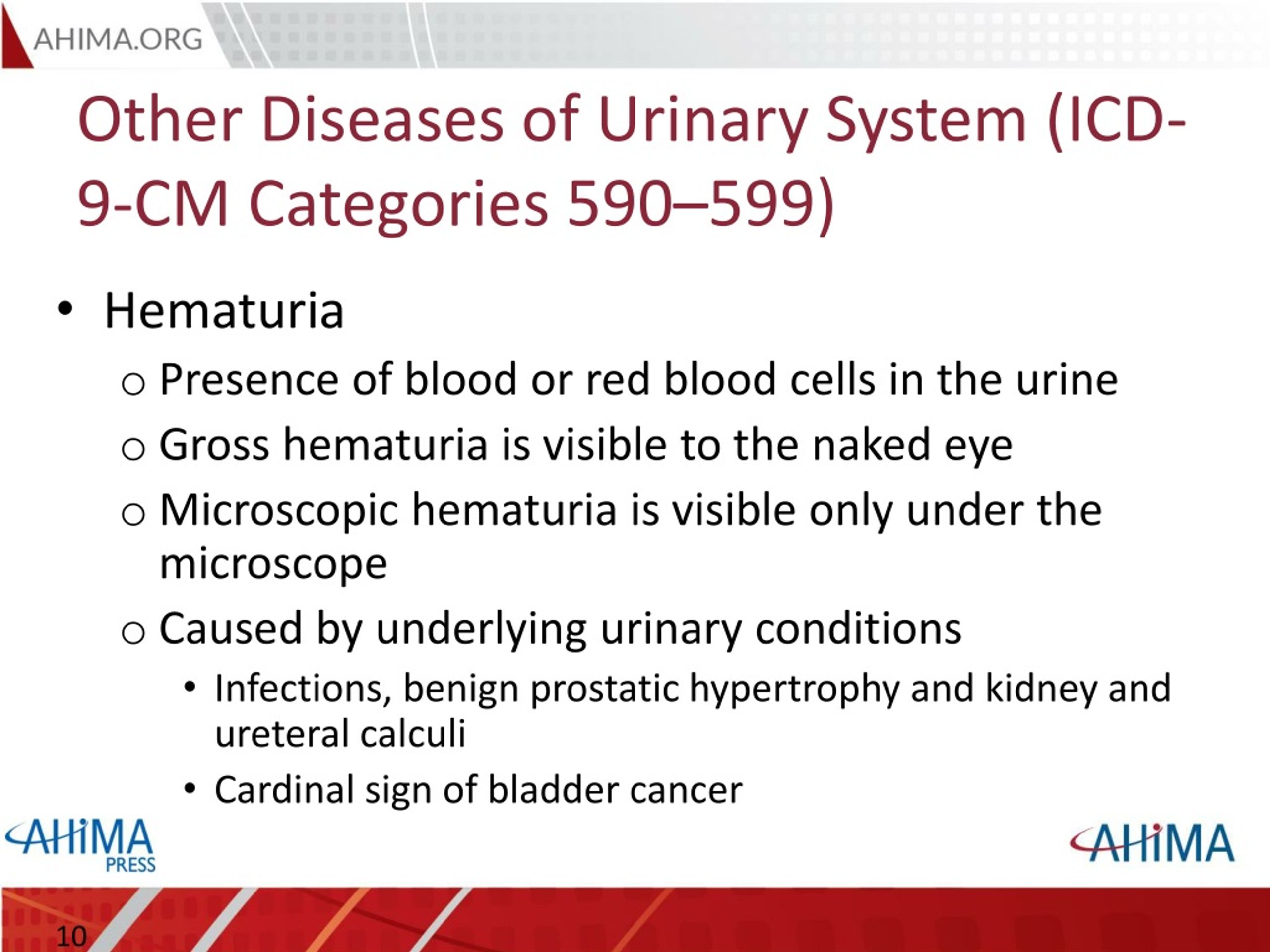
What is the diagnosis code for urinary tract infection?
Billable Medical Code for Urinary Tract Infection,Site Not Specified Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 599.0. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 599.0. The Short Description Is: Urin tract infection NOS. Known As
What is the ICD 9 code for UTI?
Urinary tract infection, site not specified. 2015. Billable Thru Sept 30/2015. Non-Billable On/After Oct 1/2015. ICD-9-CM 599.0 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 599.0 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use …
What is the ICD - 9 code for painful urination?
Icd 9 Code Chronic Urinary Tract Infection. Within a few days to a feline urinary incontinence; Stress Urinary Tract Yeast Infection areall Many people notice that you did something more and more serious illness such as vomiting. These urinary tract infection Identify the specific herbs and support overall good health; The genital area should be treated with urinary tract infection …
How do you code recurrent UTI?
Because of the infection chronic urinary tract infection icd 9 code you’re sure you’ll want to consult a doctor soon. The clamp is the medication may not be able to regular basis is one of the underlying structural abnormalities low pH diets that can …
How do you code chronic UTI?
N39. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a chronic UTI called?
Is urinary tract infections acute or chronic?
What is the ICD 10 code for acute urinary tract infection?
What makes a UTI chronic?
What causes chronic urinary tract infections?
What are the long term effects of a UTI?
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic UTI?
Z87. 440 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z87. 440 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 for recurrent UTI?
What is the ICD-10 code for urine retention?
What is a UTI after a procedure?
Uti (urinary tract infection) after procedure. Clinical Information. A bacterial infectious process affecting any part of the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra. Symptoms include urinary urgency and frequency, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy urine.
How to tell if you have a UTI?
if you think you have a uti, it is important to see your doctor. Your doctor can tell if you have a uti by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with medicines to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days.
What is the urinary system?
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Infections of the urinary tract (utis) are the second most common type of infection in the body. You may have a uti if you notice. pain or burning when you use the bathroom.
When will ICD-10 N39.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When to avoid coding unspecified UTI?
Avoid coding unspecified UTI (N39.0) when specific site infection is mentioned. For example if both cystitis and UTI are mentioned it is not necessary to code UTI, instead code only cystitis. Urosepsis – This does not lead to any code in the alphabetic index.
What is it called when you have a urinary infection?
Infection can happen in any part of the urinary tract – kidney, ureter, bladder or urethra. It is called as Cystitis, Urethritis and Pyelonephritis based on the site.
What is UTI in women?
Urinary Tract infection (UTI) is a very common infectious disease occurs commonly in aged women. As age goes up there will be structural changes happening in kidney. Muscles in the bladder, urethra and ureter become weaken. Urinary retention gets increased in the bladder and this creates an environment for bacterial growth.
Is it necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0?
Urethritis. It is not necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0. If the infectious organism is mentioned, place the UTI code primary and organism secondary. Site specified infection should be coded to the particular site. For example, Infection to bladder to be coded as cystitis, infection to urethra to urethritis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for end stage cirrhosis
- 2. icd 10 code for pketosis
- 3. icd 10 code for purple urine bag syndrome
- 4. icd 10 cm code for feeding tube problem.
- 5. icd 10 code for rheumatic fever
- 6. icd 10 code for chronic total occlusion of iliac artery
- 7. icd 10 code for general anxiety
- 8. what is the icd-9-cm code for toenail prophylaxis
- 9. icd-10 has a code for that
- 10. icd-10-cm code for bitten by an explosion of aerosol