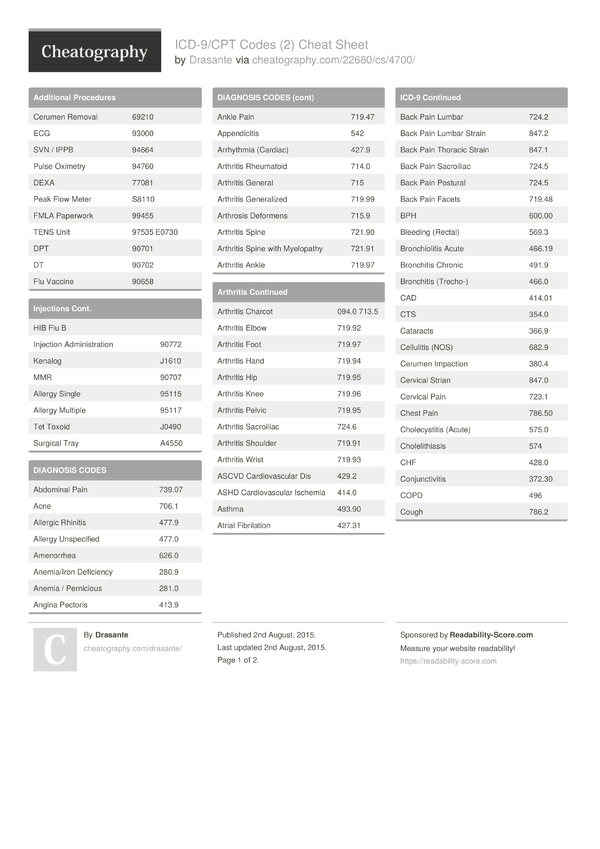
| Condition:1 | Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria syndrome |
|---|---|
| Category:2 | Other |
| SNOMED CT Code:3 | 30287008—Hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria syndrome UMLS CUI:4C0268540 |
| ICD-9-CM Code:5 | 270.6—Disorders of urea cycle metabolism |
| ICD-10-CM Code:6 | E72.4—Disorders of ornithine metabolism |
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperammonemia?
Disorder of urea cycle metabolism, unspecified Disorder of the urea cycle metabolism; Disorder of urea cycle metabolism; Hyperammonemia; hyperammonemia-hyperornithinemia-homocitrullinemia syndrome E72.4; transient hyperammonemia of newborn (P74.6); Hyperammonemia ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E72.29 [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 270.6 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 270.6 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What are the risk factors for hyperammonemia due to neonatal onset disorders?
Survivors of the neonatal onset and childhood/adult onset disorders share common risks for encephalopathies, metabolic, inborn; and respiratory alkalosis due to hyperammonemia. ICD-10-CM E72.20 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 642 Inborn and other disorders of metabolism Convert E72.20 to ICD-9-CM
What is the differential diagnosis of hyperammonemia?
Differential Diagnosis Hyperammonemia is itself a condition that may result from a multitude of disorders, as described above. Laboratory and radiological investigations should be done to rule out CNS diseases with clinical findings resembling those seen in hyperammonemia.
How do you code hyperammonemia?
hyperammonemia-hyperornithinemia-homocitrullinemia syndrome. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E72.4. Disorders of ornithine metabolism. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ... transient hyperammonemia of newborn ( ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P74.6. Transitory hyperammonemia of newborn.
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperammonemia?
E72. 20 - Disorder of urea cycle metabolism, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What diagnosis covers ammonia level?
If your results show high ammonia levels in the blood, it may be a sign of one of the following conditions: Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis. Hepatic encephalopathy. Kidney disease or kidney failure.
What enzyme is deficient in hyperammonemia?
Hyperammonemia is mild in arginase deficiency, and the associated neuronal damage is due to elevated levels of arginine. Other enzymatic defects causing hyperammonemia are associated with additional metabolic abnormalities. Ketosis and acidosis are associated with organic acidemias such as isovaleric acidemia.
What is high ammonia level called?
After being produced, ammonia is normally removed from the body by the liver and kidneys. Ammonia testing is typically ordered to diagnose and monitor elevated ammonia levels, also known as hyperammonemia. In adults, high ammonia levels are usually the result of liver damage that causes poor liver function.
What can cause hyperammonemia?
Hyperammonemia is due to defect in detoxification or overproduction of ammonia. Defects in the urea cycle lead to the most severe hyperammonemia. Other causes of hyperammonemia include various metabolic defects such as certain organic acidurias, fatty acid oxidation defects, drugs and liver disease.
