Hyperinsulinism (functional) E16.1 ectopic E16.1 therapeutic misadventure T38.3 (from administration of insulin)
What is the ICD-10-CM diagnosis code for hyperinsulinemia?
Harris' (organic hyperinsulinism) 251.1. hypoglycemic (familial) (neonatal) 251.2. functional 251.1. 251.0. ICD9Data.com. 251.2. ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 251.1 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
What is the ICD 9 code for hypoglycemia?
6 result found: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E16.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Other hypoglycemia. Hyperinsulinism; Hyperinsulinism, iatrogenic; Hyperplasia of pancreatic islet beta cell; Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), reactive; Iatrogenic hyperinsulinism; Reactive hypoglycemia; diabetes with hypoglycemia (E08.649, E10.649, E11.649, E13.649); hypoglycemia in infant of …
What is hyperinsulinemia?
Harris' (organic hyperinsulinism) 251.1. hypoglycemic (familial) (neonatal) 251.2. functional 251.1. 251.0. ICD9Data.com. 251.2. ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 251.1 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD 9 Codes. A federal government website managed and paid for by the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 7500 Security Boulevard, Baltimore, MD 21244.
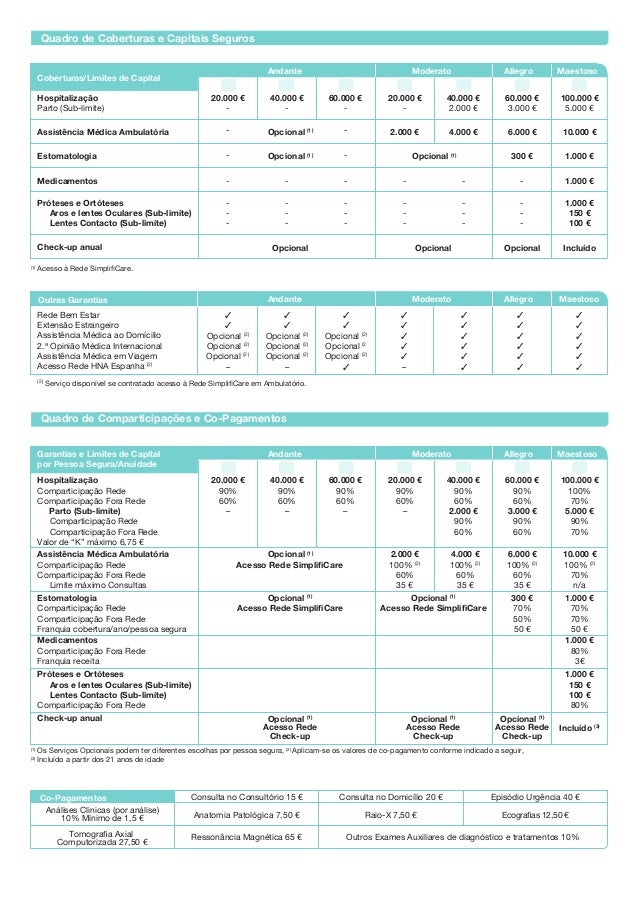
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperinsulinemia?
E16. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is hyperinsulinemia associated with hypoglycemia?
How is Hyperinsulinism diagnosed?
What is the ICD-10 code for insulin?
Is hyperinsulinemia the same as insulin resistance?
What is the difference between hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance?
What is transient hyperinsulinemia?
What is postprandial hyperinsulinemia?
What is compensatory hyperinsulinemia?
What is the ICD-10 code for pure hypercholesterolemia?
What is the ICD-10 code for acute bronchitis?
What are the codes for acute prostatitis resulting from streptococcus?
Is hyperinsulinemia a disease?
While it is often mistaken for diabetes or hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinemia can result from a variety of metabolic diseases and conditions, as well as non-nutritive sugars in the diet. While hyperinsulinemia is often seen in people with early stage type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is not the cause of the condition and is only one symptom of the disease.
Is hyperinsulinemia a liver condition?
Adipocytes will generate triglycerides in the presence of insulin but refers to a liver condition rather than a pancreatic one.
Is hyperinsulinemia a symptom of diabetes mellitus?
