Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What is the ICD 10 code for small bowel obstruction?
The ICD code K56 is used to code Bowel obstruction Bowel obstruction or intestinal obstruction is a mechanical or purposeful obstruction of the intestines, stopping the conventional transit of the merchandise of digestion. It may happen at any degree distal to the duodenum of the small gut and is a medical emergency.
What is the ICD 10 code for gastric bypass?
- 0D168Z4 - Bypass Stomach to Cutaneous, Endo
- 0D168Z9 - Bypass Stomach to Duodenum, Endo
- 0D168ZA - Bypass Stomach to Jejunum, Endo
- 0D168ZB - Bypass Stomach to Ileum, Endo
- 0D168ZL - Bypass Stomach to Transverse Colon, Endo
What is the ICD 10 code for HX of gastroparesis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Gastroparesis K31.84 ICD-10 code K31.84 for Gastroparesis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now.
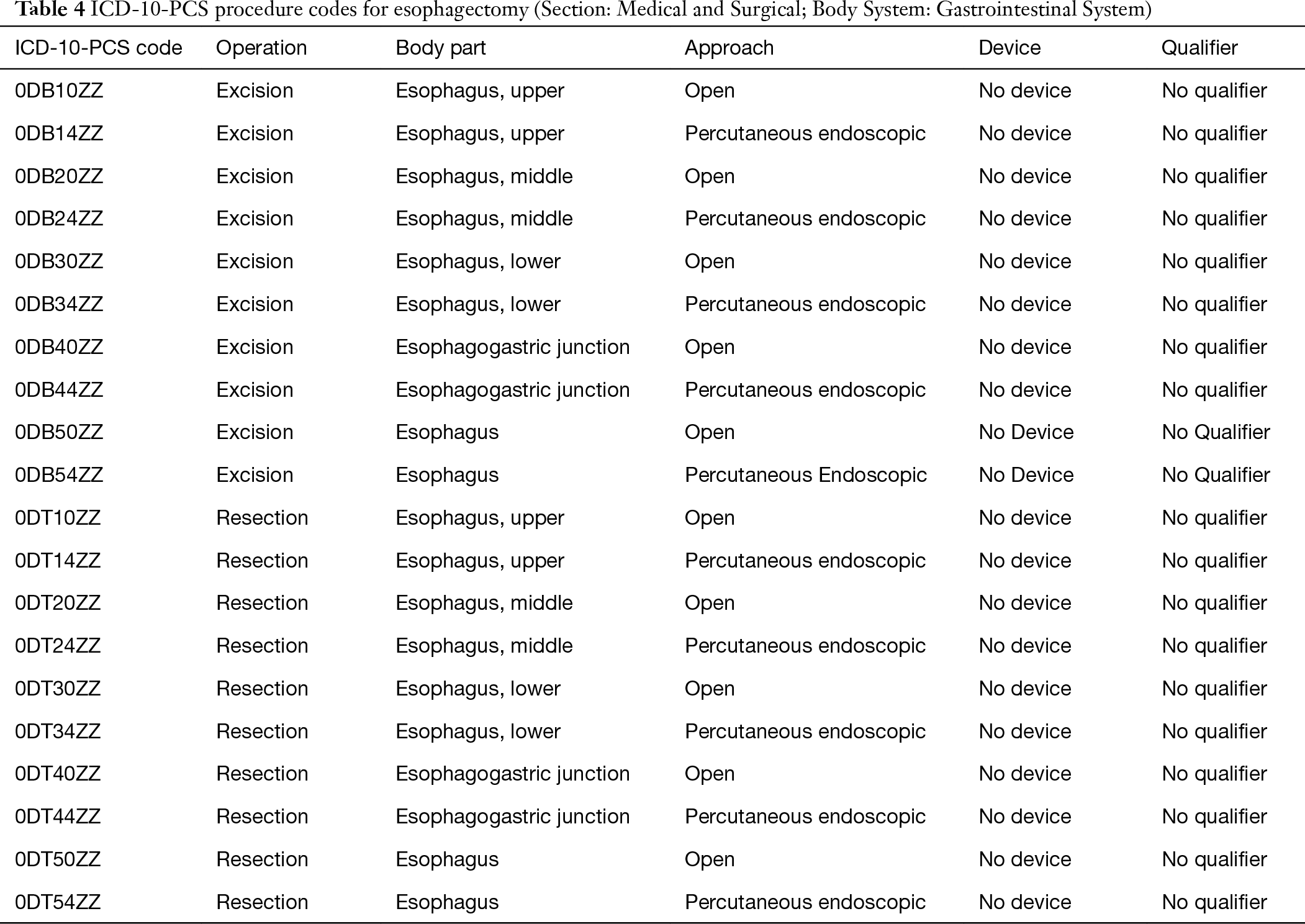
How do you code a gastric outlet obstruction?
