Is pulmonary embolism a deadly disease?
Personal history of pulmonary embolism (V12.55) ICD-9 code V12.55 for Personal history of pulmonary embolism is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -PERSONS WITH POTENTIAL HEALTH HAZARDS RELATED TO PERSONAL AND FAMILY HISTORY (V10-V19). Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
Which findings suggest pulmonary embolism?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code V12.55 Personal history of pulmonary embolism Short description: Hx pulmonary embolism. ICD-9-CM V12.55 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, V12.55 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
Is autopsy a sure diagnosis of pulmonary embolism?
Billable Medical Code for Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 415.1. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 415.1. This excludes chronic pulmonary embolism (416.2), personal history of pulmonary embolism (V12.55), that complicating: abortion (634-638 with.6, 639.6), ectopic or …
Would death from a pulmonary embolism be quick?
Not Valid for Submission. V12.55 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of personal history of pulmonary embolism. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent. ICD-9: V12.55. Short Description:
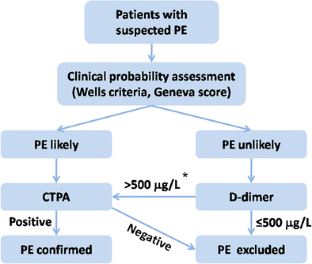
How do you code a history of a pulmonary embolism?
711.
What is the ICD-9 code for pulmonary embolism?
ICD-9 code 415.1 for Pulmonary embolism and infarction is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISEASES OF PULMONARY CIRCULATION (415-417).
What is the ICD-10 code for history of pulmonary embolism?
Personal history of pulmonary embolism Z86. 711 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary embolism 2021?
Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale 9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I26.
What is the ICD 9 code for primary pulmonary hypertension?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 416.0 : Primary pulmonary hypertension.
What is the ICD-9-CM code for hyponatremia?
ICD-9-CM 276.1 converts directly to: 2022 ICD-10-CM E87. 1 Hypo-osmolality and hyponatremia.
What's the ICD-10-CM code for acute pulmonary embolism PE?
Pulmonary embolism ICD-10-CM I26. 09 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 175 Pulmonary embolism with mcc or acute cor pulmonale.
What is ICD-10 diagnosis code for personal history of DVT?
Z86.712022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z86. 71: Personal history of venous thrombosis and embolism.
What is the ICD-10 code for personal history of blood clots?
ICD-10-CM Code for Personal history of venous thrombosis and embolism Z86. 71.
What is the CPT code for pulmonary embolism?
Basics about CTA (CPT code 71275) for Pulmonary Embolism Treatment. Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) is performed to find any diagnosis present in blood vessels (angio).Feb 5, 2022
What is the ICD-10 code for segmental pulmonary embolism?
Single subsegmental pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale. I26. 93 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is Subsegmental pulmonary embolism?
Subsegmental pulmonary embolism (SSPE) affects the 4th division and more distal pulmonary arterial branches. SSPE can be isolated or affect multiple subsegments, be symptomatic or incidental (unsuspected) and may or may not be associated with deep vein thrombosis.Feb 20, 2019
What is the ICd 10 code for pulmonary embolism?
V12.55 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of personal history of pulmonary embolism. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Information for Patients. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause.
How to tell if you have a blood clot on your leg?
Symptoms of a blood clot include warmth, swelling, pain, tenderness and redness of the leg. The goal of treatment is to break up clots and help keep other clots from forming. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Coughing up blood.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
What is a code note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. Code first - Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.
What does excludes2 mean?
An excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition represented by the code, but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code, it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together, when appropriate.
What is the 7th character in a code?
The 7th character must always be the 7th character in the data field. If a code that requires a 7th character is not 6 characters, a placeholder X must be used to fill in the empty characters.
What is the treatment for pulmonary hypertension?
Medical treatment is initiated based on disease severity and symptomatology but generally includes anticoagulant therapy. For more symptomatic pulmonary hypertension secondary to chronic thromboembolic disease, patients may be placed on sildenafil (Viagra) for arterial dilation.
Where is DVT found?
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot develops in a deep vein. Typically located in the legs and thighs, DVT can be found anywhere in the body and occurs when the blood thickens and clumps together. Deep veins are found within groups of muscles and superficial veins are located close to the skin.
Where are deep veins located?
Deep veins are found within groups of muscles and superficial veins are located close to the skin. If a blood clot develops in a deep vein, it may be serious because it can break loose and travel to the lungs—a condition called pulmonary embolism (PE).
Why do you need an inferior vena cava filter?
An inferior vena cava filter may be placed in patients who cannot tolerate anticoagulation therapy or are at high risk of developing further clots due to underlying medical conditions. In rare cases and usually with larger emboli, surgery will sometimes be needed.
What is the best treatment for clots?
Additionally, anticoagulant therapy is used to prevent the formation of more clots and allows the body to reabsorb the existing clots faster. Anticoagulation typically involves IV heparin, along with oral warfarin (Coumadin). Subcutaneous low-molecular weight heparin (Lovenox) may be substituted for intravenous heparin.
What is a Greenfield filter?
The Greenfield filter may be inserted for acute, chronic, recurrent DVT or the susceptibility for recurrence. The physician is responsible for providing the acuity of the condition. There are no specific guidelines for when DVT is considered chronic. The code assignment for chronic DVT is based solely on physician documentation.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for reactive airway disease unspecified
- 2. icd 10 code for patella femoral strain
- 3. icd 10 cm code for patient is currently status post right total hip replacement 1 year ago
- 4. icd-10-cm code for facial hair growth women
- 5. icd 10 code for acute right cerebellar
- 6. 2017 icd 10 diagnosis code for chronic diastolic heart failure
- 7. icd 10 code for intentional self harm stabbing sharp object
- 8. icd 10 code for tearfulness
- 9. icd 9 code for pancreatic adenoma
- 10. icd 10 code for ribs sprain/strain