What is hypophosphatemic rickets?
Hypophosphatemic rickets (previously called vitamin D-resistant rickets) is a disorder in which the bones become painfully soft and bend easily, due to low levels of phosphate in the blood. [1] Symptoms usually begin in early childhood and can range in severity.
What is the ICD 10 code for rickets?
Rickets, active. E55.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E55.0 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E55.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 E55.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypophosphatemia?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to E83.31: Disorder (of) - see also Disease metabolism NOS E88.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E88.9 Hypophosphatemia, hypophosphatasia (acquired) (congenital) (renal) E83.39 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E83.39 Osteomalacia M83.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M83.9
What is the ICD 9 code for phosphorus metabolism?
Disorders of phosphorus metabolism Short description: Dis phosphorus metabol. ICD-9-CM 275.3 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 275.3 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
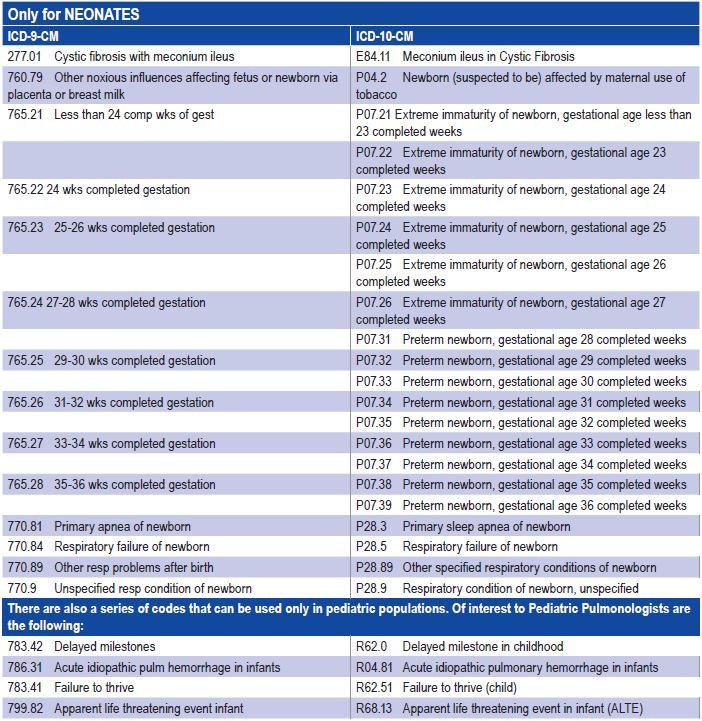
What is the ICD 10 code for Hypophosphatemia?
E83. 31 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E83.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypomagnesemia?
ICD-10 code E83. 42 for Hypomagnesemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What ICD 10 covers phosphorus?
39.
What is hypomagnesemia?
Magnesium deficiency is a condition in which the amount of magnesium in the blood is lower than normal. The medical name of this condition is hypomagnesemia.
What diagnosis code will cover magnesium?
Disorders of magnesium metabolism, unspecified E83. 40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E83. 40 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does Hypophosphatemia mean?
Hypophosphatemia is defined as an adult serum phosphate level of fewer than 2.5 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The normal level of serum phosphate in children is considerably higher and 7 mg/dL for infants. Hypophosphatemia is a relatively common laboratory abnormality and is often an incidental finding.
What is hyperphosphatemia?
Hyperphosphatemia—that is, abnormally high serum phosphate levels—can result from increased phosphate intake, decreased phosphate excretion, or a disorder that shifts intracellular phosphate to extracellular space.
What is familial hypophosphatemia?
Familial hypophosphatemia is a term that describes a group of rare inherited disorders characterized by impaired kidney conservation of phosphate and in some cases, altered vitamin D metabolism.
What genes are involved in rickets?
Other genes that can be responsible for the condition include the CLCN5, DMP1, ENPP1, FGF23, and SLC34A3 genes. [2] The genes associated with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets are involved in keeping a proper balance of phosphate in the body.
What is the genetic cause of rickets?
Most commonly hypophosphatemic rickets is due to changes in the PHEX gene and inherited in an X-linked dominant manner ( X-linked hypophosphatemia ). Less commonly it is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner (often called Dent disease );
How do you know if you have rickets?
The symptoms of hypophosphatemic rickets usually begin in infancy or early childhood. Specific symptoms and severity can vary greatly among affected children. The condition can be so mild that there are no noticeable symptoms, or so severe that it causes bowing of the legs and other bone deformities; bone pain; joint pain; and short stature. Other symptoms may include premature closure of the skull bones in babies ( craniosynostosis ); limited joint movement; and dental abnormalities. [1] [2] If left untreated, symptoms worsen over time. [2]
What causes rickets to bend?
Hypophosphatemic rickets (previously called vitamin D-resistant rickets) is a disorder in which the bones become painfully soft and bend easily, due to low levels of phosphate in the blood. [1] Symptoms usually begin in early childhood and can range in severity. Severe forms may cause bowing of the legs and other bone deformities; bone pain; joint pain; poor bone growth; and short stature. In some affected babies, the space between the skull bones closes too soon ( craniosynostosis ). This sometimes results in developmental abnormalities. [1]
What is a patient registry?
Patient Registry. A registry supports research by collecting of information about patients that share something in common, such as being diagnosed with Hypophosphatemic rickets. The type of data collected can vary from registry to registry and is based on the goals and purpose of that registry.
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
What is the function of genes that regulate the production of phosphate?
Many of these genes directly or indirectly regulate a protein that normally inhibits the kidneys' ability to reabsorb phosphate into the blood. Mutations affecting the function of these genes increase the production (or reduce the breakdown) of the protein, causing the protein to be overactive.
How do you know if you have rickets?
The symptoms of hypophosphatemic rickets usually begin in infancy or early childhood. Specific symptoms and severity can vary greatly among affected children. The condition can be so mild that there are no noticeable symptoms, or so severe that it causes bowing of the legs and other bone deformities; bone pain; joint pain; and short stature. Other symptoms may include premature closure of the skull bones in babies ( craniosynostosis ); limited joint movement; and dental abnormalities. [1] [2] If left untreated, symptoms worsen over time. [2]
What is a ricket?
Hypophosphatemic rickets (previously called vitamin D-resistant rickets) is a disorder in which the bones become painfully soft and bend easily, due to low levels of phosphate in the blood. [1] Symptoms usually begin in early childhood and can range in severity. Severe forms may cause bowing of the legs and other bone deformities; bone pain; joint pain; poor bone growth; and short stature. In some affected babies, the space between the skull bones closes too soon ( craniosynostosis ). This sometimes results in developmental abnormalities. [1]
Is hypophosphatemic rickets inherited?
Hypophosphatemic rickets is most often inherited in an X-linked dominant manner. This means that the gene responsible for the condition is located on the X chromosome, and having only one mutated copy of the gene is enough to cause the condition.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for female
- 2. icd 10 code for aggressive behavior
- 3. icd 10 code for purhenon end stage denutz
- 4. icd 10 code for anterior dislocation left shoulder.
- 5. icd 9 code for alcohol abuse
- 6. icd 10 code for right shoulder bankart tear
- 7. icd 10 code for renal mass unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for anteroseptal infarct
- 9. icd-10 code for skin fissure 4th right toe
- 10. icd 10 code for chronic serous right otitis media