Want to know more about Dexur's Capabilities? Get In Touch
| ICD Code | Description |
| 25060 | Diabetes with neurological manifestation ... |
| 25061 | Diabetes with neurological manifestation ... |
| 25062 | Diabetes with neurological manifestation ... |
| 25063 | Diabetes with neurological manifestation ... |
What is the ICD 9 code for diabetic neuropathy?
Diagnosis Code 250.60. ICD-9: 250.60. Short Description: DMII neuro nt st uncntrl. Long Description: Diabetes with neurological manifestations, type II or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled. This is the 2014 version of the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 250.60.
What is the ICD 9 code for diabetes mellitus?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 250.* : Diabetes mellitus (dye-a-bee-teez) a disease in which the body does not properly control the amount of sugar in the blood. As a result, the level of sugar in the blood is too high.
What is the CPT code for type 2 diabetes type 2?
250.60 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of diabetes with neurological manifestations, type ii or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled.
What are the ICD-9 gems and how are they used?
The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
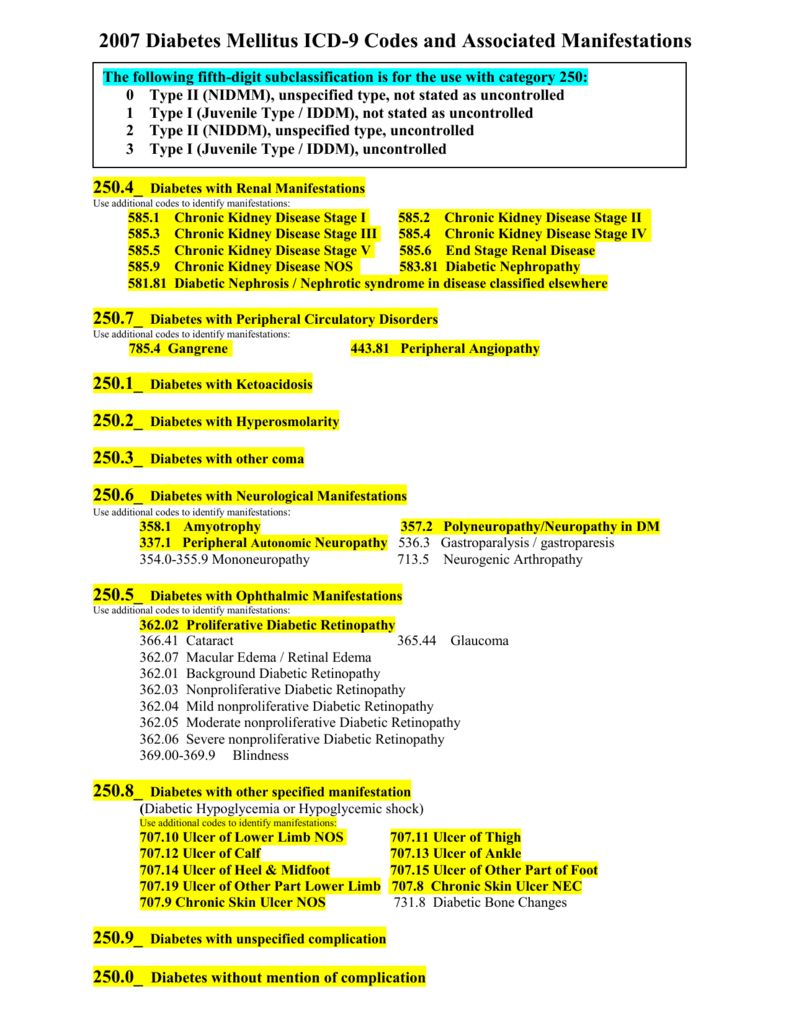
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes with neurological manifestations?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications- E11. 4- Codify by AAPC.
How do you code diabetes and neuropathy?
ICD-9-CM Coding If either peripheral or autonomic neuropathy is caused by diabetes, then a code from subcategory 250.6 will be sequenced first followed by code 357.2 for polyneuropathy in diabetes or code 337.1 for peripheral autonomic neuropathy.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic neuropathy?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified- E11. 40- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-9 code for diabetes mellitus?
Table 5ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes defining diabetesDescriptionICD-9-CM codeDiabetes mellitus without mention of complications250.0xDiabetes with ketoacidosis250.1xDiabetes with hyperosmolarity250.2xDiabetes with other coma250.3x8 more rows
What is Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy unspecified?
What is diabetic neuropathy? Diabetic neuropathy is a serious and common complication of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It's a type of nerve damage caused by long-term high blood sugar levels. The condition usually develops slowly, sometimes over the course of several decades.
Can you code E11 9 and E11 22 together?
So yes, use the appropriate combination codes, being E11. 22, I12. 9 and N18. 3.