While hyperinsulinemia is often seen in people with early stage type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is not the cause of the condition and is only one symptom of the disease. Type 1 diabetes only occurs when pancreatic beta-cell function is impaired. Hyperinsulinemia can be seen in a variety of conditions including diabetes mellitus type 2, ...
Is hyperinsulinemia a metabolic syndrome?
These conditions are collectively known as Metabolic syndrome. This close association between hyperinsulinemia and conditions of metabolic syndrome suggest related or common mechanisms of pathogenicity. Hyperinsulinemia has been shown to "play a role in obese hypertension by increasing renal sodium retention".
Why does hyperinsulinemia occur in neonates?
Hyperinsulinemia in neonates can be the result of a variety of environmental and genetic factors. If the mother of the infant is a diabetic and does not properly control her blood glucose levels, the hyperglycemic maternal blood can create a hyperglycemic environment in the fetus.
How long does it take for hyperinsulinemia to subside?
The hyperinsulinemia condition subsides after one to two days.
Does adipose tissue cause hyperinsulinemia?
On the other hand, adipose tissue is known to secrete various metabolites, hormones and cytokines that may play a role in causing hyperinsulinemia. Specifically cytokines secreted by adipose tissue directly affect the insulin signalling cascade, and thus insulin secretion.
What are the causes of hyperinsulinism?
Congenital hyperinsulinism is caused by mutations in at least 11 different genes, including ABCC8 (responsible for about 45 % of the cases), KCNJ11, GLUD1, GCK, HK1, HADH , HNF4A, HNF1A, SLC16A1, UCP2, and PGM1. Inheritance may be autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant. [1] [4] Some cases are caused by loss of genetic material in a region ...
What is the name of the disease where the beta cells produce insulin?
Listen. Congenital hyperinsulinism is a disease where there are abnormally high levels of insulin, a hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancrea s that helps control blood sugar levels. Because of the high levels of insulin, people with this disease have frequent episodes of low blood sugar ( hypoglycemia) that can even occur after eating.
What is the best treatment for hypoglycemia?
Medications may include diazoxide, octreotide, and glucagon. [5] . Surgery to remove part of the pancreas might be required in severe cases. [3] [4] Genetic testing may help to guide the best treatment. [4]
What are the complications of low blood sugar?
Repeated episodes of low blood sugar increase the risk for serious complications such as breathing difficulties, seizures, intellectual disability, vision loss, brain damage, and coma.
What is a syndrome of abnormally low blood glucose level?
HYPOGLYCEMIA- . a syndrome of abnormally low blood glucose level. clinical hypoglycemia has diverse etiologies. severe hypoglycemia eventually lead to glucose deprivation of the central nervous system resulting in hunger; sweating; paresthesia; impaired mental function; seizures; coma; and even death.
What is the term for a low blood glucose level?
HYPOGLYCEMIA- . a syndrome of abnormally low blood glucose level. clinical hypoglycemia has diverse etiologies. severe hypoglycemia eventually lead to glucose deprivation of the central nervous system resulting in hunger; sweating; paresthesia; impaired mental function; seizures; coma; and even death.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is low?
Hypoglycemia means low blood glucose, or blood sugar. Your body needs glucose to have enough energy. After you eat, your blood absorbs glucose. If you eat more sugar than your body needs, your muscles, and liver store the extra. When your blood sugar begins to fall, a hormone tells your liver to release glucose.
What is the condition that causes high blood sugar levels?
Congenital hyperinsulinism Congenital hyperinsulinism is a condition that causes individuals to have abnormally high levels of insulin, which is a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels. People with this condition have frequent episodes of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!". An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 09 code for rotator cuff with stiffness
- 2. icd 10 cm code for left arm pain
- 3. icd 10 code for acetabular labral tear
- 4. icd 10 code for acute exacerbation of diastolic heart failure
- 5. cpt icd 10 code for prinzmetal angina
- 6. icd 9 code for morbidly obese
- 7. icd 10 pcs code for mri brain
- 8. icd 10 code for skin tear left lower leg
- 9. icd 10 code for genetic sutibility
- 10. icd-10 code for medical conultation