How is an ovarian cyst detected?
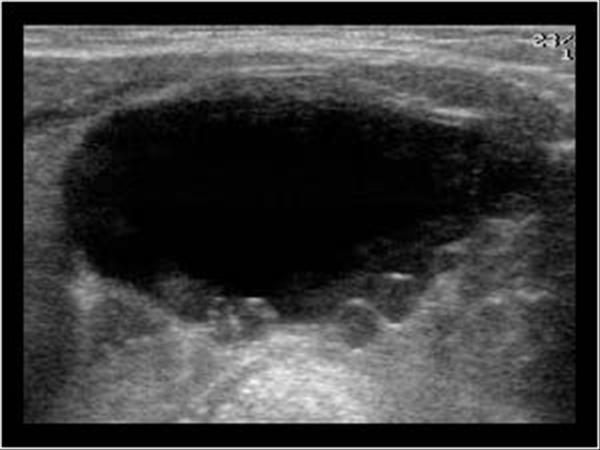
Ultrasound is often the first test done if a problem with the ovaries is suspected. It can be used to find an ovarian tumor and to check if it is a solid mass (tumor) or a fluid-filled cyst. It can also be used to get a better look at the ovary to see how big it is and how it looks inside.
What are the complications of ovarian cyst?
These include:
- severe, acute, unilateral abdominal or groin pain around the ovary,
- significant deterioration of health
- elevated body temperature
- nausea and vomiting
Would ovarian cysts cause painful urination?
Urination may hurt if your bladder is inflamed. This may occur even if you don't have an infection. Something pressing against the bladder (like an ovarian cyst) or irritation from a kidney stone that is stuck near the entrance to the bladder can also cause painful urination.
Does ovarian cyst cause irregular periods?
Yes: The excess estrogen from the ovarian cyst brings future ovulation to a halt and causes periods to be irregular until the cyst is resolved. I have ovarian cyst im trying to get pregnant is is it hard to get pregnant cause the irregular periods? Good news: Ovarian cysts are rather common and not a reason for infertility.
What is the ICD-10 code for ovarian cyst?
ICD-10 code N83. 20 for Unspecified ovarian cysts is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the ICD-10 code for pelvic cyst?
ICD-10-CM Code for Intra-abdominal and pelvic swelling, mass and lump R19. 0.
What is the diagnosis code for left ovarian cyst?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified ovarian cyst, left side- N83. 202- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for complex left ovarian cyst?
N83. 292 - Other ovarian cyst, left side. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral ovarian follicles?
Follicular cyst of ovary, unspecified side The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N83. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N83.
What is diagnosis code R19 00?
R19. 00 Intra-abd and pelvic swelling, mass and lump, unsp site - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the ICD-10 code for left ovarian mass?
Unspecified ovarian cyst, left side N83. 202 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N83. 202 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for adnexal cyst?
Other ovarian cysts ICD-10-CM N83. 291 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 742 Uterine and adnexa procedures for non-malignancy with cc/mcc.
What is left adnexal cyst?
An adnexal (ad-nek-suhl) mass is a growth that develops around the uterus, usually in your ovaries, fallopian tubes and neighboring connective tissues. Some adnexal tumors are fluid-filled, while others are solid. They can appear at any age, and most of them go away on their own within a few months.
What is a Paraovarian cyst?
A paraovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac found in the fallopian tubes near your ovaries. It might also be called paratubal cyst or a hydatid cyst of Morgagni. These cysts usually don't cause any symptoms and often aren't discovered unless you have surgery or other problems.
What does adnexal mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (ad-NEK-sul…) A lump in tissue near the uterus, usually in the ovary or fallopian tube. Adnexal masses include ovarian cysts, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, and benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) tumors.
What is the dermoid cyst?
A dermoid cyst is a growth of normal tissue enclosed in a pocket of cells called a sac. This tissue grows in or under your skin in an unexpected location. Dermoid refers to something that's like skin. A cyst is a lump or bump that may contain fluid or other material.
What is a unspecified ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac in or on a person's ovary. The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They produce eggs and hormones. Ovarian cysts are very common. They often occur during ovulation.
What N83 209?
N83. 209 Unspecified ovarian cyst, unspecified side - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What does adnexal mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (ad-NEK-sul…) A lump in tissue near the uterus, usually in the ovary or fallopian tube. Adnexal masses include ovarian cysts, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, and benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) tumors.
What is the CPT code for ovarian cystectomy?
58925To excise an ovarian cyst means that the ob-gyn removes the cyst by cutting. If this is the case, you should use 58925 (Ovarian cystectomy, unilateral or bilateral), Trice says.
Known As
Ovarian cyst is also known as complex ovarian cyst, complicated ovarian cyst, corpus albicans cyst of ovary, cyst of ovary, cyst of ovary in pregnancy, endometrial cystoma of ovary, functional cyst of ovary, functional ovarian cyst, germinal inclusion cyst of ovary, hemorrhagic cyst of ovary, hyperreactio luteinalis, left ovarian cyst, luteal cystic ovary disease, ovarian cyst, ovarian cyst in pregnancy, right ovarian cyst, ruptured cyst of ovary, ruptured ovarian cyst, serous cyst of ovary, serous ovarian cyst, simple cystoma of the ovary, and theca-lutein cyst of ovary.
Ovarian Cyst Definition and Symptoms
An ovarian cyst is a fluid filled pocket in, or on the surface of, an ovary. If these cysts rupture they can produce very serious symptoms. Warning signs and symptoms that a person may have ovarian cysts present are menstrual irregularities, pelvic pain, pressure on the rectum, nausea, a heaviness in the abdomen, and pain during bowel movements.
What is the ICd 10 code for ovarian cyst?
620.2 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other and unspecified ovarian cyst. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Does a cyst on the ovary hurt?
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac. In most cases a cyst on the ovary does no harm and goes away by itself. Most women have them sometime during their lives. Cysts are rarely cancerous in women under 50. Cysts sometimes hurt - but not always. Often, a woman finds out about a cyst when she has a pelvic exam.
What are the symptoms of cysts in the ovary?
Symptoms include pelvic and abdominal pain and irregular periods. Fluid-filled closed cavity or sac in the ovary that is lined by epithelium; can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. General term for cysts and cystic diseases of the ovary. Code History.
What is a D27 cyst?
neoplastic ovarian cyst ( D27.-) polycystic ovarian syndrome ( E28.2) Stein-Leventhal syndrome ( E28.2) Other and unspecified ovarian cysts. Clinical Information. A cyst is a fluid-filled sac. In most cases a cyst on the ovary does no harm and goes away by itself. Most women have them sometime during their lives.
What are some examples of PCOs?
Of health and human services office on women's health. A cyst that arises from the ovary. Representative examples include simple, complex, corpus luteum, and endometrioid cysts.
Can a woman with a cyst be cancerous?
Cysts are rarely cancerous in women under 50. Cysts sometimes hurt - but not always. Often, a woman finds out about a cyst when she has a pelvic exam. If you're in your childbearing years or past menopause, have no symptoms, and have a fluid-filled cyst, you may choose to monitor the cyst.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for r19.7
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for hepatic lobe mass
- 3. icd 10 code for cervical tendonitis
- 4. icd 10 cm code for contact with a catfish barb
- 5. icd 10 code for joint pain and sweeling
- 6. icd 10 code for draining superficial hematoma
- 7. icd 10 code for acf
- 8. icd 10 code for weak urinary stream
- 9. icd 10 code for congential laryngomalacia
- 10. icd 10 code for growing skull fracture