M76.31 is a billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of iliotibial band syndrome, right leg. The code is valid for the year 2020 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Full Answer
How to get rid of iliotibial band syndrome?
Iliotibial Band Syndrome ICD 9 Code Billable Medical Code for Other Disorders of Muscle, Ligament, and Fascia Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 728.89 Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 728.89. Also Known As Atherosclerotic ischemic ulcer Abnormally decreased muscle contraction, Atheroscl
What are the best treatments for iliotibial band syndrome?
Standard of Care: Iliotibial Band Syndrome ICD 9 Codes: 726.69 (enthesopathy of knee NOS) Secondary diagnoses may be added as applicable: 719.46 (knee pain), 719.45 (pelvic/ thigh
What is an iliotibial band?
Oct 01, 2021 · Iliotibial band syndrome, left leg. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. M76.32 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.32 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How to pronounce iliotibial band syndrome?
Short description: Muscle/ligament dis NEC. ICD-9-CM 728.89 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 728.89 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for iliotibial band?
ICD-10 code: M76. 3 Iliotibial band syndrome - gesund.bund.de.
What is iliotibial band pain syndrome?
Iliotibial band syndrome is where a tendon called the iliotibial band gets irritated or swollen from rubbing against your hip or knee bones. The tendon is on the outside of your leg, and it goes from the top of your pelvic bone down to your knee. It rubs against your bones when it gets too tense (tight).Oct 19, 2021
What is the iliotibial band and where is it located?
Your iliotibial band is a strong, thick band of tissue that runs down the outside of your thigh. It extends all the way from your hip bones to the top of your shinbone. When you bend and extend your leg, this band moves over the outer lower edge of your thighbone.
How is iliotibial band diagnosed?
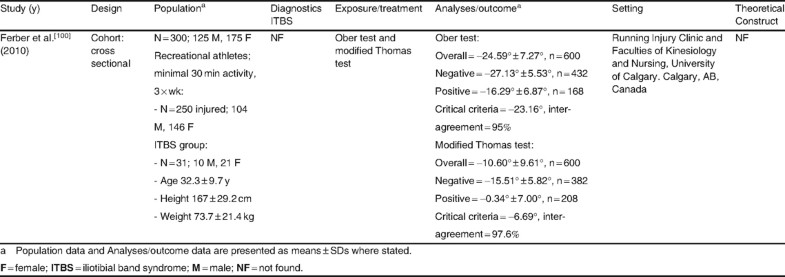
The Ober test is the most common physical test given to patients with suspected IT band pain. The Ober test requires the patient to lie on his or her side, with the affected side facing up. The doctor supports and guides the affected leg backwards, towards the patient's rear, and gently drops it down towards the table.
WHAT DOES IT band stand for?
The IT band stands for Ilio-tibial Band and is the longest tendon in the body. It originates out of a hip flexor muscle called TFL (Tensor Fascia Latae) at the Iliac Crest (pelvic bone) and attaches down at the outside of the tibia (shin bone).Nov 1, 2019
How do you treat iliotibial band syndrome?
Treatmentsresting and avoiding activities that aggravate the IT band.applying ice to the IT band.massaging the area.taking anti-inflammatory medications, which are often available over the counter.receiving ultrasounds and electrotherapies to reduce tension.undergoing physical therapy.
Where does iliotibial band get its name?
It originates at the anterolateral iliac tubercle portion of the external lip of the iliac crest and inserts at the lateral condyle of the tibia at Gerdy's tubercle....Iliotibial tractFMA51048Anatomical terminology8 more rows
Where does the iliotibial band attach?
The ITB is generally viewed as a band of dense fibrous connective tissue that passes over the lateral femoral epicondyle and attaches to Gerdy's tubercle on the anterolateral aspect of the tibia.
What connects to the IT band?
The gluteal or buttock muscle fibers and the tensor fascia latae (muscles of the hip joint) attach to it, and the band acts to coordinate muscle function and stabilize the knee during running. Iliotibial band syndrome describes the pain caused by inflammation of the band as it crosses the lateral femoral epicondyle.
What is a positive Ober test?
The examiner must continue to stabilize at the hip to ensure there is no movement. The test result is positive if the patient is unable to adduct the leg parallel to the table in a neutral position.
Is it IT band syndrome or something else?
Iliotibial band syndrome (also known as: IT band syndrome, ITB syndrome, or ITBS) is one of the most common overuse injuries among runners. It occurs when the iliotibial band—a thick band of connective tissue that runs from the outside of your hip to the outside of the knee—is tight or inflamed.Oct 7, 2021
Will an MRI SHOW IT band syndrome?
