What is the ICD 9 code for Guillain-Barre syndrome?
Icd 9- acute infective polineuritis. They are the codes used by doctors or hospitals to Bill your insurance for your Guillain-Barre Syndrome procedures.
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome and how is it treated?
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a condition where the immune system attacks part of the nervous system, resulting in progressive weakness throughout the body. These symptoms can quickly spread, eventually paralyzing your whole body. In its most severe form, Guillain-Barré syndrome is a medical emergency.
How does Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) cause weakness?
In most cases of GBS, the immune system damages the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons of many peripheral nerves; however, it also may also damage the axons themselves. As a result, the nerves cannot transmit signals efficiently and the muscles begin to lose their ability to respond to the brain's commands. This causes weakness.
Why is Guillain-Barré syndrome called an autoimmune disease?
Since the body’s own immune system does the damage, GBS is called an autoimmune disease (“auto” meaning “self”). Normally the immune system uses antibodies (molecules produced in an immune response) and special white blood cells to protect us by attacking infecting microorganisms (bacteria and viruses).
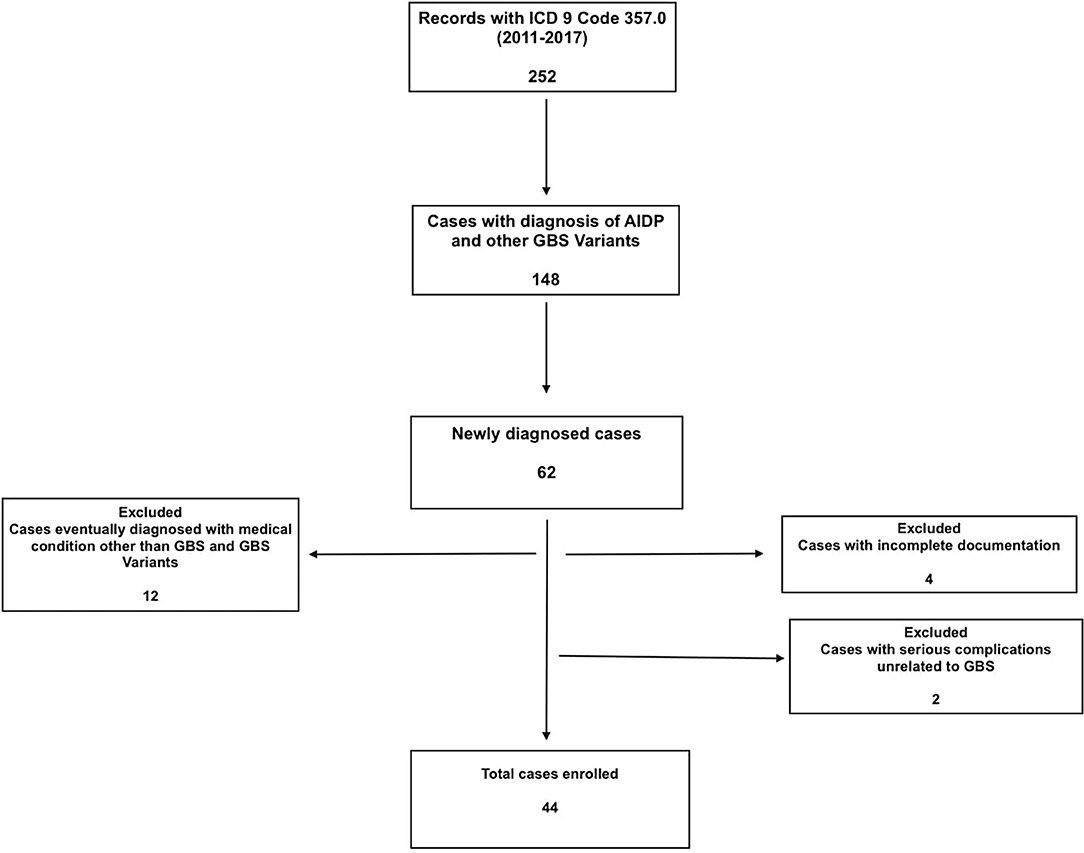
What is the ICD-10 code for Guillain-Barre?
ICD-10 code G61. 0 for Guillain-Barre syndrome is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is R68 89 diagnosis code?
ICD-10 code R68. 89 for Other general symptoms and signs is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Can Covid cause Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been shown to be associated with a lot of neurological complications, of whom Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) is an important post-infectious consequentiality.
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome Wikipedia?
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system.
Is R68 89 billable code?
R68. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R68. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Z00 01?
ICD-10 code Z00. 01 for Encounter for general adult medical examination with abnormal findings is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the most common cause of Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Infection with Campylobacter jejuni, which causes diarrhea, is one of the most common causes of GBS. About 1 in every 1,000 people with Campylobacter infection in the United States gets GBS.
Is Guillain Barré an autoimmune disease?
Since the body's own immune system does the damage, GBS is called an autoimmune disease (“auto” meaning “self”). Normally the immune system uses antibodies (molecules produced in an immune response) and special white blood cells to protect us by attacking infecting microorganisms (bacteria and viruses).
When does Guillain-Barré syndrome occur after Covid?
The development of neurological symptoms in a time interval after infection is the classical phenotype of GBS. In most cases, the onset of the neurological symptoms related to GBS was about 1 to 4 weeks after the diagnosis of COVID-19. However, in 2 cases, the symptoms coincided with the diagnosis.
What are the different types of Guillain-Barré syndrome?
There are three different forms of GBS: Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, which predominantly affects the myelin. The commonest form in America and Europe. Acute motor axonal neuropathy which affects the axons of the nerves going to the muscles.
What is GBS in medical term?
Key facts. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare condition in which a person's immune system attacks the peripheral nerves. People of all ages can be affected, but it is more common in adults and in males. Most people recover fully from even the most severe cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
ICD-10 Equivalent of 357.0
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use this equivalent ICD-10-CM code, which is an exact match to ICD-9 code 357.0:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 357.0
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What is the G65.0 code?
G65.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of sequelae of guillain-barre syndrome. The code G65.0 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the name of the disorder that attacks the peripheral nervous system?
Also called: Acute idiopathic polyneuritis, Acute inflammatory polyneuropathy, Infectious polyneuritis, Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome. Guillain-Barre syndrome is a rare disorder that causes your immune system to attack your peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS nerves connect your brain and spinal cord with the rest of your body.
What is Miller Fisher syndrome?
Miller Fisher syndrome, another type of Guillain-Barré syndrome, involves cranial nerves, which extend from the brain to various areas of the head and neck. Miller Fisher syndrome is characterized by three features: weakness or paralysis of the muscles that move the eyes (ophthalmoplegia), problems with balance and coordination (ataxia), and areflexia. People with this condition can have other signs and symptoms common in Guillain-Barré syndrome, such as muscle weakness.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gram negative bacteria infection
- 2. icd 10 code for osteochondral lesion of right knee
- 3. how to write a icd 10 code for
- 4. icd 10 code for urinary hesiatncy
- 5. icd 10 code for aparkinson's
- 6. icd 10 code for localized edema
- 7. icd 10 code for neuromuscular scoliosis with thoracic insufficiency syndrome
- 8. icd-9 code for osteopenia
- 9. 2019 icd 10 code for osteophyte at the talonavicular joint
- 10. icd 10 cm code for sprain, left elbow