What is the ICD 9 code for diabetes mellitus?
2014 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 250.* : Diabetes mellitus (dye-a-bee-teez) a disease in which the body does not properly control the amount of sugar in the blood. As a result, the level of sugar in the blood is too high.
What are the ICD-10-CM coding guidelines?
The ICD-10-CM coding guidelines established by the National Center for Health Care (NCHC) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for ICD-10-CM assist healthcare professionals and medical coders in selecting the appropriate diagnosis codes to report for a specific patient encounter.
What is the ICD 10 code for Secondary diabetes mellitus?
postprocedural diabetes mellitus ( E13.-) secondary diabetes mellitus NEC ( E13.-) type 1 diabetes mellitus ( E10.-) Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is the difference between ICD 10 and ICD 9 codes?
ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are a way for doctors to record diagnoses in a succinct universal language. ICD-10 codes refer to the codes from the 10th Revision of the classification system. ICD-10 officially replaced ICD-9 in the US in October of 2015.
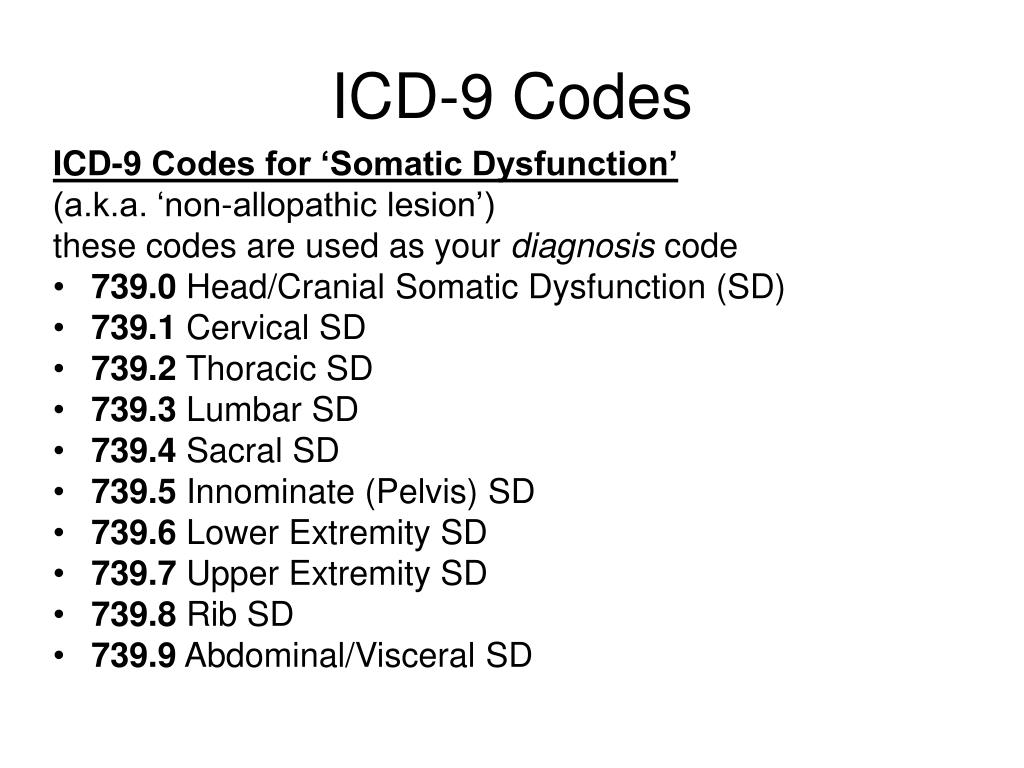
What is the ICD-9 code for diabetes mellitus?
250.0xTable 5ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes defining diabetesDescriptionICD-9-CM codeDiabetes mellitus without mention of complications250.0xDiabetes with ketoacidosis250.1xDiabetes with hyperosmolarity250.2xDiabetes with other coma250.3x8 more rows
What is the ICD-10 code for pre DM?
The ICD-10 code for prediabetes is R73. 09.
How do you code DM with hypertension?
