Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for atelectasis?
| ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 J98.11 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of atelectasis. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code J981 is used to code Atelectasis
What is the pathophysiology of bibasilar atelectasis?
Damage to the lung walls can cause a collapse leading to bibasilar atelectasis. Air can escape from the lung into the space between the chest wall and the lung from diseases such as COPD or pneumonia.
What happens if bibasilar atelectasis is left untreated?
The treatment of bibasilar atelectasis will depend on the underlying cause. When left untreated, bibasilar atelectasis can lead to complications like low blood oxygen, lung scarring, respiratory failure, and pneumonia. What Causes Crackles in the Lungs?
How to diagnose and treat atelectasis?
Atelectasis 1 Diagnosis. A doctor's examination and plain chest X-ray may be all that is needed to diagnose atelectasis. ... 2 Treatment. Treatment of atelectasis depends on the cause. ... 3 Preparing for your appointment. Unless you require emergency care, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner.
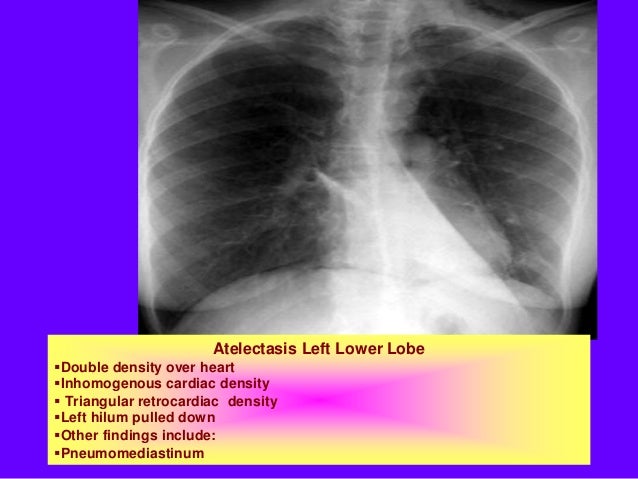
What is the ICD-10 code for basilar atelectasis?
ICD-10 code J98. 11 for Atelectasis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is basilar atelectasis?
Bibasilar atelectasis is a condition that happens when you have a partial collapse of your lungs. This type of collapse is caused when the small air sacs in your lungs deflate. These small air sacs are called alveoli. Bibasilar atelectasis specifically refers to the collapse of the lower sections of your lungs.
What atelectasis means?
Overview. Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
Where is the basilar part of the lung?
Portion of a structure that forms its base-the bottom part or part opposite the apex of the structure-or a branch serving that portion of the structure; e.g., the basal part of the lungs (formed by the four basal bronchopulmonary segments of each side) served by basal parts of the right and left pulmonary arteries.
What are the 3 types of atelectasis?
The term atelectasis can also be used to describe the collapse of a previously inflated lung, either partially or fully, because of specific respiratory disorders. There are three major types of atelectasis: adhesive, compressive, and obstructive.
Is atelectasis the same as pneumothorax?
Atelectasis is caused by a blockage of the air passages (bronchus or bronchioles) or by pressure on the outside of the lung. Atelectasis is not the same as another type of collapsed lung called pneumothorax, which occurs when air escapes from the lung.
Is Mild Bibasilar atelectasis common?
Share on Pinterest Bibasilar atelectasis is most common after a major surgical procedure. It is most common for a person to experience bibasilar atelectasis after they have undergone a major surgical procedure, involving general anesthesia.
Which type of atelectasis is the most common?
Obstructive atelectasis is the most common type and results from reabsorption of gas from the alveoli when communication between the alveoli and the trachea is obstructed. The obstruction can occur at the level of the larger or smaller bronchus.
What is ICD-10 code R51?
ICD-10 code R51 for Headache is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What does the first letter in the alphanumeric ICD-10 code represent?
Codes in the ICD-10-CM code set can have anywhere from three to seven characters. The more characters there are, the more specific the diagnosis. The first character is always alpha (i.e., a letter), but characters two through seven can be either alpha or numeric.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypoxia?
R09.02R09. 02 - Hypoxemia | ICD-10-CM.
What Is Bibasilar Atelectasis?
In medical terms, bibasilar atelectasis definition refers to a partial or complete collapse of a lung or both lungs. We have two lungs—the left and...
Classifications of Bibasilar Atelectasis
The word atelectasis comes from the Greek terms ateles and ektasis, which mean “incomplete” and “expansion,” respectively. There are multiple types...
Bibasilar Atelectasis Signs and Symptoms
Bibasilar atelectasis can be mild, affecting only a small portion of the lungs. It is usually the bottom portion, and is therefore asymptomatic. If...
Who Is at Risk For Bibasilar Atelectasis?
You may be at risk for bibasilar atelectasis when you have a blocked airway or are unable to cough, take a deep breath, sigh, or yawn. Other factor...
Bibasilar Atelectasis Causes
Most people suffer from atelectasis due to being put under general anesthesia during surgery. There are also a number of other causes associated wi...