Adult hypertrophic pyloric stenosis K31. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K31. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is pyloric stenosis the same as gastric outlet obstruction?
Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the pylorus, the opening from the stomach, into the small intestine. This type of blockage is also referred to as a gastric outlet obstruction. Normally, food passes easily from the stomach into the duodenum through a valve called the pylorus.
What is the gastric outlet?
Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO) is a clinical syndrome characterized by epigastric abdominal pain and postprandial vomiting due to mechanical obstruction. The term gastric outlet obstruction is a misnomer since many cases are not due to isolated gastric pathology, but rather involve duodenal or extraluminal disease.
Where is the gastric outlet located?
Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO) is a medical condition where there is an obstruction at the level of the pylorus, which is the outlet of the stomach.
Is gastroparesis the same as gastric outlet obstruction?
Gastroparesis is a medical condition characterized by delayed emptying of the stomach when there is no mechanical gastric outlet obstruction. Its cause is most commonly idiopathic, a diabetic complication or a result of abdominal surgery.
What is partial gastric outlet obstruction?
ABSTRACT. Gastric outlet obstruction is a common condition in which mechanical obstruction in the distal stomach, pylorus, or duodenum causes nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and early satiety.
What causes a gastric outlet obstruction?
Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO) is a result of any disease process that causes a mechanical impediment to gastric emptying. It can be caused by mechanical causes as well as motility disorders and typically is associated with abdominal pain, postprandial vomiting, early satiety, and weight loss.
What is malignant gastric outlet obstruction?
Malignant gastric outlet obstruction (MGOO) is a clinical condition characterized by the mechanical obstruction of the pylorus or the duodenum due to tumor compression/infiltration, with consequent reduction or impossibility of an adequate oral intake.
Do I have gastric outlet obstruction?
Nausea and vomiting are the cardinal symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction (GOO). Vomiting usually is described as nonbilious, and it characteristically contains undigested food particles. In the early stages of obstruction, vomiting may be intermittent and usually occurs within 1 hour of a meal.
What is functional outlet obstruction?
Functional outlet obstruction, part of the spectrum of functional constipation, is suspected when patients present with select symptoms. Diagnosis is commonly made with anorectal manometry, electromyography, and rectal evacuation tests.
What is the procedure for gastric outlet obstruction?
The operation usually performed is an antrectomy, the removal of the antral portion of the stomach. Other surgical approaches include: vagotomy, the severing of the vagus nerve, the Billroth I, a procedure which involves anastomosing the duodenum to the distal stomach, or a bilateral truncal vagotomy with gastrojejunostomy .
What is the pathophysiology of a peptic ulcer?
Pathophysiology. In a peptic ulcer it is believed to be a result of edema and scarring of the ulcer, followed by healing and fibrosis, which leads to obstruction of the gastroduodenal junction (usually an ulcer in the first part of the duodenum).
What is an X-ray of the abdomen?
X-ray of abdomen of a person with gastric outlet obstruction taken while on their side. There is a prominent gastric air bubble, gastric air-fluid level, and a dilated stomach with particulate matter within it. Specialty. General surgery, gastroenterology.
What is the procedure to remove the stomach?
The operation usually performed is an antrectomy , the removal of the antral portion of the stomach. Other surgical approaches include: vagotomy, the severing of the vagus nerve, the Billroth I, a procedure which involves anastomosing the duodenum to the distal stomach, or a bilateral truncal vagotomy with gastrojejunostomy .
What are the symptoms of peptic ulcers?
Signs and symptoms. The main symptom is vomiting , which typically occurs after meals, of undigested food devoid of any bile. A history of previous peptic ulcers and loss of weight is not uncommon. In advanced cases, signs to look for on physical examination are wasting and dehydration.
Can a pseudocyst cause gastric compression?
A pancreatic pseudocyst can cause gastric compression. Pyloric mucosal diaphragm could be a rare cause. Malignant. Tumours of the stomach, including adenocarcinoma (and its linitis plastica variant), lymphoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumours.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hypertension emergency
- 2. icd-10-cm code for olecranon bursitis of the elbow
- 3. icd-10 code for mesenteric neoplasm
- 4. icd 9 code for chronic care management
- 5. icd 10 code for anxiety disorder nos
- 6. icd 10 code for lung changes
- 7. what is the icd-10-pcs code for ruptured spleen
- 8. icd 10 code for tick bite left hip
- 9. icd 10 code for history of dm type 2 controlled
- 10. icd-10 code for traumatic soft tissue injury