What are the types of hyperammonemia?
Specific types Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 606762 - hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome (glutamate dehydrogenase 1) Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 238970 - hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute metabolic encephalopathy?
ICD-10 code G93. 41 for Metabolic encephalopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
How is hyperammonemia treated?
Rifaximin has become the most effective antibiotic of choice in the treatment of hyperammonemia because of its safety, efficacy, and tolerability [62]. Rifaximin is a nonsystemic, GI site-specific antibiotic as a result of the addition of a nonabsorbable pyridoimidazole ring.
What is hyperammonemia syndrome?
The hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia (HI/HA) syndrome is a form of congenital hyperinsulinism in which affected children have recurrent symptomatic hypoglycemia together with asymptomatic, persistent elevations of plasma ammonium levels.
What happens during hyperammonemia?
In most hyperammonemic episodes, patients may present with a loss of appetite, vomiting, lethargy, and behavior abnormalities associated with hallucinations, sleep disorders, ataxia, and even seizures. These episodes are usually related to periods of high protein intake, systemic infection, or catabolic stress.
Is hyperammonemia a symptom of hepatic encephalopathy?
Minimal hepatic encephalopathy is most likely the result of hyperammonemia. Elevated ammonia levels are detected in most patients. Similarly, the subtle neurological changes of minimal hepatic encephalopathy can be improved by the administration of lactulose.
What is the most common cause of hyperammonemia in children?
An acquired disease-causing hyperammonemia in children is Reye syndrome, a childhood disorder that occurs most commonly after influenza or varicella infection and ingestion of aspirin. Hyperammonemia is coupled with elevated liver enzymes and lactic acidosis. Hepatomegaly is usually seen on examination. Liver Disease.
How many live births are there in the United States with hyperammonemia?
A gross estimate on the incidence of urea cycle disorders is 1 in 250,000 live births in the United States and 1 in 440,000 live births internationally. [11] Pathophysiology.
What is the term for elevated ammonia levels?
Hyperammonemia is a metabolic condition characterized by raised levels of ammonia, a nitrogen-containing compound. Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin. Hyperammonemia most commonly presents with neurological signs and symptoms that may be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying abnormality.
What is the name of the condition where ammonia is elevated?
Hyperammonemia - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Hyperammonemia is a metabolic condition characterized by the raised levels of ammonia, a nitrogen-containing compound. Normal levels of ammonia in the body vary according to age. Hyperammonemia can result from various congenital and acquired conditions in which it may be the principal toxin.
Why does ammonia rise in the liver?
Ammonia levels rise if the liver is unable to metabolize this toxic compound as a result of an enzymatic defect or hepatocellular damage. ...
How long does it take for argininosuccinate to cause hyperammonemia?
Defects in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) and argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS) result in hyperammonemia that presents in the first 24 to 48 hours of life. Hyperammonemia is mild in arginase deficiency, and the associated neuronal damage is due to elevated levels of arginine.
Which organs are affected by ammonia?
Skeletal muscle: Amino acid transamination and the purine-nucleotide cycle. Abnormalities in the urea cycle or liver disorders may lead to increased levels of ammonia, which is then transported to the brain, skeletal muscle, and kidneys for elimination.
What is an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the deficiency of one of the enzymes necessary for
Clinical Information. A genetic inborn error of metabolism characterized by the deficiency of one of the enzymes necessary for the urea cycle. It results in accumulation of ammonia in the body. A laboratory test result indicating increased levels of ammonia in the blood. Elevated level of ammonia in the blood.
What is elevated ammonia?
Elevated level of ammonia in the blood. It is a sign of defective catabolism of amino acids or ammonia to urea. Inherited errors in the metabolic reactions occurring in the liver that convert ammonia to urea, resulting from inborn genetic mutations. Rare congenital metabolism disorders of the urea cycle.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E72.20. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for screening ovarian cancer
- 2. icd 10 code for foraminal stensosis of cervical
- 3. icd 10 code for neurogenic bladder with chronic foley catheter
- 4. icd-10 code for uvj stone with hydronephrosis
- 5. icd-10 code for side effect of covid vaccine
- 6. icd 10 code for cyclothymia
- 7. what is the icd-10 code for annual wellness visit
- 8. icd 9 code for positive rheumatoid factor
- 9. find icd 10 code for pernicious anemia
- 10. icd 10 code for homicidal ideation