If the provider has specifically documented that the hypertension was caused by the diabetes, then you would code the hypertension as a circulatory complication. Only the terms listed in the index under "diabetes with" should be coded as a complication with specific documentation linking them.
What is the ICD-10 code for each type of diabetes?
E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus. E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus. E13, Other specified diabetes mellitus.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.
Can you code hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia at the same time?
If the patient does have documented hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia in addition to the diagnosis of uncontrolled diabetes, ICD-10-CM codes would be used to show that the diabetes is with hyperglycemia and/or hypoglycemia.
Can diabetes be secondary to hypertension?
High blood pressure (hypertension) can lead to many complications of diabetes, including diabetic eye disease and kidney disease, or make them worse. Most people with diabetes will eventually have high blood pressure, along with other heart and circulation problems.
Can you code hypertension and pulmonary hypertension together?
Primary pulmonary hypertension — also called heritable PAH, idiopathic PAH, primary group 1 pulmonary hypertension, and primary PAH — is reported using I27....Note New Codes for Pulmonary Hypertension.New CodesDescriptionI27.22Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease Group 2 pulmonary hypertension5 more rows•Jan 2, 2018
What is DM and hypertension?
Abstract. Diabetes mellitus and hypertension are common diseases that coexist at a greater frequency than chance alone would predict. Hypertension in the diabetic individual markedly increases the risk and accelerates the course of cardiac disease, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, retinopathy, and nephropathy.
What is the ICD-10 for diabetes mellitus type 2?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Is diabetes mellitus type 1 or type 2?
The main difference between the type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that type 1 diabetes is a genetic condition that often shows up early in life, and type 2 is mainly lifestyle-related and develops over time. With type 1 diabetes, your immune system is attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas.
How do you code DM and CKD?
Q&A: Reporting diabetes, CKD, and HTN in ICD-10-CME11. 649, Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypoglycemia without coma.G93. 41, metabolic encephalopathy.E11. 22, Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic CKD.I12. 9, hypertensive CKD with stage 1 through 4 CKD, or unspecified CKD.N18. 2, CKD, stage 2 (mild)
What is the ICd 10 code?
The ICD-10-CM coding guidelines established by the National Center for Health Care (NCHC) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for ICD-10-CM assist healthcare professionals and medical coders in selecting the appropriate diagnosis codes to report for a specific patient encounter.
What is the code for gestational diabetes?
Codes for gestational diabetes are in subcategory O24.4. These codes include treatment modality — diet alone, oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin — so you do not need to use an additional code to specify medication management. Do not assign any other codes from category O24 with the O24.4 subcategory codes.
What is the default type of diabetes?
The guidelines state that if the type of diabetes is not documented, the default is type 2. The guidelines also instruct to use additional codes to identify long-term control with insulin (Z79.4) or oral hypoglycemic drugs (Z79.84). You would not assign these codes for short-term use of insulin or oral medications to bring down a patient’s blood ...
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
For gestational diabetes (diabetes that occurs during pregnancy) women should be assigned a code under the 024.4 subheading and not any other codes under the 024 category.
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
The “unspecified” codes can be used when not enough information is known to give a more specific diagnosis; in that case, “unspecified” is technically more accurate than a more specific but as yet unconfirmed diagnosis. For more guidelines on using ICD-10 codes for diabetes mellitus, you can consult this document.
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
If the type of diabetes that the patient has is not documented in the medical record, E11 codes for type 2 diabetes should be used as a default. If the medical record doesn’t say what type of diabetes the patient has but indicates that the patient uses insulin, the Type 2 diabetes codes should also be used.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 pcs code for diagnostic colonscopy for screening
- 2. icd 10 code for history of carpal tunnel syndrome unspecified
- 3. icd 9 code for soft tissue cellulitis
- 4. icd 10 code for laceration bilateral index finger
- 5. 2018 icd 10 code for cranioplasty
- 6. what icd 10 code would be used for vegetation on icd pacing wire
- 7. icd 10 code for high vitamin b12 level
- 8. icd 9 code for contusion thoracic
- 9. icd 10 code for degenerative changes left wrist
- 10. 2016 icd 10 code for pleural fluids benign.