Is peripheral neuropathy and polyneuropathy the same?
Polyneuropathy is when multiple peripheral nerves become damaged, which is also commonly called peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
What is the correct code for a patient with Type 1 diabetic neuropathy?
ICD-10 Code for Type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified- E10. 40- Codify by AAPC.
What is diabetic polyneuropathy?
Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) affects multiple peripheral sensory and motor nerves that branch out from the spinal cord into the arms, hands, legs and feet. Typically, the longest nerves — those that extend from the spine to the feet — are affected the most.
What are the ICD-10 codes for diabetes?
Coding Diabetes Mellitus in ICD-10-CM: Improved Coding for Diabetes Mellitus Complements Present Medical ScienceE08, Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition.E09, Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus.E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus.E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus.E13, Other specified diabetes mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for each type of diabetes?
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Codes for Diabetes Conversion TableICD-9ICD-10249.00E08.9 or E09.9 or E13.9249.01Aug 7, 2016
What's the diagnosis code for diabetes?
E08. 1 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition... E08. 10 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition...
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.
What is the ICD-9 code for peripheral neuropathy?
356.9ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 356.9 : Unspecified hereditary and idiopathic peripheral neuropathy.
What is the correct code for a patient with Type 1 diabetic neuropathy?
ICD-10 Code for Type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified- E10. 40- Codify by AAPC.
Is there a causal relationship between diabetes and neuropathy?
Also, 2nd Quarter 2009 Coding Clinic states that diabetes “with” neuropathy establishes a causal link between the diabetes and the neuropathy. It would be unwise to extrapolate that rule across all diabetic complications, however.
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetes?
250.60 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of diabetes with neurological manifestations, type ii or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
How to diagnose diabetic neuropathy?
Your doctor will diagnose diabetic neuropathy with a physical exam and nerve tests. Controlling your blood sugar can help prevent nerve problems, or keep them from getting worse. Treatment may include pain relief and other medicines.
What type of diabetes is associated with polyneuropathy?
Polyneuropathy associated with type I diabetes mellitus
What does it mean to have diabetes before surgery?
Preparing for surgery when you have diabetes. Diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy.
What happens if you have Type 2 diabetes?
If you have diabetes, your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Over time, this can damage the covering on your nerves or the blood vessels that bring oxygen to your nerves. Damaged nerves may stop sending messages, or may send messages slowly or at the wrong times .
Does prediabetes increase your risk of diabetes?
You have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise. Having prediabetes also increases your risk. Prediabetes means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes appear slowly.
Does type 2 diabetes show symptoms?
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes appear slowly. Some people do not notice symptoms at all. The symptoms can include
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetes?
250.63 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of diabetes with neurological manifestations, type i [juvenile type], uncontrolled. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
How to diagnose diabetic neuropathy?
Your doctor will diagnose diabetic neuropathy with a physical exam and nerve tests. Controlling your blood sugar can help prevent nerve problems, or keep them from getting worse. Treatment may include pain relief and other medicines.
Not Valid for Submission
249.60 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of secondary diabetes mellitus with neurological manifestations, not stated as uncontrolled, or unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Convert 249.60 to ICD-10
The following crosswalk between ICD-9 to ICD-10 is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
Information for Patients
Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
How does diabetes affect your body?
Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes.a blood test can show if you have diabetes. Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your glucose level and take medicine if prescribed. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases
Can diabetes cause heart disease?
It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb.
Does obesity cause insulin resistance?
Type 2 diabetes, characterized by target-tissue resistance to insulin, is epidemic in industrialized societies and is strongly associated with obesity; however, the mechanism by which increased adiposity causes insulin resistance is unclear. Adipocytes secrete a unique signalling molecule, which was named resistin (for resistance to insulin). Circulating resistin levels are decreased by the anti-diabetic drug rosiglitazone, and increased in diet-induced and genetic forms of obesity. Administration of anti-resistin antibody improves blood sugar and insulin action in mice with diet-induced obesity. Moreover, treatment of normal mice with recombinant resistin impairs glucose tolerance and insulin action. Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by adipocytes is enhanced by neutralization of resistin and is reduced by resistin treatment. Resistin is thus a hormone that potentially links obesity to diabetes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for allergic reation to antibiotic
- 2. icd 10 code for incomplete myelination
- 3. icd 10 code for lack of coordination
- 4. icd 10 code for unsatgeable left foot pressure
- 5. icd-10 code for squamous cell carcinoma of upper lip
- 6. icd 10 code for diabetic foot infection with gangrene
- 7. icd 10 code for left knee complex medial meniscus tear
- 8. icd 10 code for right colon perforation
- 9. icd 10 code for falling backwards
- 10. icd 10 cm code for insect sting