How serious is fluid on the lungs?
Fluid on the lung sounds serious and it is. If the tiny air sacs inside the lungs become waterlogged, this produces pulmonary oedema, a frightening condition that causes severe breathing difficulties, coughing, anxiety and distress.
What can cause fluid in the lungs?
Lung infections. Bacterial infections of the lung, such as pneumonia, can cause sections of the lungs to swell and edema to develop in that area. Exposure to toxins. Inhaled toxins, including chlorine and ammonia, as well as toxins from your body (inhaled vomit) can cause fluid in the lungs.
What causes lungs to fill with fluid?
What Causes Lungs To Fill Up With Fluid?
- Heart problems: people suffering from heart attack, cardimyopathy and congestive heart failure are at a risk of developing pulmonary edema. ...
- When cardiac muscles are damaged, the oxygenated blood is not pumped out as it should be. ...
- Infections such as pneumonia, lung abscess can also give rise to fluid and pus in the lungs. ...
Why do lungs fill with fluid?
This condition, called pleural effusion, causes fluid to build up around the lungs, making it harder for the lung to fully expand and take in enough air. Low levels of oxygen in the blood: Lung cancer can decrease red blood cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs up to the heart and the rest of the body.

What is diagnosis code R09 89?
89 for Other specified symptoms and signs involving the circulatory and respiratory systems is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary venous congestion?
514 - Pulmonary congestion and hypostasis. ICD-10-CM.
How do you code pulmonary edema?
J81. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the diagnosis code for chest congestion?
R09. 8 Other specified symptoms and signs involving the circulatory and respiratory systems.
What is the ICD 10 code for fluid overload?
E87.70ICD-10 code E87. 70 for Fluid overload, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD 10 code for pleural effusion?
8 for Pleural effusion in other conditions classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary edema?
ICD-10 code J81. 0 for Acute pulmonary edema is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is an acute pulmonary edema?
Acute pulmonary oedema is a medical emergency which requires immediate management. 1. It is characterised by dyspnoea and hypoxia secondary to fluid accumulation in the lungs which impairs gas exchange and lung compliance.
Do you code pulmonary edema with CHF?
Whenever a patient has an acute episode of CHF, acute pulmonary edema is considered inherent in the exacerbation of CHF. Therefore, acute pulmonary edema that has a cardiogenic etiology is not coded separately.
What is the ICD 10 code for congestion of upper airway?
J39. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J39. 3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the CPT code for pneumonia?
The CPT code for PNEUMOVAX 23 is 90732. This CPT code is effective as of January 2017 as set forth in the Current Procedural Terminology 2017.
What causes chest congestion?
What Causes Chest Congestion? Chest congestion is caused when excess fluids (mucus and phlegm) accumulate in the lungs because the mucus membranes have gone into overproduction. They go into overproduction when bacteria or a virus irritates the membranes, causing inflammation.
Is interstitial edema the same as pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary interstitial edema represents a form of pulmonary edema resulting from pathological fluid buildup in the interstitial spaces due to increased hydrostatic driving pressure.
Why is there pulmonary edema in heart failure?
Pulmonary edema is often caused by congestive heart failure. When the heart is not able to pump efficiently, blood can back up into the veins that take blood through the lungs. As the pressure in these blood vessels increases, fluid is pushed into the air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs.
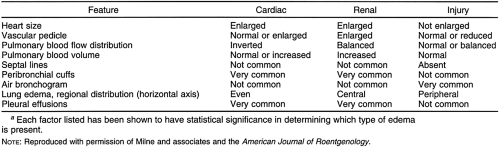
How would you describe pulmonary edema on CXR?
On CXR, there is increase in pulmonary parenchymal opacification with Kerley lines, peribronchial cuffing, enlarged pulmonary arteries, with a normal sized left ventricle, normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, enlarged pulmonary artery (PA), and right heart. Pleural and pericardial effusions are usually present.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 511.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 511.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity?
Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity resulting from excessive transudation or exudation from the pleural surfaces. It is a sign of disease and not a diagnosis in itself
Not Valid for Submission
518.4 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute edema of lung, unspecified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 518.4 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Edema means swelling caused by fluid in your body's tissues. It usually occurs in the feet, ankles and legs, but it can involve your entire body.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity?
Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity resulting from excessive transudation or exudation from the pleural surfaces. It is a sign of disease and not a diagnosis in itself.
What is a pleural disorder?
Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by an increase in amounts of fluid within the pleural cavity. Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough and marked chest discomfort. An abnormal collection of fluid between the thin layers of tissue (pleura) lining the lung and the wall of the chest cavity.
When will the ICD-10 J90 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What causes fluid to leak from the blood vessels to the lung tissues?
High-altitude pulmonary edema. In normal lungs, air sacs (alveoli) take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. In high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE), it's theorized that vessels in the lungs constrict, causing increased pressure. This causes fluid to leak from the blood vessels to the lung tissues and eventually into the air sacs.
Why does fluid build up in the lungs?
Most often, the fluid buildup in the lungs is due to a heart condition. If pulmonary edema is not heart related, it's called noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. Sometimes, pulmonary edema can be caused by both a heart problem and a non-heart problem.
What is cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is caused by increased pressures in the heart.
How long does it take for pulmonary edema to heal?
With treatment, most people with this type of pulmonary edema recover in about 24 hours.
Why is pulmonary edema so hard to breathe?
Overview. Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the numerous air sacs in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. In most cases, heart problems cause pulmonary edema. But fluid can collect in the lungs for other reasons, including pneumonia, exposure to certain toxins and medications, ...
How high can you travel to get pulmonary edema?
People who travel to high-altitude locations above 8,000 feet (about 2,400 meters) are more likely to develop high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE). It usually affects those who do not first become acclimated to the elevation (which can take from a few days to a week or so).
What are the symptoms of pulmonary edema?
Sudden (acute) pulmonary edema signs and symptoms. Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) or extreme shortness of breath that worsens with activity or when lying down. A feeling of suffocating or drowning that worsens when lying down. A cough that produces frothy sputum that may be tinged with blood.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right hip fracture status post orif
- 2. icd 10 code for pfapa syndrome
- 3. icd 10 cm code for tear foraminal annular
- 4. icd 10 code for gestational diabetes complicating childbirth
- 5. icd code for elevated psa
- 6. icd 10 code for face contusion
- 7. icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm first stage 4 tissue blocks
- 8. icd 10 pcs code for anal exam under anesthesia
- 9. icd 10 code for acute kidney insufficiency
- 10. icd 10 code for homelessness