What is the ICD 10 code for Ludwig's angina?
The ICD code K122 is used to code Ludwig's angina. Ludwig's angina, otherwise known as angina ludovici, is a serious, potentially life-threatening cellulitis, or connective tissue infection, of the floor of the mouth, usually occurring in adults with concomitant dental infections and if left untreated, may obstruct the airways,...
What is the ICD 9 code for angina pectoris?
2013 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 413.* : Angina pectoris A disorder characterized by substernal discomfort due to insufficient myocardial oxygenation.
What is the history of Ludwig's angina?
It is named after a German physician, Wilhelm Frederick von Ludwig, who first described this condition in 1836. Ludwig's angina is a form of severe, widespread cellulitis of the floor of the mouth, usually with bilateral involvement.
What is the PMID for Ludwig's angina?
PMID 3277567. ^ Spitalnic SJ, Sucov A (July 1995). "Ludwig's angina: case report and review". The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 13 (4): 499–503. doi: 10.1016/0736-4679 (95)80007-7.
See more
What is the ICD 10 code for Ludwig's angina?
K12. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K12. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for submandibular abscess?
The drainage is usually performed via an intraoral approach, however, sometimes it is performed extraorally. On some occasions a combination of these techniques is employed. The ICD-10-AM code for submandibular abscess is K12. 2 Cellulitis and abscess of mouth.
What is the ICD 10 code for oral abscess?
ICD-10 code K12. 2 for Cellulitis and abscess of mouth is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
Can you code abscess and Cellulitis together?
682.5 - Cellulitis and abscess of buttock is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM.
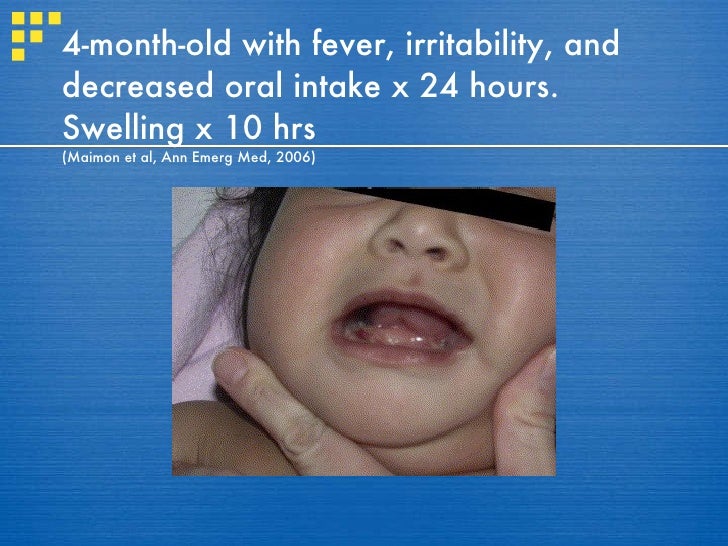
What is Ludwig's angina?
Ludwig angina is an infection of the floor of the mouth under the tongue. It is due to a bacterial infection of the teeth or jaw.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What bacteria causes Ludwig angina?
Streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria are the most common types of bacteria that lead to Ludwig's angina, especially Streptococcus viridans, Staphylococcus epidermis, and Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the ICD-10 code for odontogenic infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code A69 A69.
What is the ICD-10 code for periodontal abscess?
ICD-10 Code for Periapical abscess without sinus- K04. 7- Codify by AAPC.
Can you Bill 10061 twice?
CPT 10061 was denied by Medicare for frequency because it may only be billed once per DOS per patient.
What is the difference between 10060 and 10160?
No to both questions. CPT code 10060 includes incision and drainage, and you stated no incision was made. CPT code 10160 includes puncture and aspiration, and you stated no aspiration was made. The puncture as indicated in your scenario above would be part of the E/M service performed for the patient at that encounter.
What is the difference between 10060 and 26010?
For example, there is a considerable difference in reimbursement between CPT codes 10060 and 26010. According to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS), average reimbursement for code 10060 is $121.68, while the average reimbursement for code 26010 is $272.88.
What is Ludwig's angina?
Ludwig's angina is a form of severe diffuse cellulitis with bilateral involvement, primarily of the submandibular space with the sublingual and submental spaces also being involved. It presents with an acute onset and spreads very rapidly meaning early diagnosis and immediate treatment planning is key to saving lives.
What is the most important factor in treating Ludwig's Angina?
Airway management. Placement of an endotracheal tube to aid breathing. Airway management has been found to be the most important factor in treating patients with Ludwig's Angina, i.e. it is the “primary therapeutic concern”. Airway compromise is known to be the leading cause of death from Ludwig's Angina.
What does it mean to have angina?
Placing it into context, Ludwig's angina refers to the feeling of strangling and choking, secondary to obstruction of the airway, which is the most serious potential complication of this condition.
What is the method of taking pus samples from Ludwig's angina?
One of the traditionally used methods is taking culture samples although it has some limitations. By taking pus samples from a patient with Ludwig's angina, the microbiology were found to be commonly polymicrobial and anaerobic.
What is the condition called when the airway is compromised?
Ludwig's angina (lat.: Angina ludovici) is a type of severe cellulitis involving the floor of the mouth. Early on the floor of the mouth is raised and there is difficulty swallowing saliva, which may run from the person's mouth. As the condition worsens, the airway may be compromised with hardening of the spaces on both sides of the tongue.

Overview
Signs and symptoms
Ludwig's angina is a form of severe, widespread cellulitis of the floor of the mouth, usually with bilateral involvement. Infection is usually primarily within the submandibular space, and the sublingual and submental spaces can also be involved. It presents with an acute onset and spreads very rapidly, therefor early diagnosis and immediate treatment planning is vital and lifesaving. The external signs may include bilateral lower facial swelling around the jaw and uppe…
Causes
The most prevalent cause of Ludwig's angina is dental related, accounting for approximately 75% to 90% of cases. Infections of the lower second and third molars are usually implicated due to their roots extending below the mylohyoid muscle. Periapical abscesses of these teeth also result in lingual cortical penetration, leading to submandibular infection.
Other causes such as oral ulcerations, infections secondary to oral malignancy, mandible fractur…
Diagnosis
Infections originating in the roots of teeth can be identified with a dental X-ray. A CT scan of the neck with contrast material is used to identify deep neck space infections. If there is suspicion of the infection of the chest cavity, a chest scan is sometimes done.
Angioneurotic oedema, lingual carcinoma and sublingual hematoma formation following anticoagulation should be ruled out as possible diagnoses.
Treatment
For each patient, the treatment plan should be consider the patient's stage of infection, airway control, and comorbidities. Other things to consider include physician experience, available resources, and personnel are critical factors in formulation of a treatment plan. There are four principles that guide the treatment of Ludwig's Angina: Sufficient airway management, early and aggressive antibiotic therapy, incision and drainage for any who fail medical management or for…
Etymology
The term “angina”, is derived from the Latin word “angere”, which means “choke”; and the Greek word “ankhone”, which means “strangle”. Placing it into context, Ludwig's angina refers to the feeling of strangling and choking, secondary to obstruction of the airway, which is the most serious potential complication of this condition.
See also
• Anticor
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 v code for tamoxifen use
- 2. icd 10 code for ared
- 3. icd-10 code for rectosigmoid polyp
- 4. icd 10 cm code for hx nasal scc
- 5. icd 10 code for lesion left cheek
- 6. icd 10 code for right subscapular pain
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for charcot disease of feet
- 8. icd 10 code for mf
- 9. icd 10 code for late effect cva slurred speech
- 10. icd 10 diagnosis code for bipolar disorder