IT band syndrome is diagnosed after a physical examination and review of symptoms. An MRI scan may be performed to confirm a diagnosis of this condition, as MRI images may show a thickening of the band, which is often the cause of irritation.
What is the iliotibial band?
Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome is the second most common knee injury next to patellofemoral pain syndrome1 and is considered an overuse injury often associated with lateral knee pain, lateral femoral condyle pain, hip pain or lateral thigh pain. Typically, a patient with ITB syndrome has more pain when the knee is flexed to 30 degrees than with full knee extension or knee flexion.2 ITB syndrome was initially considered to be a result of constant friction of the ITB during knee flexion and extension over the lateral femoral condyle as would occur with running3 or cycling2. More recently, it has been suggested that ITB symptoms may develop more from the compression of the fat and connective tissue between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle or from imbalances of the hip musculature.4 Other authors5, 6 propose that ITB syndrome may be related to strain rate as opposed to the degree of strain. Strain is the change in length during running divided by resting length, while strain rate is the change in strain divided by time.5, 6 Further, evidence based on MRI demonstrates chronic inflammation and pathological changes between the distal ITB and the lateral femoral condyle7 although there is no evidence of an actual inflamed lateral bursa.2, 8 These newer findings challenge the medical management and physical therapy interventions for ITB syndrome.
What are the causes of ITB syndrome?
Strength, endurance, flexibility and coordination of the muscles and structures at the hip can be contributing factors of ITB syndrome. The TFL can be tight and strong leading to increased hip flexion in stance and internal rotation at the hip. The gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles can be lengthened and weak. The combination of these two factors can lead to a postural pattern with a Trendelenberg sign or compensated Trendelenberg sign. Poor muscle control at the hip additionally causes increased hip adduction and knee varus or valgus placing added strain to the ITB tissues.6 It is not clearly understood if hip abductor weakness is the direct cause of ITB syndrome or if the timing/performance of the hip abductor muscles affects the amount of hip adduction during the stance phase of gait leading to a strain of the tissues.14 A study by Fredericson et al,9 demonstrated significant decreases in gluteus medius muscle strength on the affected limb for long distance runners with a significant increase in gluteus medius muscle strength and painfree running after a six week training program. Lavine14 explores the possibility of a low hamstring to quadriceps muscle strength ratio associated with ITB syndrome.
What causes lateral knee pain?
ITB syndrome is common cause of lateral knee pain in 22% of lower extremity injuries.14 There is a 1.6-12% incidence in runners14 especially in marathon runners1 and 22% in military recruits.2 It can also occur in cycling (15% of overuse injuries at the knee)14, dancing, volleyball, tennis, football, skiing, weight lifting, and aerobics2, 14 as well as in soccer, basketball and field hockey in female college athletes and in competitive rowers.14 Men (28%) and women (62%)1 can develop ITB syndrome . Men less than 34 years old may be more susceptible1 but no other age differences were found.
What are the factors that contribute to ITB?
Researchers have proposed several biomechanical factors leading to ITB syndrome but there remains limited, well conducted, scientific studies to support these factors.2 Most authors suggest it may be a combination of factors that likely leads to the development of ITB symptoms some of which include improper training techniques, biomechanical abnormalities, increased running mileage and muscle imbalance. 12, 15, 16
Is there evidence for a treatment for inflammation in the acute phase?
There is not strong evidence for effectively treating inflammation in the acute phase but individuals who received anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs, corticosteroids through phonophoresis or injection) showed significant improvement compared to controls.14
The ICD code M763 is used to code Iliotibial band syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS or ITBFS, for iliotibial band friction syndrome) is a common injury to the knee, generally associated with running, cycling, hiking or weight-lifting (especially squats).
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code M76.32 and a single ICD9 code, 726.5 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M76.31 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is the knee joint made of?
Your knee joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the knee joint move. When any of these structures is hurt or diseased, you have knee problems. Knee problems can cause pain and difficulty walking.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for seen for inability to get along with boss and workmates
- 2. icd 10 code for right basal ganglia infarct
- 3. icd 10 code for contact with unspecified sharp object
- 4. icd 10 code for high risk homosexual behavior
- 5. icd 10 cm code for history of postpartum hemorrhage.
- 6. icd-10 code for incontinence of bowel and bladder
- 7. icd 10 code for hhrt
- 8. icd-10 code for organic mood syndrome dementia
- 9. icd 10 code for gout not active
- 10. icd 10 code for j96.11