Patients selected for chart review were adults ( 18 years old) with the ICD-9 code 585.3 (CKD stage 3) recorded in their EMR. A registry of these patients was pulled from each practice and given to the research team for analysis.
What is the ICD 9 code for cardiac disease?
- due to calcified coronary lesion (severely) 414.4 lipid rich plaque 414.3
- graft - see Arteriosclerosis, bypass graft
- native artery 414.01 of transplanted heart 414.06
What is the ICD 9 code for kidney calculus?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 592.9 : Urinary calculus, unspecified. Home > 2015 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes > Diseases Of The Genitourinary System 580-629 > Other Diseases Of Urinary System 590-599 > Calculus of kidney and ureter 592-.
What is ICD - 9 code for chronic kidney injury?
ICD-9-CM Coding Chronic Kidney Disease • 585.1, Chronic kidney disease, Stage I • 585.2, Chronic kidney disease, Stage II (mild) • 585.3, Chronic kidney disease, Stage III (moderate) • 585.4, Chronic kidney disease, Stage IV (severe) • 585.5, Chronic kidney disease, Stage V • Excludes: Chronic kidney disease, stage V requiring
How do you code acute on chronic kidney disease?
What is the most common cause of acute kidney failure?
- acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
- severe or sudden dehydration.
- toxic kidney injury from poisons or certain medications.
- autoimmune kidney diseases, such as acute nephritic syndrome and interstitial nephritis.
- urinary tract obstruction.
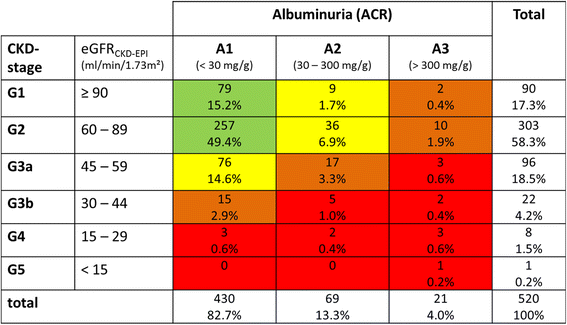
What is the ICD-10 code for CKD?
ICD-10 code N18. 9 for Chronic kidney disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the ICD-10 code for CKD 3?
N18. 30- Chronic Kidney Disease stage 3 unspecified.
How do you code Chronic kidney disease?
Coding CKD. Documenting the stage of CKD—not the GFR—is vital for accurate coding. If the stage is not documented, then code 585.9, Chronic kidney disease, is assigned. If a provider documents both a stage of CKD and ESRD, then only the code for ESRD (585.6) is assigned.
What is the ICD-10 code for CKD Stage 5?
ICD-10 code: N18. 5 Chronic kidney disease, stage 5.
What is the difference between Chronic kidney disease 3a and 3b?
Stage 3a means you have an eGFR between 45 and 59, and Stage 3b means you have an eGFR between 30 and 44.
Which of the following codes are correct when coding hypertensive chronic kidney disease stage 3?
N18. 3, Chronic kidney disease, stage 3 (moderate), N18.
What is the ICD 10 code for CKD Stage 4?
ICD-10 code: N18. 4 Chronic kidney disease, stage 4.
What is unspecified CKD?
chronic kidney disease (ckd) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should. This damage can cause wastes to build up in your body. It can also cause other problems that can harm your health. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of ckd.
Can you code E11 22 and N18 9?
6).” Code N18. 9 is not included in this range of codes and provides no further specificity. In this case, only E11. 22 would be needed for DM with CKD of unspecified stage.
What is the ICD-10 code for ESRD on hemodialysis?
ESRD is reported as 585.6 in ICD-9-CM and N18. 6 in ICD-10-CM. Additional guidance is provided in ICD-10-CM under N18. 6 to use additional codes to identify dialysis status (Z99.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for dialysis?
ICD-10 code Z99. 2 for Dependence on renal dialysis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is diagnosis code n185?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N18. 5: Chronic kidney disease, stage 5.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 585.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 585.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is the function of kidneys?
Their main job is to filter wastes and excess water out of your blood to make urine. They also keep the body's chemical balance, help control blood pressure, and make hormones.chronic kidney disease (ckd) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should.
What does CKD mean in medical terms?
They also keep the body's chemical balance, help control blood pressure, and make hormones.chronic kidney disease (ckd) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should. This damage can cause wastes to build up in your body. It can also cause other problems that can harm your health.
How to treat kidney failure?
The only treatment options for kidney failure are dialysis or a kidney transplantation.you can take steps to keep your kidneys healthier longer: choose foods with less salt (sodium) keep your blood pressure below 130/80. keep your blood glucose in the target range, if you have diabetes. Codes.
What causes renal failure?
Gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function resulting in renal failure. Causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Impairment of the renal function due to chronic kidney damage.
Can CKD cause kidney failure?
Ckd can get worse over time. Ckd may lead to kidney failure.
What causes renal failure?
Gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function resulting in renal failure. Causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney. Impairment of the renal function due to chronic kidney damage.
What is the function of kidneys?
Their main job is to filter wastes and excess water out of your blood to make urine. They also keep the body's chemical balance, help control blood pressure, and make hormones.chronic kidney disease (ckd) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should.
Why is my kidney unable to remove waste?
This damage may leave kidneys unable to remove wastes. Causes can include genetic problems, injuries, or medicines. You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close family member with kidney disease. chronic kidney disease damages the nephrons slowly over several years.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for skin tear of left hand
- 2. icd 10 code for inguinal lymphadenopathy
- 3. icd-9 code for observation following work accident?
- 4. icd 10 code for right elbow injury
- 5. icd 9 code for right elbow abrasion
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for cellulitis
- 7. icd 10 code for n39
- 8. icd 9 code for bony lesion
- 9. code for routine eye exam in icd -10
- 10. icd 10 code for pregnancy due date