Bibasilar Atelectasis Diagnosis
Since doctors may misdiagnose bibasilar atelectasis as pneumothorax, a proper diagnosis requires explicit testing. You can expect a complete blood...
Bibasilar Atelectasis Treatment
Treatment of bibasilar atelectasis will depend on the underlying cause. We’ll examine in detail some of the treatment options for bibasilar atelect...
Bibasilar Atelectasis Prevention
You can prevent bibasilar atelectasis by not ingesting foreign objects and avoiding the use of tobacco, as well the use of anesthetic services when...
Complications of Bibasilar Atelectasis
If not treated, there are various bibasilar atelectasis complications that can develop into something more severe. The following are possible compl...
Final Thoughts on Bibasilar Atelectasis
Bibasilar atelectasis is a partial or complete collapse of one or both lungs. The various types of bibasilar atelectasis include resorptive obstruc...
What is bibasilar atelectasis?
In medical terms, bibasilar atelectasis definition refers to a partial or complete collapse of a lung or both lungs. We have two lungs—the left and the right—both containing lobes. The left lung has two lobes, and the right lung has three lobes. There are tiny air sacs shaped like balloons containing blood vessels arranged in clusters ...
What is obstructive bibasilar atelectasis?
In obstructive bibasilar atelectasis, something is obstructing the airway, such as a mucus plug, foreign object, blood clot, narrowing airway, or an abnormal growth or damage to the lung. Read on to learn more about the potential causes of obstructive bibasilar atelectasis.
How to expand lungs after atelectasis?
When atelectasis is caused by surgery, your doctor may recommend certain steps to help you expand your lungs. For instance, deep breathing exercises are very important after surgery. A device called an incentive spirometer may be used to measure the speed of breathing and how much you’re breathing.
Can bibasilar atelectasis be diagnosed as pneumothorax?
Bibasilar Atelectasis Diagnosis. Since doctors may misdiagnose bibasilar atelectasis as pneumothorax, a proper diagnosis requires explicit testing. You can expect a complete blood count test, a performance test of the kidneys, serum electrolytes check, and a physical examination.
Is bibasilar atelectasis asymptomatic?
Bibasilar atelectasis can be mild, affecting only a small portion of the lungs. It is usually the bottom portion, and is therefore asymptomatic. If it affects a greater portion, or the entire lung, there are key symptoms to be aware of, including: Wheezing. Fever.
Where does the word "atelectasis" come from?
The word atelectasis comes from the Greek terms ateles and ektasis, which mean “incomplete” and “expansion,” respectively. There are multiple types of atelectasis, which correspond to the biological mechanisms that lead to the state of collapse.
Is a lesion obstruction a lung disease?
In this type, there is not a lesion obstruction. That being said, it is often linked to a number of diseases, including recurrent atelectasis, pneumonitis, and bronchiectasis of the middle lobe—a lung disease where there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways.
What is the treatment for atelectasis?
If a tumor is causing the atelectasis, treatment may involve removal or shrinkage of the tumor with surgery, with or without other cancer therapies (chemotherapy or radiation).
What tests are needed to diagnose atelectasis?
A doctor's examination and plain chest X-ray may be all that is needed to diagnose atelectasis. However, other tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis or determine the type or severity of atelectasis. They include:
Can atelectasis go away without treatment?
Mild atelectasis may go away without treatment. Sometimes, medications are used to loosen and thin mucus. If the condition is due to a blockage, surgery or other treatments may be needed.
Treatment for mild atelectasis
If you’re experiencing mild atelectasis, your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
Surgical procedures for atelectasis
If your atelectasis isn’t severe enough to require treatment at home, your doctor may recommend a surgical procedure to prevent it from getting worse.
Surgery for mild atelectasis
A surgical procedure may be performed to prevent mild atelectasis that isn’t severe enough to require a home treatment plan.
Surgery for moderate or severe atelectasis
If your atelectasis is severe enough, you may require a surgical procedure to prevent it from getting worse.
Preventing atelectasis
You can prevent atelectasis by avoiding certain activities and eating smaller meals. For example, you may be able to avoid lying down when you exhale by changing your posture more often.
Outcome of atelectasis
Having mild atelectasis or moderate or severe atelectasis doesn’t always mean you’ll need surgery, but it can be a serious condition.
Mild atelectasis
If you have mild atelectasis, your atelectasis may be temporary and mild enough to resolve with conservative treatments.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 e code for corneal abrasion by metal
- 2. icd 10 code for lle amputation
- 3. icd 10 code for hematuria gross
- 4. icd 10 code for cmc arthritis
- 5. icd-10 code for acute brain syndrome
- 6. icd 10 code for superficial valvular insufficiency right leg vein
- 7. icd 10 code for tumor on bladder
- 8. icd 10 cm code for fall from a nonmotorized scooter
- 9. icd-10-cm code for hyperlipedemia associates with diabetes
- 10. icd-10 code for multifocal pneumonia