What is the ICD 10 code for Coats'disease?
The ICD code H350 is used to code Coats' disease. Coats’ disease, (also known as exudative retinitis or retinal telangiectasis, sometimes spelled Coates' disease), is a rare congenital, nonhereditary eye disorder, causing full or partial blindness, characterized by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina.
What is the ICD 9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 556.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 556.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What are the symptoms of Coats disease?
Over time, Coats disease may also lead to retinal detachment, glaucoma, and clouding of the lens of the eye (cataracts). In most cases, only one eye is affected.
What are the ICD-9 codes for infectious and parasitic diseases?
This is a shortened version of the first chapter of the ICD-9: Infectious and Parasitic Diseases. It covers ICD codes 001 to 139.
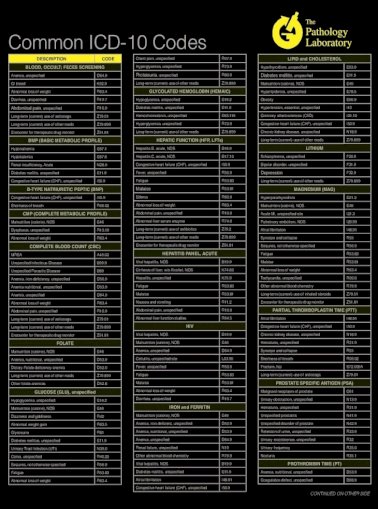
What is coats disease?
Listen. Coats disease is an eye disorder characterized by abnormal development of the blood vessels in the retina (retinal telangiectasia). Most people begin showing symptoms in childhood. Early signs and symptoms vary but may include vision loss, " crossed eyes " (strabismus), and a white mass in the pupil behind the lens of the eye (leukocoria).
What is coats plus syndrome?
When Coats disease occurs with additional abnormalities that affect the brain, bones, gastrointestinal system, and other parts of the body, it is called Coats plus syndrome and is caused by mutations in the CTC1 gene. [4] Last updated: 8/17/2017.
When do coats start?
The signs and symptoms of Coats disease typically begin at an early age (between ages 6 and 8). [3] . The disorder may occur at any age, but the majority of people with Coats disease are diagnosed in the first two decades of life. Some people may have few or no symptoms, while others are very severely affected. [1] .
Is coats disease inherited?
Isolated Coats disease is not an inherited condition. [1] . Rarely , Coats disease can be a feature of an underlying, inherited genetic syndrome. For example, it is a key feature of a condition called Coats plus syndrome, which is characterized by Coats disease plus abnormalities of the brain, bones, gastrointestinal system, ...
Is coats disease a genetic disorder?
However, this has not been proven. [1] Coats disease has been reported as one feature of several genetic syndrome s. [3] . In these cases, the underlying cause of each syndrome may be responsible for Coats disease.
Can coats disease cause cataracts?
Over time, Coats disease may also lead to retinal detachment, glaucoma, and clouding of the lens of the eye ( cataracts ). In most cases, only one eye is affected. Coats disease is not inherited and the underlying cause is not known.
What is Coates disease?
Coats’ disease, (also known as exudative retinitis or retinal telangiectasis, sometimes spelled Coates' disease), is a rare congenital, nonhereditary eye disorder, causing full or partial blindness, characterized by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina. Coats' disease can also fall under glaucoma.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H35.029 and a single ICD9 code, 362.12 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 diagnosis code for costochondritis
- 2. icd 10 cm code for impaired instrumental activities of daily living
- 3. icd 10 code for violent outbursts
- 4. icd 10 code for sensitivity to sound
- 5. icd 10 code for high white blood cell
- 6. icd 10 cm code for prominent colonic stool
- 7. icd 10 code for basal cell carcinoma right lower eyelid
- 8. icd 10 code for patient on hemodialysis
- 9. icd code for behavior risk for hiv
- 10. icd 10 code for right upper back wound