530.82 Esophageal reflux (530.81) ICD-9 code 530.81 for Esophageal reflux is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISEASES OF ESOPHAGDUODENUM
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption.
What is the ICD 9 code for esophageal cancer?
2011 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 530.*. : Diseases of esophagus. A finding indicating the lack of adequate relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter resulting in difficulty swallowing food. A motility disorder of the esophagus in which the lower esophageal sphincter (near the cardia) fails to relax resulting in functional obstruction of the esophagus, and dysphagia.
What are the ICD-9-CM index entries for esophageal reflux?
ICD-9-CM 530.81 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 530.81 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal hernia?
Short description: Other dsrders esophagus. ICD-9-CM 530.89 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 530.89 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal bleeding?
ICD-9-CM 569.89 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 569.89 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
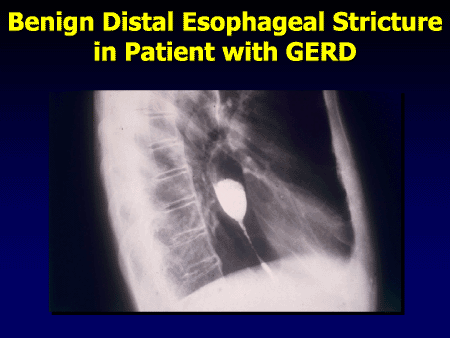
What is the ICD-10 code for esophageal wall thickening?
What is the code for a stricture of the esophagus?
What is the diagnosis code K22 8?
What is ICD-10 code for chronic inflammation of the esophagus?
What is the ICD-10 code for eosinophilic esophagitis?
What is the ICD-10 code for esophageal spasm?
What does thickening of the esophageal wall mean?
What does GE junction mean?
What K31 89?
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for esophagitis?
K20. 91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K20. 91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is inflammation of esophagus?
What is Grade A esophagitis?
What is the pathology of the esophagus?
Pathological processes in the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that carries food, liquids and saliva from your mouth to the stomach. You may not be aware of your esophagus until you swallow something too large, too hot or too cold. You may also become aware of it when something is wrong.
What is the esophagus?
Disorder of the esophagus, the portion of the digestive canal between the pharynx and stomach. Pathological processes in the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that carries food, liquids and saliva from your mouth to the stomach.
What is a non-neoplastic disorder?
Disorder of esophagus. Esophageal mass. Clinical Information. A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder that affects the esophagus. Representative examples of non-neoplastic disorders include esophagitis and esophageal ulcer. Representative examples of neoplastic disorders include carcinomas, lymphomas, and melanomas.
What is the most common problem with the esophagus?
The most common problem with the esophagus is gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). It happens when a band of muscle at the end of your esophagus does not close properly. This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. Over time, gerd can cause damage to the esophagus.
Can GERD cause heartburn?
This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. Over time, gerd can cause damage to the esophagus. Other problems include heartburn and cancer .treatment depends on the problem. Some get better with over-the-counter medicines or changes in diet.
What is the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach?
The esophagus is the tube that carries food, liquids and saliva from your mouth to the stomach. You may not be aware of your esophagus until you swallow something too large, too hot or too cold. You may also become aware of it when something is wrong.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hemorrhoids from pregnancy
- 2. icd 10 code for bleeding of the belly button
- 3. icd 10 code for unspecified fall broke eyeglasses
- 4. icd 10 code for right clavicle fracture in newborn
- 5. icd 10 code for preseptal cellulietis left lower lid
- 6. lumbar puncture to obtain cerebrospinal fluid for analysis icd-10 code
- 7. icd 10 code for rh negative in pregnancy
- 8. icd 10 code for non healing wound left knee
- 9. icd 10 code for prostatomegaly
- 10. icd code for adjustment disorder